J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2010 Dec;18(4):148-150. 10.4250/jcu.2010.18.4.148.
Spontaneous Systemic Tumor Embolism Caused by Tumor Invasion of Pulmonary Vein in a Patient with Advanced Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of internal medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. haesunfree@hotmail.com
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2177317
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2010.18.4.148
Abstract
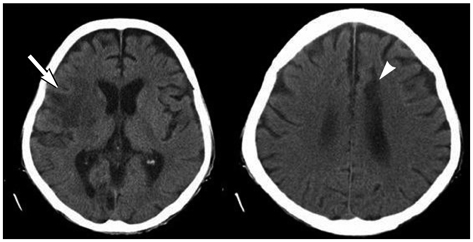
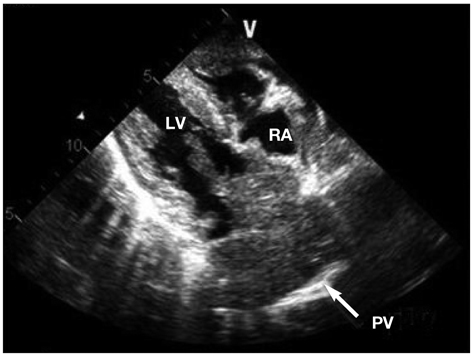
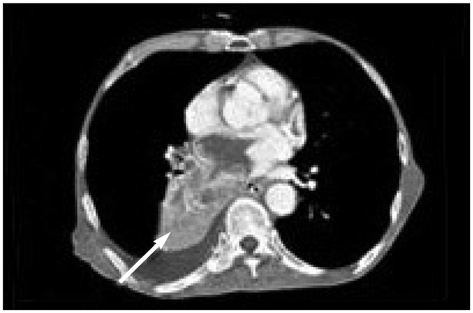
- We describe a 72-year-old man who presented with left hemiparesis due to acute cerebral infarction in the right fronto-temporal lobe. Three months prior to admission, he was hospitalized for right hemiparesis due to the acute cerebral infarction in the left anterior cerebral artery territory. To investigate the cause of his recurrent embolic event, a chest computed tomography scan and echocardiography were performed, which revealed advanced lung cancer invading contiguously through the pulmonary veins to the right main pulmonary artery and left atrium. Tumor embolism is a rare cause of stroke, occurring with primary or metastatic neoplasms of the lung. Echocardiography is a useful tool in patients with cerebral embolic episodes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, Ford E, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott M, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Nichol G, O'Donnell C, Roger V, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong N, Wylie-Rosett J, Hong Y. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009. 119:480–486.2. Sacco RL, Adams R, Albers G, Alberts MJ, Benavente O, Furie K, Goldstein LB, Gorelick P, Halperin J, Harbaugh R, Johnston SC, Katzan I, Kelly-Hayes M, Kenton EJ, Marks M, Schwamm LH, Tomsick T. American Heart Association. American Stroke Association Council on Stroke. Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention. American Academy of Neurology. Guidelines for prevention of stroke in patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Council on Stroke: co-sponsored by the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline. Stroke. 2006. 37:577–617.
Article3. O'Neill BP, Dinapoli RP, Okazaki H. Cerebral infarction as a result of tumor emboli. Cancer. 1987. 60:90–95.4. Isada LR, Salcedo EE, Homa DA, Cohen GI, Rice TW. Intraoperarive transesophageal echocardiographic localization of tumor embolus during pneumonectomy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1992. 5:551–554.
Article5. Whyte RI, Starkey TD, Orringer MB. Tumor emboli from lung neoplasms involving the pulmonary vein. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992. 104:421–425.
Article6. Ascione L, Granata G, Accadia M, Marasco G, Santangelo R, Tuccillo B. Ultrasonography in embolic stroke: the complementary role of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography in a case of systemic embolism by tumor invasion of the pulmonary veins in a patient with unknown malignancy involving the lung. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2004. 5:304–307.
Article7. Imaizumi K, Murate T, Ohno J, Shimokata K. Cerebral infarction due to a spontaneous tumor embolus from lung cancer. Respiration. 1995. 62:155–156.
Article8. Navi BB, Kawaguchi K, Hriljac I, Lavi E, DeAngelis LM, Jamieson DG. Multifocal stroke from tumor emboli. Arch Neurol. 2009. 66:1174–1175.
Article9. Gandhi AK, Pearson AC, Orsinelli DA. Tumor invasion of the pulmonary veins: a unique source of systemic embolism detected by transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1995. 8:97–99.
Article10. Cheitlin MD, Armstrong WF, Aurigemma GP, Beller GA, Bierman FZ, Davis JL, Douglas PS, Faxon DP, Gillam LD, Kimball TR, Kussmaul WG, Pearlman AS, Philbrick JT, Rakowski H, Thys DM, Antman EM, Smith SC Jr, Alpert JS, Gregoratos G, Anderson JL, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Fuster V, Jacobs AK, Gibbons RJ, Russell RO. ACC. AHA. ASE. ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 Guideline Update for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography: summary article. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASE Committee to Update the 1997 Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography). J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003. 16:1091–1110.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulmonary Vein Thrombosis Caused by Lobar Pneumonia
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Caused by Tumor Emboli from the Site of
- A Case of Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma With Pulmonary Tumor Embolism
- Acute Peripheral Arterial Tumorous Embolism after Lung Cancer Surgery
- A Case of Pulmonary Vein Aneurysm Simulating Lung Tumor