J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2010 Jun;36(3):177-185. 10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.3.177.
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) monoclonal antibody and DNA topoisomerase inhibitor reduce growth of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma in a murine model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea. ywpark@gwnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Anatomy, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 2189945
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.3.177
Abstract
- INTRODUCTION
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is expressed in human epithelial tumors including salivary cancers, and known to be correlated with tumor progression and poor clinical courses in some epithelial tumors. In this study, we determined the therapeutic effect of the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody Erbitux (C225, cetuximab) in combination with the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor irinotecan (CPT-11) on human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC) cells growing in nude mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
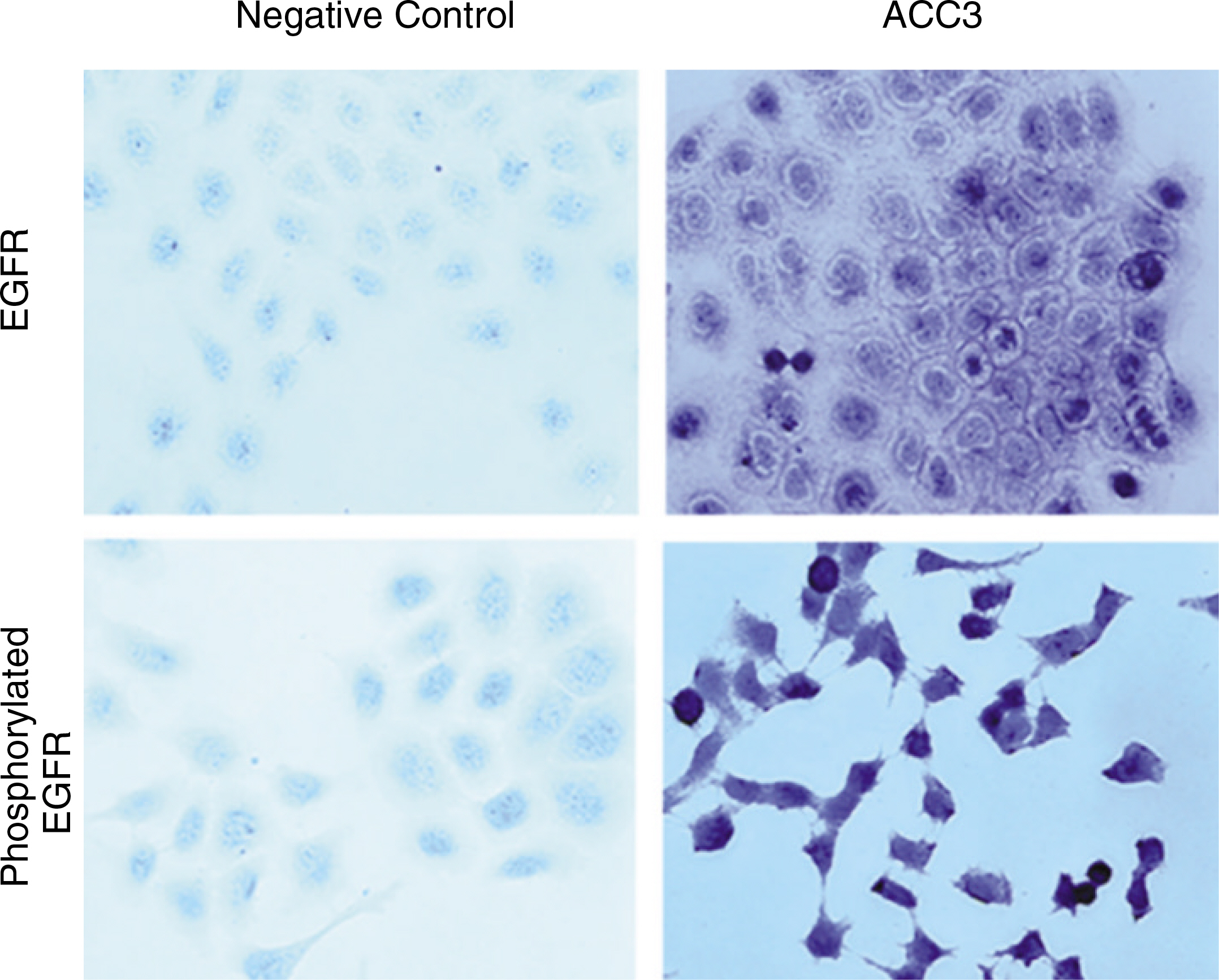
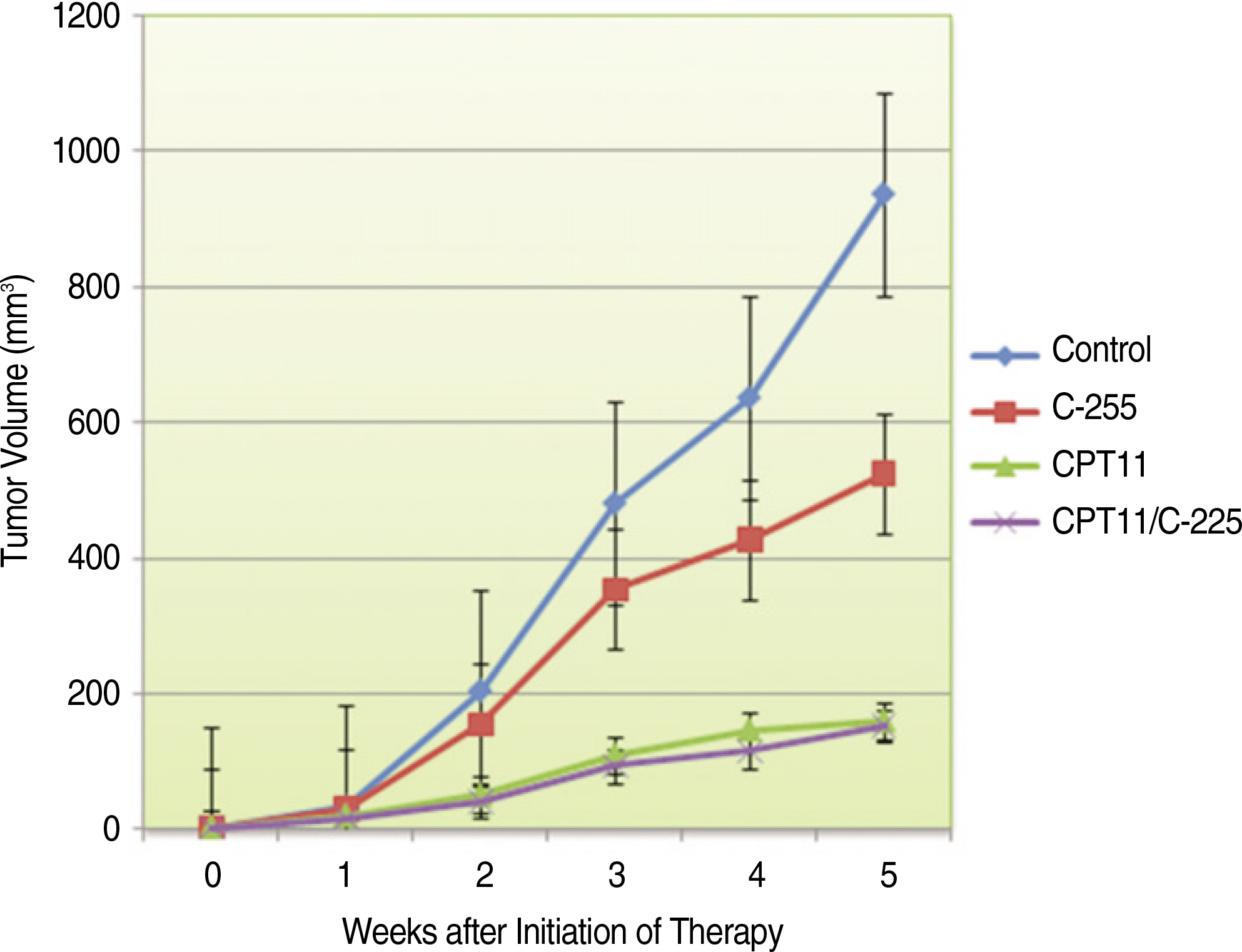
At first, immunocytochemical analysis for the expression of EGFR and phosphorylated EGFR (pEGFR) on a human salivary ACC cell line (ACC3). To determine the in vivo effects of Erbitux and CPT-11, nude mice with orthotopic parotid tumors were randomized to receive intraperitoneal Erbitux (1 mg) two times per week, intraperitoneal Irinotecan (50 mg/kg) once per week, Erbitux plus CPT-11, or placebo. (control) Tumor volume and weight were measured. And mechanisms of in vivo activity of Erbitux and/or CPT-11 were determined by immunohistochemical/immunofluorescent analyses.
RESULTS
Immunocytochemical staining of ACC3 demonstrated that EGFR was expressed and phosphorylated. CPT-11 inhibited ACC tumor growth in nude mice. Tumors of mice treated with CPT-11 and CPT-11 plus Erbitux exhibited increased tumor cell apoptosis and decreased microvessel density, which correlated with a decrease in the tumor volume in nude mice. But, CPT-11 seems not to be synergistic with Erbitux in our ACC3 model system.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody and the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor will be effective in the treatment of recurred or metastatic lesions of salivary ACC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenoids
Animals
Antibodies, Monoclonal
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized
Apoptosis
Camptothecin
Carcinoma, Adenoid Cystic
Cell Line
Cetuximab
DNA
DNA Topoisomerases, Type I
Humans
Mice
Mice, Nude
Microvessels
Parotid Neoplasms
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Salivary Gland Neoplasms
Tumor Burden
Antibodies, Monoclonal
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized
Camptothecin
DNA
DNA Topoisomerases, Type I
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Licitra L, Locati LD, Bossi P, Cantu `G. Head and neck tumors other than squamous cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2004; 16:236–41.
Article2. Jones AS, Hamilton JW, Rowley H, Husband D, Helliwell TR. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Otolaryngol. 1997; 22:434–43.
Article3. Laurie SA, Licitra L. Systemic therapy in the palliative management of advanced salivary grand cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2673–8.4. Airoldi M, Cortesina G, Giordano C, Pedani F, Cavalot A, Marcato P, et al. Update and perspectives on nonsurgical treatment of salivary gland malignancies. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2003; 23:368–76.5. Kuwai T, Nakamura T, Sasaki T, Kim SJ, Fan D, Villares GJ, et al. Phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor on tumor-associated endothelial cells is a primary target for therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Neoplasia. 2008; 10:489–500.
Article6. Herbst RS, Hong WK. IMC-C225, an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody for treatment of head and neck cancer. Semin Oncol. 2002; 29(5 Suppl 14):18–30.
Article7. Park YW, Kim JH. Immunohistochemical assays for the expression of epidermal growth factor-signaling proteins in adenoid cystic carcinoma of human salivary glands. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 28:499–510.8. Younes MN, Park YW, Yazici YD, Gu M, Santillan AA, Nong X, et al. Concomitant inhibition of epidermal growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases reduces growth and metastasis of human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma in an orthotopic nude mouse model. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006; 5:2696–705.
Article9. Agulnik M, Cohen EW, Cohen RB, Chen EX, Vokes EE, Hotte SJ, et al. Phase II study of lapatinib in recurrent or metastatic epidermal growth factor receptor and/or erbB2 expressing adenoid cystic carcinoma and non adenoid cystic carcinoma malignant tumors of the salivary glands. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:3978–84.10. Dahse R, Driemel O, Schwarz S, Dahse J, Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Berndt A, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain mutations are rare in salivary gland carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 2009; 100:623–5.
Article11. Dahse R, Driemel O, Schwarz S, Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Berndt A, Kosmehl H, et al. KRAS status and epidermal growth factor receptor expression as determinants for anti-EGFR therapies in salivary gland carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2009; 45:826–9.
Article12. Rothenberg ML. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: review and update. Ann Oncol. 1997; 8:837–55.
Article13. Rivory LP. Irinotecan (CPT-11): a brief overview. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996; 23:1000–4.
Article14. Larsen AK, Gobert C. DNA topoisomerase I in oncology: Dr. Jekyll or Mr. Hyde? Pathol Oncol Res. 1999; 5:171–8.15. Saijo N. Preclinical and clinical trials of topoisomerase inhibitors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000; 922:92–9.
Article16. Friedman HS, Keir ST, Houghton PJ. The emerging role of irinotecan (CPT-11) in the treatment of malignant glioma in brain tumors. Cancer. 2003; 97(9 Suppl):2359–62.
Article17. Rothenberg ML, Cox JV, DeVore RF, Hainsworth JD, Pazdur R, Rivkin SE, et al. A multicenter, phase II trial of weekly irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with previously treated colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 1999; 85:786–95.
Article18. Ross PJ, Teoh EM, A' hern RP, Rhys-Evans PH, Harrington KJ, Nutting CM, et al. Epirubicin, cisplatin and protracted venous infusion 5-Fluorouracil chemotherapy for advanced salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2009; 21(4):311–4.
Article19. Park YW, Chung SH. An experimental study for establishment of orthotopic salivary tumor models in mice. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 33:81–93.20. Park YW. Targeted molecular therapy in a murine model of oral squamous cell carcinoma with an epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 31:8–17.21. Raynal C, Pascussi JM, Leguelinel G, Breuker C, Kantar J, Lallemant B, et al. Pregnane X Receptor (PXR) expression in colorectal cancer cells restricts irinotecan chemosensitivity through enhanced SN-38 glucuronidation. Mol Cancer. 2010; 9:46.
Article22. Louvet C, Andre ′ T, Gamelin E, Garcia ML, Saavedra A, Lenaers G, et al. A phase I-II, dose-escalating trial of ZD9331 in combination with irinotecan (CPT-11) in previously pretreated metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Bull Cancer. 2004; 91:279–84.23. Kokawa K, Nishimura R, Fujii T, Umesaki N. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with irinotecan and mitomycin-C for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Anticancer Res. 2007; 27:2721–7.24. Mrozek E, Kolesar J, Young D, Allen J, Villalona-Calero M, Shapiro CL. Phase II study of sequentially administered low-dose mitomycin-C (MMC) and irinotecan (CPT-11) in women with metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Ann Oncol. 2008; 19:1417–22.
Article25. Argiris A, Buchanan A, Brockstein B, Kolesar J, Ghebremichael M, Pins M, et al. Docetaxel and irinotecan in recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer: a phase 2 trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancer. 2009; 115:4504–13.26. Bastos BR, Hatoum GF, Walker GR, Tolba K, Takita C, Gomez J, et al. Efficacy and toxicity of chemoradiotherapy with carboplatin and irinotecan followed by consolidation docetaxel for unresectable stage III nonsmall cell lung cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5(4):533–9.27. Ciardiello F, Bianco R, Damiano V, de Lorenzo S, Pepe S, de Placido S, et al. Antitumor activity of sequential treatment with topotecan and anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody C225. Clin Cancer Res. 1999; 5:909–16.28. Huang SM, Bock JM, Harari PM. Epidermal growth factor receptor blockade with C225 modulates proliferation, apoptosis, and radiosensitivity in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:1935–40.29. Buchsbaum DJ, Bonner JA, Grizzle WE, Stackhouse MA, Carpenter M, Hicklin DJ, et al. Treatment of pancreatic cancer xenografts with Erbitux (IMC-C225) anti-EGFR antibody, gemcitabine, and radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 54:1180–93.
Article30. Bonner JA, Giralt J, Harari PM, Cohen R, Jones C, Sur RK, et al. Prolongs survival in patients with locoregionally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a phase III study of high does radiation therapy with and without cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:5507.31. Harari PM. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition strategies in oncology. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004; 11:689–708.
Article32. Gill GN, Kawamoto T, Cochet C, Le A, Sato JD, Masui H, et al. Monoclonal anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies which are inhibitors of epidermal growth factor binding and antagonists of epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984; 259:7755–60.33. Prewett MC, Hooper AT, Bassi R, Ellis LM, Waksal HW, Hicklin DJ. Enhanced antitumor activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody IMC-C225 in combination with irinotecan (CPT-11) against human colorectal tumor xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 2002; 8:994–1003.34. Koizumi F, Kanzawa F, Ueda Y, Koh Y, Tsukiyama S, Taguchi F, et al. Synergistic interaction between the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (“Iressa”) and the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor CPT-11 (irinotecan) in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2004; 108:464–72.
Article35. Kim S, Prichard CN, Younes MN, Yazici YD, Jasser SA, Bekele BN, et al. Cetuximab and irinotecan interact synergistically to inhibit the growth of orthotopic anaplastic thyroid carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:600–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cellular and molecular characterization of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands
- Targeted Molecular Therapy in a Murine Model of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor
- Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor, Transforming Growth Factor-alphaand Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Human Trophoblast and Decidua
- Antivascular Therapy via Inhibition of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in an Orthotopic Murine Model of Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
- Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor, Transforming Growth Factor-alpha and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Human Fallopian Tube at Various Menstrual Stages