J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2012 Dec;20(4):216-217. 10.4250/jcu.2012.20.4.216.
Infective Endocarditis with Dissection of Sinus of Valsalva Mimicking Type A Aortic Dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. haesun@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2177413
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.4.216
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
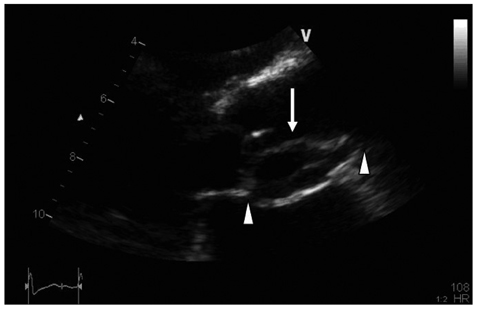
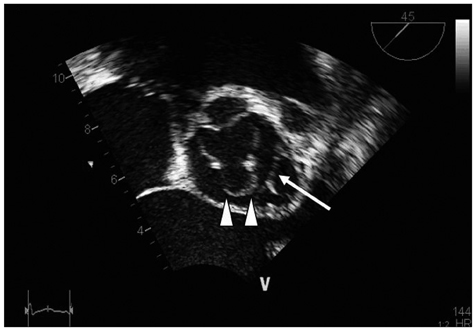
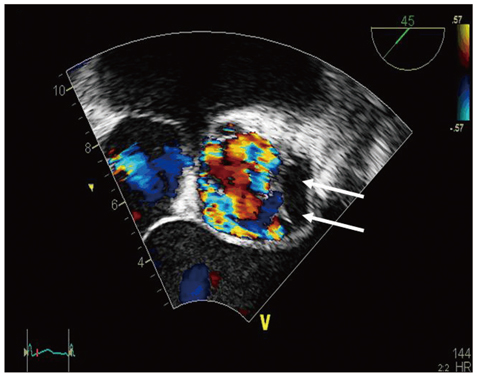
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ikenaga S, Minami Y, Itoh H, Suzuki K, Hamano K. [Acceleration of aortic regurgitation due to localized aortic dissection; report of a case]. Kyobu Geka. 2004. 57:388–390.2. Zhao G, Seng J, Yan B, Wei H, Qiao C, Zhao S, Zhao W, Zhi X. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of ruptured aneurysm in sinus of Valsalva. Chin Med J (Engl). 2003. 116:1047–1050.3. Islam MN, Alimuzzaman M, Khan MN, Bashar MA, Zafar A. Ruptured aneurysm of the sinus of Valsalva. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 1996. 22:19–26.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delayed Rupture of Sinus of Valsalva after Infective Endocarditis: A Case Report
- Simultaneous Aortic and Tricuspid Valve Endocarditis due to Complication of Sinus of Valsalva Rupture
- Evaluation of Localized Aortic Dissection at Sinus of Valsalva by Coronary CT Angiography with Multiplanar Reformation: A Case Report
- Delayed Rupture of the Right Sinus of Valsalva into the Right Atrium after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- A Case of Retrograde Dissection at the Right Sinus of Valsalva Resulted from Dissection of Right Coronary Artery during Ergonovine Test