J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2008 Jun;43(3):301-307. 10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.3.301.
Navigation versus Radiographic Measurements in the Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy using Computer Assisted Surgery (CAS)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. bdkyung@khmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2186445
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.3.301
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To compare the measurements using a navigation system and radiographic measurement in an open wedge high tibial osteotomy under navigation control.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
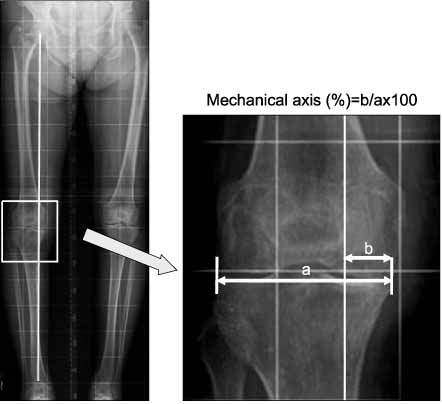
From July, 2005 to January, 2007, 32 open wedge high tibial osteotomies were performed using a navigation system for osteoarthritis of the knee. The postoperative mechanical axis % (MA%), which is planned on the navigation system, were 62%. The mechanical axis (MA) and MA% were measured on the navigation system. The preoperative and postoperative MA and MA% were measured on the radiographs. The angles measured with the navigation system and radiographs were compared.
RESULTS
On the navigation system, the mean MA before osteotomy was varus 8.8degrees. The mean MA and MA% after fixation were valgus 2.9degrees and 57.7%. On the radiographs, the mean MA was varus 9.7degrees preoperatively and valgus 4.0degrees postoperatively. The mean MA% was 10.2% preoperatively and valgus 64.4% postoperatively. There were positive correlations between the values measured with the navigation system and the radiographs (r>0.5, p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
There were significant correlations between the values measured with the navigation system and radiographs in an open wedge high tibial osteotomy using a navigation system. The correction angle from the navigation system is reliable, predictable and controllable during surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Amendola A, Fowler PJ, Litchfield R, Kirkley S, Clatworthy M. Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy using a novel technique: early results and complications. J Knee Surg. 2004. 17:164–169.2. Asik M, Sen C, Kilic B, Goksan SB, Ciftci F, Taser OF. High tibial osteotomy with Puddu plate for the treatment of varus gonarthrosis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006. 14:948–954.
Article3. Bae DK, Mun MS, Kwon OS. A newly designed miniplate staple for high tibial osteotomy. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 1997. 56:167–170.4. Bae DK, Yoon KH, Kwon OS, Kim YC, Shin DJ. Results and survivorship of high tibial osteotomy. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002. 37:357–363.
Article5. Bauer GC, Insall J, Koshino T. Tibial osteotomy in gonarthrosis (osteo-arthritis of the knee). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969. 51:1545–1563.
Article6. Coventry MB, Ilstrup DM, Wallrichs SL. Proximal tibial osteotomy. A critical long-term study of eighty-seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993. 75:196–201.
Article7. Dahl MT. Preoperative planning in deformity correction and limb lengthening surgery. Instr Course Lect. 2000. 49:503–509.8. Dejour H, Neyret P, Boileau P, Donell ST. Anterior cruciate reconstruction combined with valgus tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994. 299:220–228.
Article9. Ellis RE, Tso CY, Rudan JF, Harrison MM. A surgical planning and guidance system for high tibial osteotomy. Comput Aided Surg. 1999. 4:264–274.
Article10. Giffin JR, Stabile KJ, Zantop T, Vogrin TM, Woo SL, Harner CD. Importance of tibial slope for stability of the posterior cruciate ligament deficient knee. Am J Sports Med. 2007. 35:1443–1449.11. Giffin JR, Vogrin TM, Zantop T, Woo SL, Harner CD. Effects of increasing tibial slope on the biomechanics of the knee. Am J Sports Med. 2004. 32:376–382.
Article12. Hankemeier S, Hufner T, Wang G, et al. Navigated open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: advantages and disadvantages compared to the conventional technique in a cadaver study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006. 14:917–921.
Article13. Hohmann E, Bryant A, Imhoff AB. The effect of closed wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope: a radiographic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006. 14:454–459.
Article14. Kaper BP, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Macdonald SJ. Patellar infera after high tibial osteotomy. J Arthroplasty. 2001. 16:168–173.
Article15. Keppler P, Gebhard F, Grützner PA, et al. Computer aided high tibial open wedge osteotomy. Injury. 2004. 35:Suppl 1. S68–S78.
Article16. Kirgis A, Albrecht S. Palsy of the deep peroneal nerve after proximal tibial osteotomy. An anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:1180–1185.
Article17. Lerat JL, Moyen B, Garin C, Mandrino A, Besse JL, Brunet-Guedj E. Anterior laxity and internal arthritis of the knee. Results of the reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament associated with tibial osteotomy. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1993. 79:365–374.18. Marti CB, Gautier E, Wachtl SW, Jakob RP. Accuracy of frontal and sagittal plane correction in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2004. 20:366–372.
Article19. Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ. Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987. 69:745–749.
Article20. Nakamura E, Mizuta H, Kudo S, Takagi K, Sakamoto K. Open-wedge osteotomy of the proximal tibia hemicallotasis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001. 83:1111–1115.21. Naudie DD, Amendola A, Fowler PJ. Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy for symptomatic hyperextension-varus thrust. Am J Sports Med. 2004. 32:60–70.
Article22. Noyes FR, Barber-Westin SD, Hewett TE. High tibial osteotomy and ligament reconstruction for varus angulated anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knees. Am J Sports Med. 2000. 28:282–296.
Article23. Noyes FR, Goebel SX, West J. Opening wedge tibial osteotomy: the 3-triangle method to correct axial alignment and tibial slope. Am J Sports Med. 2005. 33:378–387.
Article24. Noyes FR, Mayfield W, Barber-Westin SD, Albright JC, Heckmann TP. Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy: an operative technique and rehabilitation program to decrease complications and promote early union and function. Am J Sports Med. 2006. 34:1262–1273.25. Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM. Osteotomies: the surgical treatment of the valgus knee. Sports Med Arthrosc. 1993. 8:419–426.26. Puddu G, Cipolla M, Cerullo G, Franco V, Giannì E. Osteotomies: the surgical treatment of the valgus knee. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2007. 15:15–22.
Article27. Rodner CM, Adams DJ, Diaz-Doran V, et al. Medial opening wedge tibial osteotomy and the sagittal plane: the effect of increasing tibial slope on tibiofemoral contact pressure. Am J Sports Med. 2006. 34:1431–1441.28. Saragaglia D, Roberts J. Navigated osteotomies around the knee in 170 patients with osteoarthritis secondary to genu varum. Orthopedics. 2005. 28:Suppl 10. S1269–S1274.
Article29. Staubli AE, De Simoni C, Babst R, Lobenhoffer P. TomoFix: a new LCP-concept for open wedge osteotomy of the medial proximal tibia--early results in 92 cases. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 2. S55–S62.30. Torgerson WR Jr, Kettelkamp DB, Igou RA Jr, Leach RE. Tibial osteotomy for the treatment of degenerative arthritis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 101:46–52.31. Wang G, Zheng G, Keppler P, et al. Implementation, accuracy evaluation, and preliminary clinical trial of a CT-free navigation system for high tibial opening wedge osteotomy. Comput Aided Surg. 2005. 10:73–85.
Article32. Wright JG, Treble N, Feinstein AR. Measurement of lower limb alignment using long radiographs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991. 73:721–723.
Article33. Yoon KH, Bae DK, Park JW, Hwang DW, Park HC, Oh H. The clinical and radiological results of open wedge high tibial valgus osteotomy -short term results-. J Korean Knee Soc. 2005. 17:193–198.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The influence of computer-assisted surgery experience on the accuracy and precision of the postoperative mechanical axis during computer-assisted lateral closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy
- A Comparative Study of the Navigated and Radiographic Measurements in Open and Closed Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Computer Assisted Surgery
- Comparison of Mechanical Axis and Dynamic Range Assessed with Weight Bearing Radiographs and Navigation System in Closed Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
- Computer-Assisted Navigation in High Tibial Osteotomy
- Navigation Guided Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy