J Korean Med Assoc.
2011 Sep;54(9):910-917. 10.5124/jkma.2011.54.9.910.
The current state of age-related hearing loss in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. schae@kumc.or.kr
- KMID: 2191175
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2011.54.9.910
Abstract
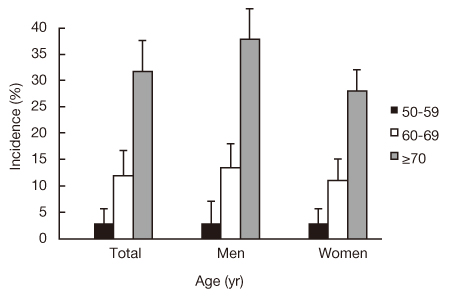
- The inevitable deterioration in hearing ability that occurs with age, age-related hearing loss (ARHL) or presbycusis, is a multifactorial process that can vary in severity from mild to profound. The number of cases of age-related hearing loss is growing due to the rapid growth of South Korea's aging population. According to the Korean Health Statistics of 2009, the incidence of unilateral hearing loss in people aged 65 or older is 17.5 percent, while the incidence of bilateral hearing loss exceeds 25.9 percent. Left untreated, age-related hearing loss of a moderate or greater degree affects communication and can decrease quality of life. Comprehensive rehabilitation by hearing aids or cochlear implant are widely available but underused in part because of social attitudes that undervalue the effect of hearing on life, in addition to the cost and stigma associated with hearing aids. Proper screening tests for ARHL should be developed and primary care physicians should screen and refer their elderly patients for assessment and remediation. In addition, development of hearing aids with a low cost of distribution and an increase in the size of government subsidies to hearing aids are imperative.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of Subjective Hearing Handicap and Perceived Stress on Quality of Communication Life of Older Adults
Younghye Go, Myonghwa Park
Korean J Adult Nurs. 2017;29(5):496-504. doi: 10.7475/kjan.2017.29.5.496.
Reference
-
1. World population ageing 1950-2050 [Internet]. United Nations. 2001. cited 2011 Jun 2. New York: United Nations Publications;Available from: http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/worldageing19502050/.2. Huang Q, Tang J. Age-related hearing loss or presbycusis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010. 267:1179–1191.
Article3. Katsarkas A, Ayukawa H. Hearing loss due to aging (presbycusis). J Otolaryngol. 1986. 15:239–244.4. Scott-Brown WG, Kerr AG, Groves J. Scott-Brown's otolaryn-gology. 1987. 5th ed. London: Butterworths.5. Janssen R, Schweitzer L, Jensen KF. Glutamate neurotoxicity in the developing rat cochlea: physiological and morphological approaches. Brain Res. 1991. 552:255–264.
Article6. Hinchcliffe R. The age function of hearing: aspects of the epidemiology. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1990. 476:7–11.7. Schuknecht HF, Gacek MR. Cochlear pathology in presbycusis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1993. 102(1 Pt 2):1–16.
Article8. Cruickshanks KJ, Klein R, Klein BE, Wiley TL, Nondahl DM, Tweed TS. Cigarette smoking and hearing loss: the epidemiology of hearing loss study. JAMA. 1998. 279:1715–1719.9. Jun BH. Korean Society of Otorhinolaryn-gology. Presbycusis. Otolaryngology head and neck surgery. 2009. 2nd ed. Seoul: Ilchokak;749–758.10. Garringer HJ, Pankratz ND, Nichols WC, Reed T. Hearing impairment susceptibility in elderly men and the DFNA18 locus. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006. 132:506–510.
Article11. Zhu M, Yang T, Wei S, DeWan AT, Morell RJ, Elfenbein JL, Fisher RA, Leal SM, Smith RJ, Friderici KH. Mutations in the gamma-actin gene (ACTG1) are associated with dominant progressive deafness (DFNA20/26). Am J Hum Genet. 2003. 73:1082–1091.
Article12. Jennings CR, Jones NS. Presbyacusis. J Laryngol Otol. 2001. 115:171–178.
Article13. Gates GA, Mills JH. Presbycusis. Lancet. 2005. 366:1111–1120.
Article14. Gates GA, Cooper JC Jr, Kannel WB, Miller NJ. Hearing in the elderly: the Framingham cohort, 1983-1985. Part I. Basic audiometric test results. Ear Hear. 1990. 11:247–256.15. 2010 Census [Internet]. Statistics Korea. 2011. cited 2011 Aug 10. Deajeon: Statistics Korea;Available from: http://www.kostat.go.kr.16. Korea National Statistical Office. Population projections for Korea. 2006. Daejeon: Korea National Statistical Office.17. Davis AC. Epidemiological profile of hearing impairments: the scale and nature of the problem with special reference to the elderly. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1990. 476:23–31.
Article18. Cruickshanks KJ, Nondahl DM, Tweed TS, Wiley TL, Klein BE, Klein R, Chappell R, Dalton DS, Nash SD. Education, occupation, noise exposure history and the 10-yr cumulative incidence of hearing impairment in older adults. Hear Res. 2010. 264:3–9.
Article19. Dillon CF, Gu Q, Hoffman HJ, Ko CW. Vision, hearing, balance, and sensory impairment in Americans aged 70 years and over :United States, 1999-2006 [Internet]. 2010. cited 2011 Aug 9. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db31.htm.20. Chang HP, Chou P. Presbycusis among older Chinese people in Taipei, Taiwan: a community-based study. Int J Audiol. 2007. 46:738–745.
Article21. Kim HN, Kim SG, Lee HK, Ohrr H, Moon SK, Chi J, Lee EH, Park K, Park DJ, Lee JH, Yi SW. Incidence of presbycusis of Korean populations in Seoul, Kyunggi and Kangwon provinces. J Korean Med Sci. 2000. 15:580–584.
Article22. Korea health statistics 2009: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANESIV-3) [Internet]. 2011. cited 2011 Aug 9. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;Available from: http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.23. Nomura K, Nakao M, Morimoto T. Effect of smoking on hearing loss: quality assessment and meta-analysis. Prev Med. 2005. 40:138–144.
Article24. Sindhusake D, Mitchell P, Smith W, Golding M, Newall P, Hartley D, Rubin G. Validation of self-reported hearing loss. The Blue Mountains Hearing Study. Int J Epidemiol. 2001. 30:1371–1378.
Article25. Matthews LJ, Lee FS, Mills JH, Schum DJ. Audiometric and subjective assessment of hearing handicap. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990. 116:1325–1330.
Article26. Hong BN, Hong HN, Lee JH. Development of a screening tool for presbycusis. Korean J Audiol. 2004. 8:49–57.27. Kim CP, Hong BN, Lee KW, Lee JH. A study on the benefit of hearing aids in geriatrics with presbyacusis. Korean J Audiol. 2006. 10:116–121.28. Moon SK, Lee JW, Choung YH, Park K. Clinical analysis of hearing aid failure. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2005. 48:13–17.29. Eshraghi AA, Rodriguez M, Balkany TJ, Telischi FF, Angeli S, Hodges AV, Adil E. Cochlear implant surgery in patients more than seventy-nine years old. Laryngoscope. 2009. 119:1180–1183.
Article