J Adv Prosthodont.
2012 Nov;4(4):239-242. 10.4047/jap.2012.4.4.239.
Prosthodontic management of worn dentition in pediatric patient with complete overlay dentures: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Shree Bankey Bihari Dental College and Research Centre, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. drprincegupta20032007@gmail.com
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Dental College, Azamgarh, Uttar Pradesh, India.
- 3Private Practitioner, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India.
- 4Department of Oral Pathology, Swami Devi Dyal Hospital and Dental College, Panchkula, Haryana, India.
- KMID: 2176424
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.4.239
Abstract
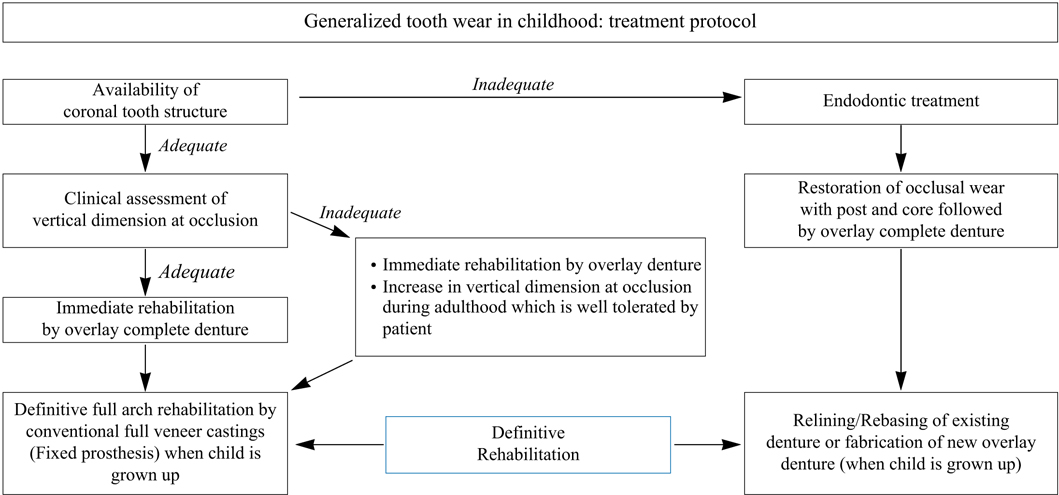
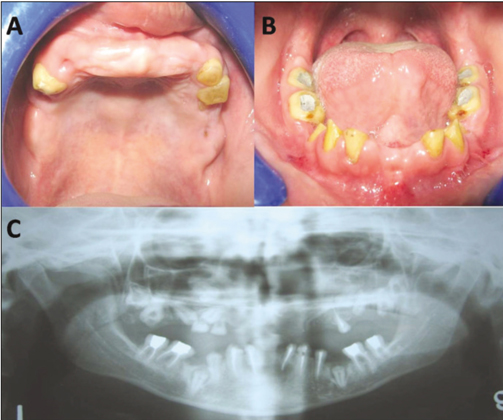
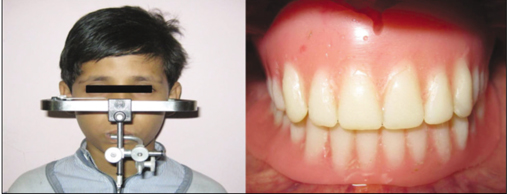
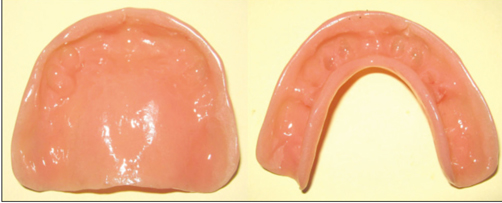
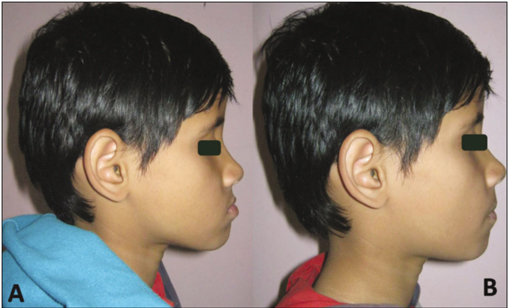
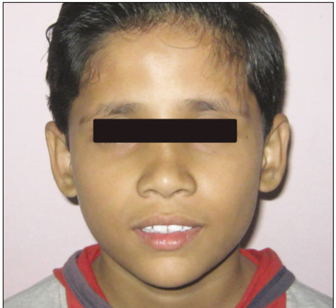
- Overlay complete dentures are simple, reversible and economical treatment modality for patients with congenital or acquired disorders that severely affect the tooth development. It satisfies both the esthetic and functional demands where the extraction of teeth is not generally indicated. In pediatric patients, the overlay dentures establish a relatively stable occlusion that improves patient's tolerance to the future treatment procedures for worn dentition. This clinical report highlights the imperative need of appropriate treatment strategy and application of maxillary and mandibular overlay dentures in a pediatric patient who suffered from congenitally mutilated and worn dentition.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lambrechts P, Braem M, Vuylsteke WM, Vanherle G. Quantitative in vivo wear of human enamel. J Dent Res. 1989. 68:1752–1754.2. Verrett RG. Analyzing the etiology of an extremely worn dentition. J Prosthodont. 2001. 10:224–233.3. Xhonga FA. Bruxism and its effect on the teeth. J Oral Rehabil. 1977. 4:65–76.4. Smith BG, Knight JK. A comparison of patterns of tooth wear with aetiological factors. Br Dent J. 1984. 157:16–19.5. Watts A, Addy M. Tooth discolouration and staining: a review of the literature. Br Dent J. 2001. 190:309–316.6. Turner KA, Missirlian DM. Restoration of the extremely worn dentition. J Prosthet Dent. 1984. 52:467–474.7. Brewer AA, Fenton AH. The overdenture. Dent Clin North Am. 1973. 17:723–746.8. Farmer JB, Connelly ME. Treatment of open occlusions with onlay and overlay removable partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent. 1984. 51:300–303.9. Gankerseer EJ. Case report: a new technique for the treatment of the severely worn dentition. Restorative Dent. 1987. 3:13–14.10. Johnson A, Winstanley RB. Use of simple overdentures in the treatment of young patients with developmental anomalies. Quintessence Dent Technol. 1987. 11:27–33.11. Fayz F, Eslami A, Graser GN. Use of anterior teeth measurements in determining occlusal vertical dimension. J Prosthet Dent. 1987. 58:317–322.12. Heinlein WD. Anterior teeth: esthetics and function. J Prosthet Dent. 1980. 44:389–393.13. Levin EI. Dental esthetics and the golden proportion. J Prosthet Dent. 1978. 40:244–252.14. Ricketts RM. The golden divider. J Clin Orthod. 1981. 15:752–759.15. Johnson A, Winstanley RB. Use of simple overdentures in the treatment of young patients with developmental anomalies. Quintessence Dent Technol. 1987. 11:27–33.16. Dawson P. Evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of occlusal problems. 1989. 2nd ed. St. Louis: CV Mosby;56–71. 500–510.17. Fayz F, Eslami A. Determination of occlusal vertical dimension: a literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 1988. 59:321–323.18. Loiselle RJ, Crum RJ, Rooney GE Jr, Stuever CH Jr. The physiologic basis for the overlay denture. J Prosthet Dent. 1972. 28:4–12.19. Schneidman E, Wilson S, Spuller RL. Complete overlay dentures for the pediatric patient: case reports. Pediatr Dent. 1988. 10:222–225.20. Chu FC, Siu AS, Newsome PR, Chow TW, Smales RJ. Restorative management of the worn dentition: 4. Generalized toothwear. Dent Update. 2002. 29:318–324.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complete mouth rehabilitation with vertical dimension increase in patient with extremely worn dentition
- Overdenture treatment in patient with severely worn dentition: a case report
- Full mouth rehabilitation with extremely worn dentition
- Maxillary full-arch fixed dental prosthesis of the elderly patient with worn dentition
- Esthetically improved complete denture by gingival shade alteration: a case report