J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Feb;44(1):136-140. 10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.1.136.
Airway Obstruction Caused by Soft Tissue Edema during an Anterior Cervical Approach: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gwangju Veterans Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. alla1013@naver.com
- KMID: 2186389
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.1.136
Abstract
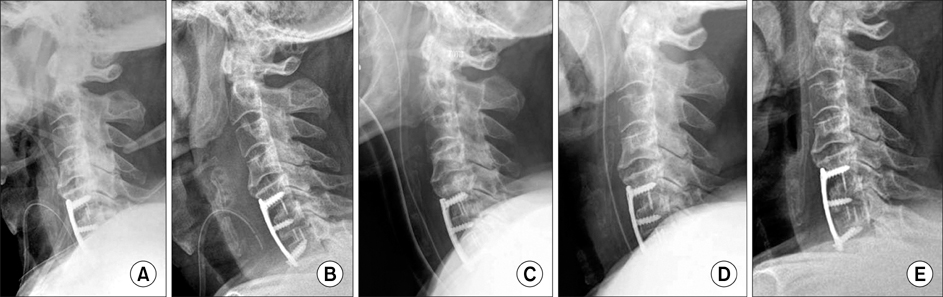
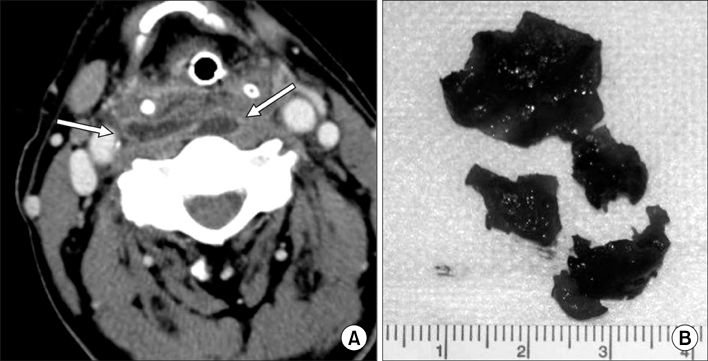
- Anterior approaches to the cervical spine for performing decompression, fusion and/or instrumentation are common and useful methods for treating many conditions, including degenerative diseases. One of the rare, but serious complications of an anterior cervical approach is respiratory insufficiency as a result of upper airway obstruction, which is due to airway narrowing and prevertebral soft tissue swelling. We experienced a case of serious airway obstruction that was caused by soft tissue edema combined with postoperative hematoma after an anterior cervical spine approach. We report here on this case and include a review of the relevant literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Apfelbaum RI, Kriskovich MD, Haller JR. On the incidence, cause, and prevention of recurrent laryngeal nerve palsies during anterior cervical spine surgery. Spine. 2000. 25:2906–2912.
Article2. Bazaz R, Lee MJ, Yoo JU. Incidence of dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a prospective study. Spine. 2002. 27:2453–2458.3. Bexton MD, Radford R. An Unusual cause of respiratory obstruction after thyroidectomy. Anaesthesia. 1982. 37:596.
Article4. Cohn I, Bornside GH. Infections. Principles of surgery. 1989. 5th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;181–215.5. Emery SE, Smith MD, Bohlman HH. Upper-airway obstruction after multilevel cervical corpectomy for myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:544–551.
Article6. Lee JT, Kingston HG. Airway obstruction due to massive lingual oedema following cleft palate surgery. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1985. 32:265–267.
Article7. O'sullivan JC, Wells DG, Wells GR. Difficult airway management with neck swelling after carotid endarterectomy. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1986. 14:460–464.8. Page C, Biet A, Zaatar R, Strunski V. Parapharyngeal abscess: diagnosis and treatment. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008. 265:681–686.
Article9. Suk KS, Kim KT, Lee SH, Park SW. Prevertebral soft tissue swelling after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with plate fixation. Int Orthop. 2006. 30:290–294.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Airway Obstruction Caused by Prevertebral Soft Tissue Swelling after Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Case Report
- Acute Pulmonary Edema Following Upper Airway Obstruction In An Adult: A case report
- Relations between Airway Narrowing and Prevertebral Soft Tissue Swelling after Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery: The Value of Lateral Neck Radiographs
- A Case of Acute Postobstructive Pulmonary Edema due to Parapharyngeal Abscess in a Child
- Acute Pulmonary Edema Associated with Upper Airway Obstruction after Endotracheal Extubation: A case report