J Clin Neurol.
2015 Oct;11(4):331-338. 10.3988/jcn.2015.11.4.331.
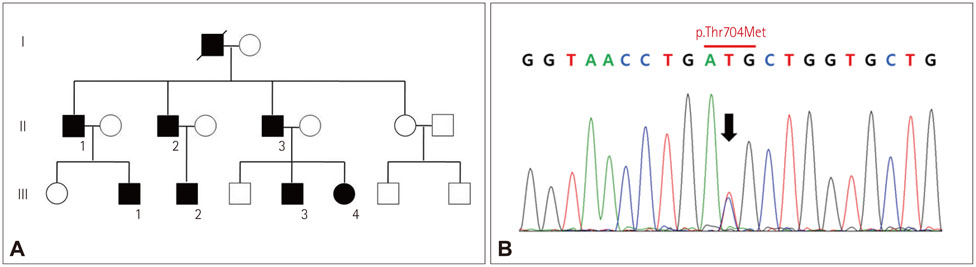
Whole-Body Muscle MRI in Patients with Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis Carrying the SCN4A Mutation T704M: Evidence for Chronic Progressive Myopathy with Selective Muscle Involvement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Research Institute of Radiological Science, Medical Convergence Research Institute, Severance Biomedical Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hayshin@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2179752
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2015.11.4.331
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (hyperKPP) is a muscle sodium-ion channelopathy characterized by recurrent paralytic attacks. A proportion of affected individuals develop fixed or chronic progressive weakness that results in significant disability. However, little is known about the pathology of hyperKPP-induced fixed weakness, including the pattern of muscle involvement. The aim of this study was to characterize the patterns of muscle involvement in hyperKPP by whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
METHODS
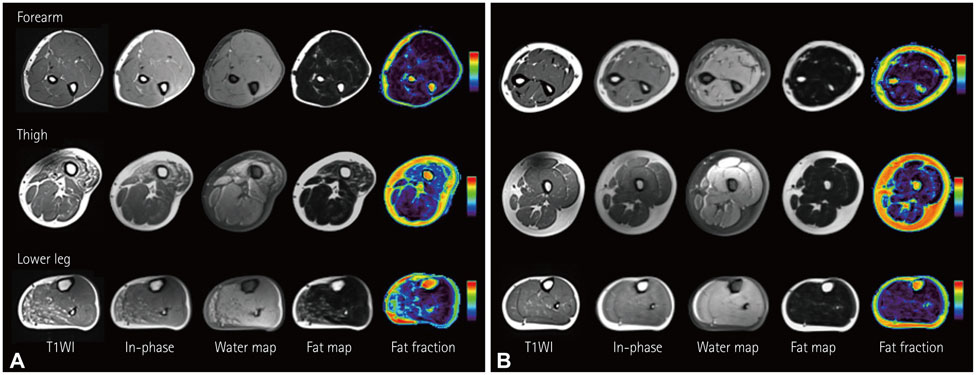
We performed whole-body muscle MRI in seven hyperKPP patients carrying the T704M mutation in the SCN4A skeletal sodium-channel gene. Muscle fat infiltration, suggestive of chronic progressive myopathy, was analyzed qualitatively using a grading system and was quantified by the two-point Dixon technique.
RESULTS
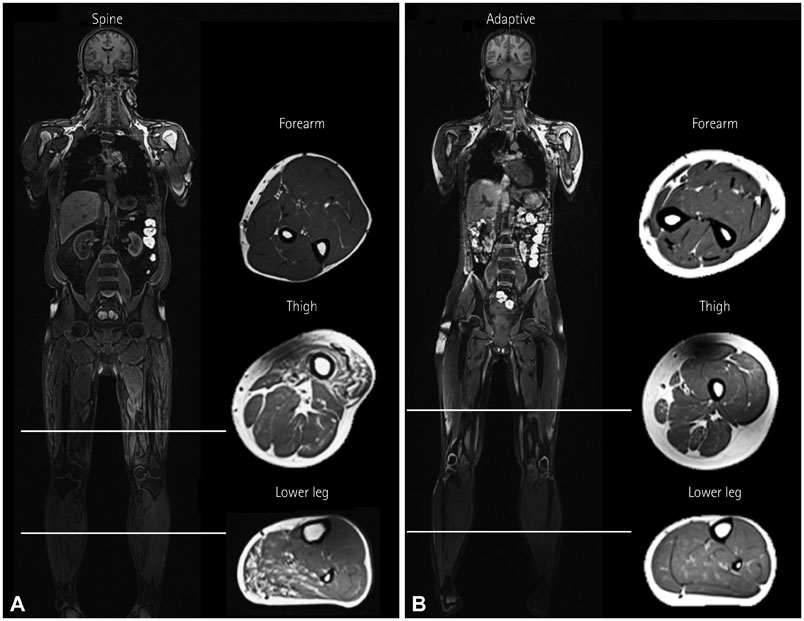
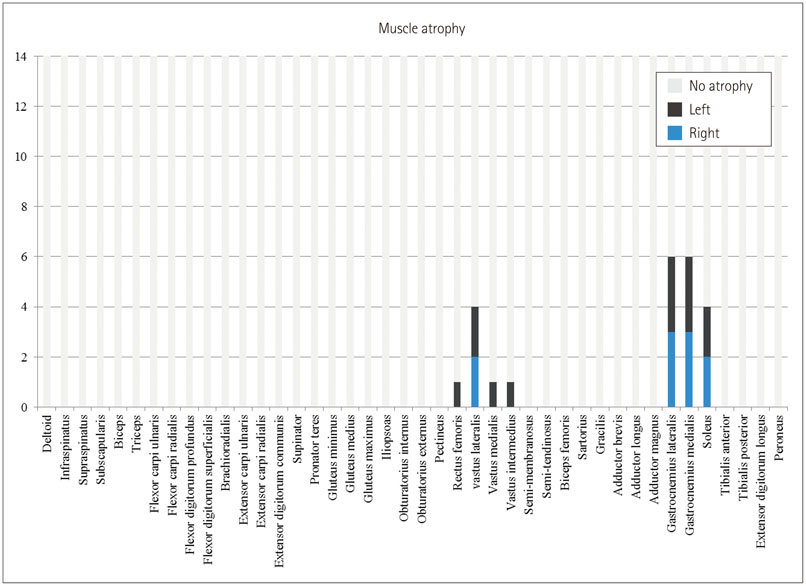
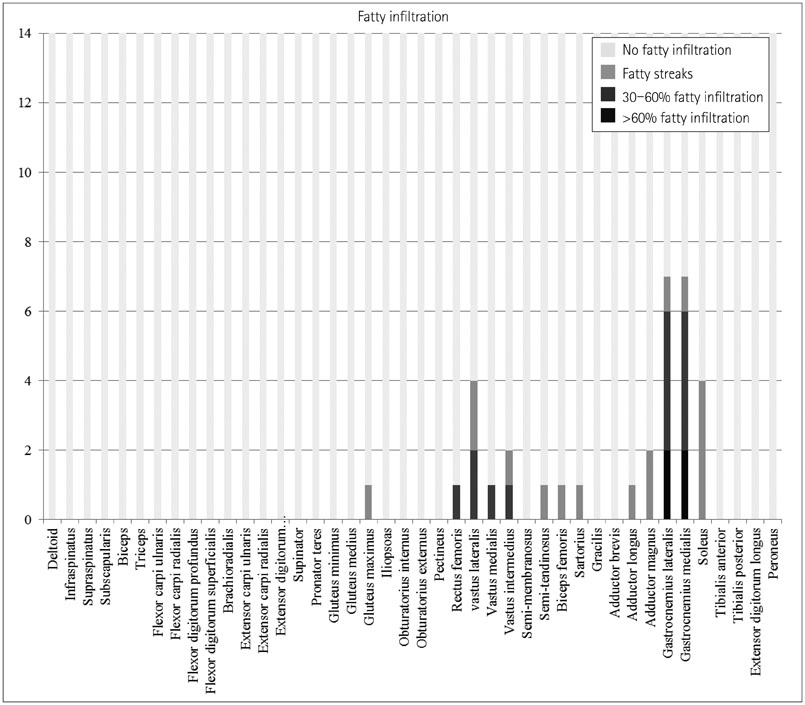
Whole-body muscle MRI analysis revealed muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration in hyperKPP patients, especially in older individuals. Muscle involvement followed a selective pattern, primarily affecting the posterior compartment of the lower leg and anterior thigh muscles. The muscle fat fraction increased with patient age in the anterior thigh (r=0.669, p=0.009), in the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg (r=0.617, p=0.019), and in the superficial posterior compartment of the lower leg (r=0.777, p=0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Our whole-body muscle MRI findings provide evidence for chronic progressive myopathy in hyperKPP patients. The reported data suggest that a selective pattern of muscle involvement-affecting the posterior compartment of the lower leg and the anterior thigh-is characteristic of chronic progressive myopathy in hyperKPP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee SC, Kim HS, Park YE, Choi YC, Park KH, Kim DS. Clinical diversity of SCN4A-mutation-associated skeletal muscle sodium channelopathy. J Clin Neurol. 2009; 5:186–191.
Article2. Ptácek LJ, George AL Jr, Griggs RC, Tawil R, Kallen RG, Barchi RL, et al. Identification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Cell. 1991; 67:1021–1027.
Article3. Bradley WG, Taylor R, Rice DR, Hausmanowa-Petruzewicz I, Adelman LS, Jenkison M, et al. Progressive myopathy in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Arch Neurol. 1990; 47:1013–1017.
Article4. Charles G, Zheng C, Lehmann-Horn F, Jurkat-Rott K, Levitt J. Characterization of hyperkalemic periodic paralysis: a survey of genetically diagnosed individuals. J Neurol. 2013; 260:2606–2613.
Article5. Miller TM, Dias da Silva MR, Miller HA, Kwiecinski H, Mendell JR, Tawil R, et al. Correlating phenotype and genotype in the periodic paralyses. Neurology. 2004; 63:1647–1655.
Article6. Amarteifio E, Nagel AM, Weber MA, Jurkat-Rott K, Lehmann-Horn F. Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and permanent weakness: 3-T MR imaging depicts intracellular 23Na overload--initial results. Radiology. 2012; 264:154–163.
Article7. Hollingsworth KG, de Sousa PL, Straub V, Carlier PG. Towards harmonization of protocols for MRI outcome measures in skeletal muscle studies: consensus recommendations from two TREAT-NMD NMR workshops, 2 May 2010, Stockholm, Sweden, 1-2 October 2009, Paris, France. Neuromuscul Disord. 2012; 22:Suppl 2. S54–S67.
Article8. Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Kakitsubata Y. Skeletal muscle disease: patterns of MRI appearances. Br J Radiol. 2012; 85:e1298–e1308.
Article9. Mendell JR, Florence J. Manual muscle testing. Muscle Nerve. 1990; 13:Suppl. S16–S20.
Article10. Mercuri E, Pichiecchio A, Counsell S, Allsop J, Cini C, Jungbluth H, et al. A short protocol for muscle MRI in children with muscular dystrophies. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2002; 6:305–307.
Article11. Quijano-Roy S, Avila-Smirnow D, Carlier RY. WB-MRI muscle study group. Whole body muscle MRI protocol: pattern recognition in early onset NM disorders. Neuromuscul Disord. 2012; 22:Suppl 2. S68–S84.
Article12. Park HJ, Hong JM, Suh GI, Shin HY, Kim SM, Sunwoo IN, et al. Heterogeneous characteristics of Korean patients with dysferlinopathy. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:423–429.
Article13. Takahashi T, Aoki M, Tateyama M, Kondo E, Mizuno T, Onodera Y, et al. Dysferlin mutations in Japanese Miyoshi myopathy: relationship to phenotype. Neurology. 2003; 60:1799–1804.
Article14. Wren TA, Bluml S, Tseng-Ong L, Gilsanz V. Three-point technique of fat quantification of muscle tissue as a marker of disease progression in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: preliminary study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:W8–W12.
Article15. Ma J. Dixon techniques for water and fat imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 28:543–558.
Article16. Smith AC, Parrish TB, Abbott R, Hoggarth MA, Mendoza K, Chen YF, et al. Muscle-fat MRI: 1.5 Tesla and 3.0 Tesla versus histology. Muscle Nerve. 2014; 50:170–176.
Article17. Noble JJ, Keevil SF, Totman J, Charles-Edwards GD. In vitro and in vivo comparison of two-, three- and four-point Dixon techniques for clinical intramuscular fat quantification at 3 T. Br J Radiol. 2014; 87:20130761.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Familial hyperkalemic periodic paralysis caused by a de novo mutation in the sodium channel gene SCN4A
- Electrophysiological Changes by Exercise and Cold Provocation Test in a Patient with Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis
- A Case of Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis Induced by Diabetic Nephropathy
- Clinical Diversity of SCN4A-Mutation-Associated Skeletal Muscle Sodium Channelopathy
- An atypical phenotype of hypokalemic periodic paralysis caused by a mutation in the sodium channel gene SCN4A