J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2013 Dec;48(6):480-485. 10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.6.480.
Late-Onset Infection of a Total Knee Arthroplasty Caused by Monomicrobial Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Patient with a Periprosthetic Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Busan Medical Center, Busan, Korea. dreun7@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2185284
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.6.480
Abstract
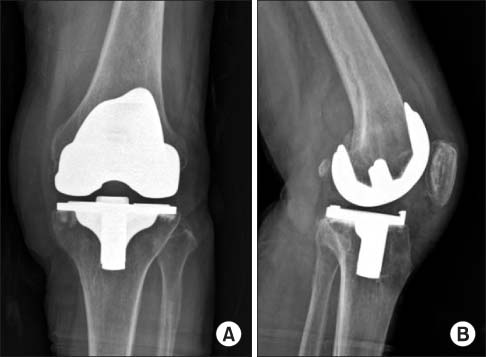
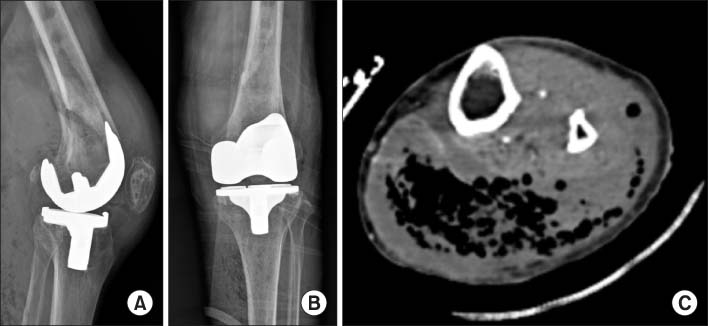
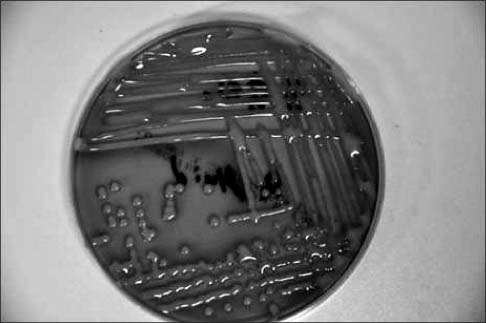
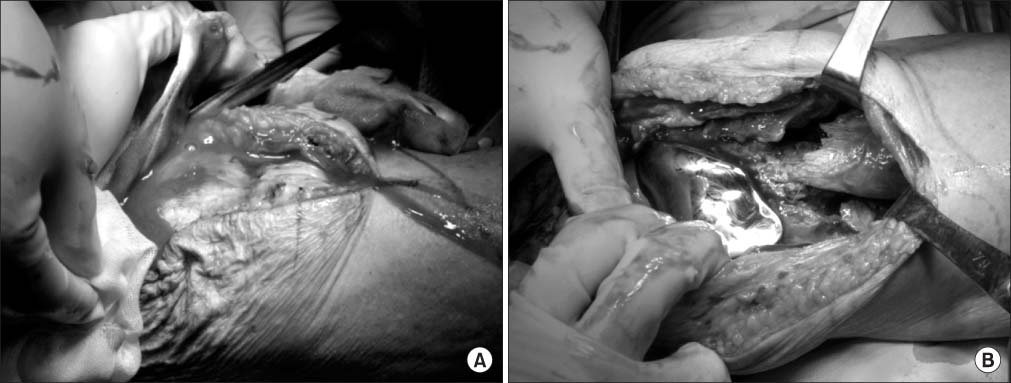
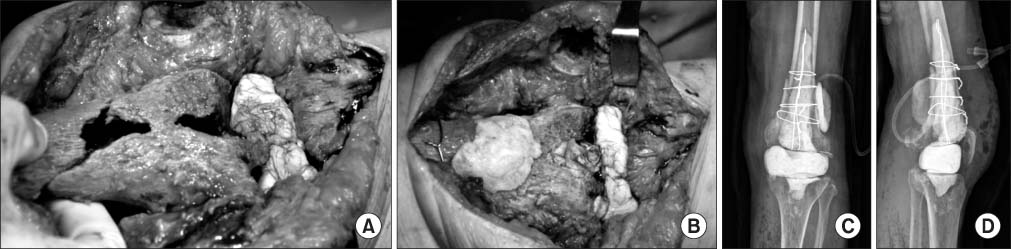
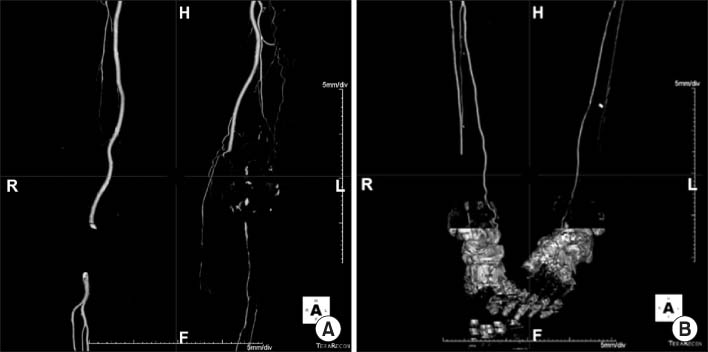
- Septic arthritis caused by Klebsiella pneumonia in adults is rare and is rarely observed after total knee arthroplasty. Acute or early onset of septic arthritis caused by K. pneumoniae has been reported after total knee arthroplasty. However, to date the only one overseas case of late K. pneumoniae infection after total knee arthroplasty has been reported, with no such case in Korea. In addition, monomicrobial infections by K. pneumoniae are not frequently found but are found primarily in the form of polymicrobial infections. The purpose of this paper is to report on a case in which an 85-year-old female patient, who had undergone a total joint arthroplasty 11 years ago, developed the late onset of septic arthritis caused by monomicrobial K. pneumonia infection with a periprosthetic fracture through literature reviews.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parasakthi N, Vadivelu J, Ariffin H, Iyer L, Palasubramaniam S, Arasu A. Epidemiology and molecular characterization of nosocomially transmitted multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int J Infect Dis. 2000; 4:123–128.
Article2. Kaandorp CJ, Van Schaardenburg D, Krijnen P, Habbema JD, van de Laar MA. Risk factors for septic arthritis in patients with joint disease. A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:1819–1825.3. Weston VC, Jones AC, Bradbury N, Fawthrop F, Doherty M. Clinical features and outcome of septic arthritis in a single UK Health District 1982-1991. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999; 58:214–219.
Article4. Schelenz S, Bramham K, Goldsmith D. Septic arthritis due to extended spectrum beta lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Joint Bone Spine. 2007; 74:275–278.
Article5. Chew LC. Septic monoarthritis and osteomyelitis in an elderly man following Klebsiella pneumoniae genitourinary infection: case report. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2006; 35:100–103.6. Park CH, Joo YE, Choi SK, Rew JS, Kim SJ. Klebsiella pneumoniae septic arthritis in a cirrhotic patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Korean Med Sci. 2004; 19:608–610.
Article7. Chodos MD, Johnson CA. Hematogenous infection of a total knee arthroplasty with Klebsiella pneumoniae in association with occult adenocarcinoma of the cecum. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:158.e9–158.e13.
Article8. Lin CC, Hsu HC, Huang CC, Chen SH. Late-onset infection of total knee arthroplasty caused by the Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia. Orthopedics. 2006; 29:1129–1131.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty in the Treatment of Periprosthetic Fracture around the Knee
- Repeated Periprosthethic Femoral Fracture in a Below Knee Amputee with Ipsilateral Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Three Staged Revision Arthroplasty Using Structural Allograft in Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection Accompanied by Fracture: A Case Report
- Periprosthetic Fractures following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Periprosthetic Fractures Following Total Knee Arthroplasty