J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2010 Jul;35(4):295-301. 10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.295.
Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. kum6139@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Microbiology and Immunology, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4BK21 Program, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2176394
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.295
Abstract
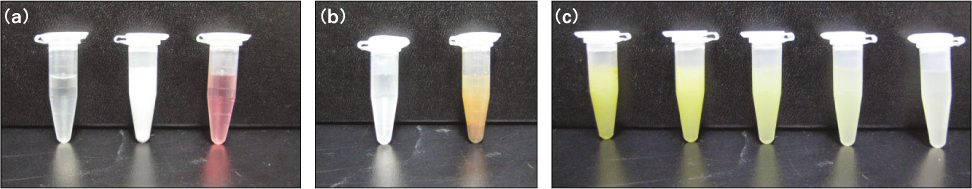
- The purposes of this study were firstly to investigate the any formation of precipitate after interaction between ALX and NaOCL and secondarily to analyze the PCA formation by using time of flight secondary ion mass (TOF-SIM) spectrometry. Mass spectrometry analysis was performed for the mixture of 0.5% ALX and 5.25% NaOCl. As controls, 2.5% CHX with 5.25% NaOCl and 1% PCA solutions were used. Any formation of precipitates in 10 tested solutions was evaluated by naked eye. Results of mass spectrum showed that the typical peak of PCA was not detected in mixed solution of ALX and NaOCl, whereas CHX/NaOCl mixture showed the same peak that found in the PCA spectrum. Precipitate formation was only observed in CHX/NaOCL mixture. The present TOF-SIM spectrometry results indicated that ALX can be a useful root canal irrigant combined with NaOCl during canal instrumentation. Further study is necessary to confirm the antimicrobial effect of ALX against endodontic pathogen before its clinical application as an endodontic irrigant.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Naenni N, Thoma K, Zehnder M. Soft tissue dissolution capacity of currently used and potential endodontic irrigants. J Endod. 2004. 30:785–787.
Article2. Park JH. The effect of solvent action of sodium hypochlorite solution on pulp tissue. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1982. 8:115–122.3. Leonardo MR, Tanomaru Filho M, Silva LA, Nelson Filho P, Bonifacio KC, Ito IY. In vivo antimicrobial activity of 2% chlorhexidine used as a root canal irrigating solution. J Endod. 1999. 25:167–171.
Article4. Kuruvilla JR, Kamath MP. Antimicrobial activity of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite and 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate separately and combined, as endodontic irrigants. J Endod. 1998. 24:472–476.
Article5. Jeansonne MJ, White RR. A comparison of 2.0% chlorhexidine gluconate and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite as antimicrobial endodontic irrigants. J Endod. 1994. 20:276–278.
Article6. Ferguson JW, Hatton JF, Gillespie MJ. Effectiveness of intracanal irrigants and medications against the yeast Candida albicans. J Endod. 2002. 28:68–71.
Article7. White RR, Hays GL, Janer LR. Residual antimicrobial activity after canal irrigation with chlorhexidine. J Endod. 1997. 23:229–231.
Article8. Jeansonne MJ, White RR. A comparison of 2.0% chlorhexidine gluconate and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite as antimicrobial endodontic irrigants. J Endod. 1994. 20:276–278.
Article9. Ohara P, Torabinejad M, Kettering JD. Antibacterial effects of various endodontic irrigants on selected anaerobic bacteria. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1993. 9:95–100.
Article10. Delany GM, Patterson SS, Miller CH, Newton CW. The effect of chlorhexidine gluconate irrigation on the root canal flora of freshly extracted nectoric teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982. 53:518–523.
Article11. Kim HJ, Park SH, Cho KM, Kim JW. Evaluation of time-dependent antimicrobial effect of sodium duchloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) on E. faecalis in the root canal. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007. 32:121–129.
Article12. Lee JK, Baik JE, Yun CH, Lee K, Han SH, Lee W, et al. Chlorhexidine gluconate attenuates the ability of lipoteichoic acid from Enterococcus faecalis to stimulate toll-like receptor 2. J Endod. 2009. 35:212–215.
Article13. Rosenthal S, Spaångberg L, Safavi K. Chlorhexidine substantivity in root canal dentin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004. 98(4):488–492.
Article14. Basrani BR, Manek S, Sodhi RN, Fillery E, Manzur A. Interaction between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine gluconate. J Endod. 2007. 33(8):966–969.
Article15. Chhabra RS, Huff JE, Haseman JK, Elwell MR, Peters AC. Carcinogenicity of p-chloroaniline in rat and mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 1991. 29:119–124.16. Burkhardt-Holm P, Oulmi Y, Schroeder A, Storch V, Braunbeck T. Toxicity of 4-chloroaniline in early life stages if Zebrafish(Danio Rerio): II. Cytopathology and regeneration of liver and gills after prolonged exposure to waterborne 4 chloaniline. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1999. 37:85–102.
Article17. Bui TB, Baumgartner JC, Mitchell JC. Evaluation of the interaction between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine gluconate and its effect on root dentin. J Endod. 2008. 34:181–185.
Article18. Zehnder M. Root canal irrigants. J Endod. 2006. 32:389–398.
Article19. Rasimick B, Nekich M, Hladek M, Musikant B, Beutch A. Interaction between chlorhexidine digluconate and EDTA. J Endod. 2008. 34:1521–1523.
Article20. Choi MS, Park SH, Cho KM, Kim JW. The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2010. 35:80–87.
Article21. McDonnell , Russell AD. Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action and resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999. 12:147–179.
Article22. Zorko M, Jerala R. Alexidine and chlorhexidine bind to lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid and prevent cell activation by antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008. 62:730–737.
Article23. Prestidge CA, Barnes TJ, Skinner W. Time-of-flight secondary-ion mass spectrometry for the surface characterization of solid-state pharmaceuticals. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007. 59(2):251–259.
Article24. Thomas J, Sem D. An in vitro spectroscopic analysis to determine whether para-chloroaniline is produced from mixing sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine. J Endod. 2010. 36:315–317.
Article25. Basrani BR, Manek S, Mathers D, Fillery E, Sodhi RN. Determination of 4-chloroaniline and its derivatives formed in the interaction of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine by using gas chromatography. J Endod. 2010. 36(2):312–314.
Article26. Barbin LE, Saquy PC, Guedes DF, Sousa-Neto MD, Estrela C, Pécora JD. Determination of para-chloroaniline and reactive oxygen species in chlorhexidine and chlorhexidine associated with calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 2008. 34(12):1508–1514.
Article27. Weatherford TW 3rd, Finn SB, Jamison HC. Effects of an alexidine mouthwash on dental plaque and gingivitis in humans over a six-month period. J Am Dent Assoc. 1977. 94:528–536.
Article28. Spolsky VW, Forsythe AB. Effects of alexidine.2HCL mouthwash on plaque and gingivitis after six months. J Dent Res. 1977. 56(11):1349–1358.
Article29. Roberts WR, Addy M. Comparison of the bisbiguanide antiseptics alexidine and chlorhexidine. I. Effect on plaque accumulation and salivary bacteria. J Clin Periodontol. 1981. 8(3):213–219.
Article30. Addy M, Roberts WR. Comparison of the bisbiguanide antiseptics alexidine and chlorhexidine. II. Clinical and in vitro staining properties. J Clin Periodontol. 1981. 8(3):220–230.
Article31. Chawner JA, Gilbert P. A comparative study of the bactericidal and growth inhibitory activities of the bis-biguanides alexidine and chlorhexidine. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989. 66(3):243–252.
Article32. Baker PJ, Coburn RA, Genco RJ, Evans RT. Structural determinants of activity of chlorhexidine and alkyl bis-biguanides against the human oral flora. J Dent Res. 1987. 66(6):1099–1106.
Article33. Yip KW, Ito E, Mao X, Au PY, Hedley DW, Mocanu JD, et al. Potential use of alexidine dihydrochloride as an apoptosis-promoting anticancer agent. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. 5(9):2234–2240.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Precipitate from a combination of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
- The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
- A Case Report of the Chemical Burns Due to Sodium Hypochlorite(NaOCl)
- Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite for Controlling Bacterial Blotch on Pleurotus ostreatus
- Attenuation of over-exposed X-ray film density by sodium hypochlorite in bleaching solution