J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Oct;52(4):384-390. 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.4.384.
Morphometric Relationship between the Cervicothoracic Cord Segments and Vertebral Bodies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. j7chang@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, St. Peter's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics-Cardiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA.
- KMID: 2190657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.4.384
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The objective of this study was to investigate the morphologic characteristics between the vertebral body and the regions of the cervical and thoracic spinal cords where each rootlets branch out.
METHODS
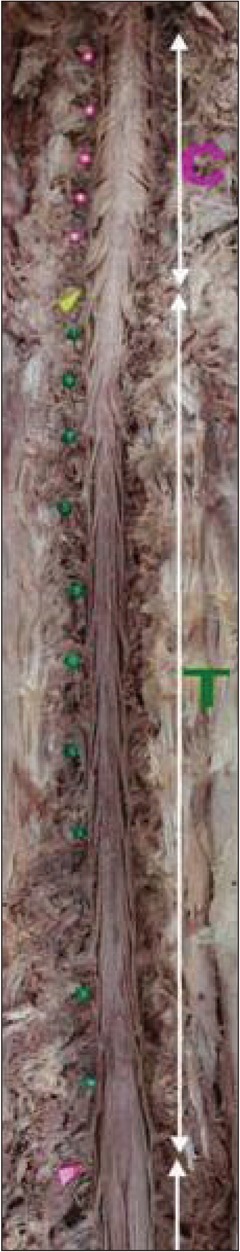
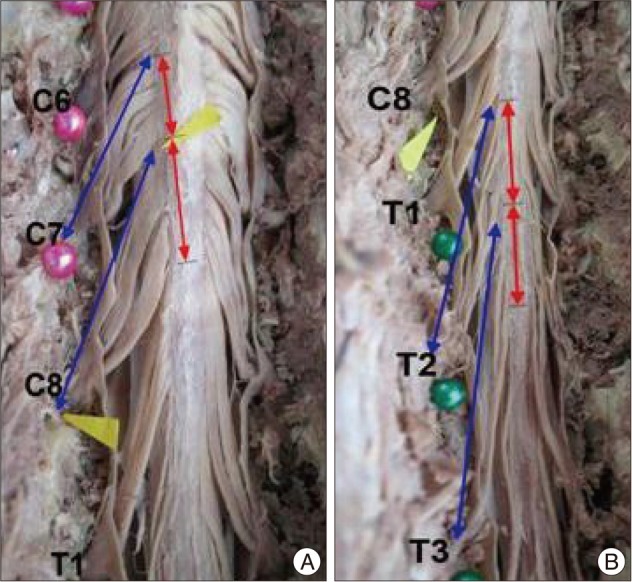
Sixteen adult cadavers (12 males and 4 females) with a mean age of 57.9 (range of 33 to 70 years old) were used in this study. The anatomical relationship between the exit points of the nerve roots from the posterior root entry zone at each spinal cord segment and their corresponding relevant vertebral bodies were also analyzed.
RESULTS
Vertical span of the posterior root entry zone between the upper and lower rootlet originating from each spinal segment ranged from 10-12 mm. The lengths of the rootlets from their point of origin at the spinal cord to their entrance into the intervertebral foramen were 5.9 mm at the third cervical nerve root and increased to 14.5 mm at the eighth cervical nerve root. At the lower segments of the nerve roots (T3 to T12), the posterior root entry zone of the relevant nerve roots had a corresponding anatomical relationship with the vertebral body that is two segments above. The posterior root entry zones of the sixth (94%) and seventh (81%) cervical nerve roots were located at a vertebral body a segment above from relevant segment.
CONCLUSION
Through these investigations, a more accurate diagnosis, the establishment of a better therapeutic plan, and a decrease in surgical complications can be expected when pathologic lesions occur in the spinal cord or vertebral body.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Long-Term Outcome of Posterior Cervical Inclinatory Foraminotomy
Juneyoung Heo, Jae Chil Chang, Hyung-Ki Park
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016;59(4):374-378. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.4.374.
Reference
-
1. Chang JC, Park HK, Bae HG, Cho SJ, Choi SK, Byun PJ. Morphometric measurement of the anatomical landmark in anterior cervical microforaminotomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2006; 39:340–346.2. Clark CR. Anatomy of the cervical spine : the Cervical Spine. 2005. ed 4. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;p. 13–15.3. Hwang JC, Bae HG, Cho SW, Cho SJ, Park HK, Chang JC. Morphometric study of the nerve roots around the lateral mass for posterior foraminotomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 47:358–364. PMID: 20539795.
Article4. Kameyama T, Hashizume Y, Ando T, Takahashi A. Morphometry of the normal cadaveric cervical spinal cord. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:2077–2081. PMID: 7825049.
Article5. Kim P, Shin WH. A guidebook for the future experts in the cervical spine surgery from neurological evaluation to microsurgical techniques. 2007. Seoul: ML Communication;p. 13.6. Kubo Y, Waga S, Kojima T, Matsubara T, Kuga Y, Nakagawa Y. Microsurgical anatomy of the lower cervical spine and cord. Neurosurgery. 1994; 34:895–890. discussion 901-902. PMID: 8052389.
Article7. Marzo JM, Simmons EH, Kallen F. Intradural connections between adjacent cervical spinal roots. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987; 12:964–968. PMID: 3441822.
Article8. Okada Y, Ikata T, Katoh S, Yamada H. Morphologic analysis of the cervical spinal cord, dural tube, and spinal canal by magnetic resonance imaging in normal adults and patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:2331–2335. PMID: 7846579.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Disc Degeneration in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
- Inferiorly Migrated Disc Fragment at T1 Body Treated by T1 Transcorporeal Approach
- Split Cord Malformation Combined with Tethered Cord Syndrome in an Adult
- Correlation of the Bone Mineral Density with Morphometric Dimensions and Characteristics of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
- Fractures and Dislocations of the Cervicothoracic Junction