Intest Res.
2014 Jul;12(3):236-244. 10.5217/ir.2014.12.3.236.
A Double-Blind, Randomized, Active Drug Comparative, Parallel-Group, Multi-Center Clinical Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Probiotics (Bacillus licheniformis, Zhengchangsheng(R) capsule) in Patients with Diarrhea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. skkim@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University, College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2174383
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.3.236
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Bacillus Licheniformis, a probiotic used in the treatment of diarrhea, has been shown to suppress the growth of pathologic bacteria. This study was performed to assess the therapeutic efficacy and safety of Zhengchangsheng(R) (Bacillus Licheniformis) in comparison with another probiotic, Bioflor(R) (Saccharomyces Boulardii) for the treatment of diarrhea.
METHODS
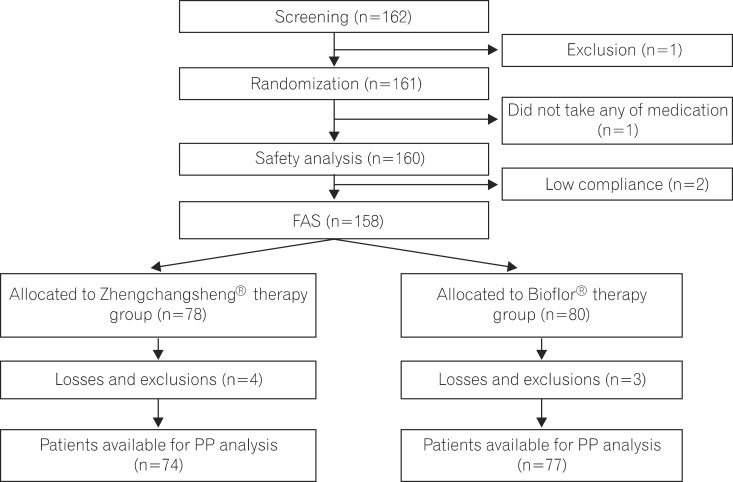
Patients with diarrhea (n=158) were randomized to receive Zhengchangsheng(R) or Bioflor(R) for 5 days. The existence or non-existence of formed feces, changes in daily stool frequency, improvement of subjective symptoms, and changes in the severity of diarrhea were compared.
RESULTS
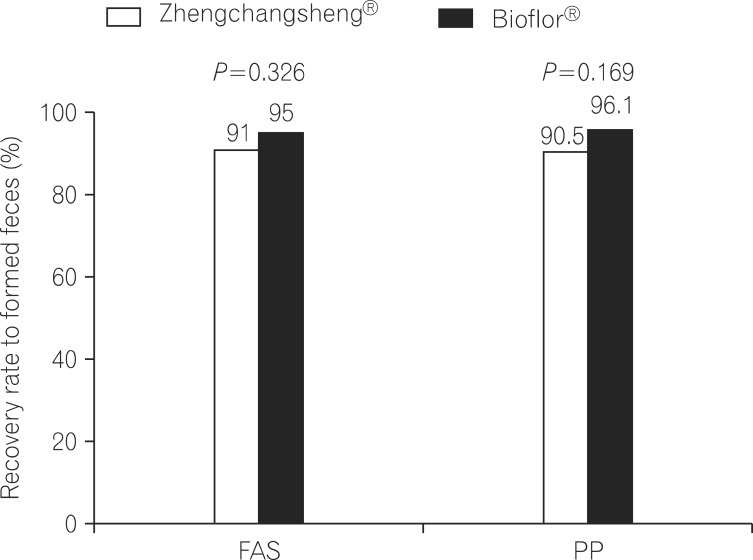
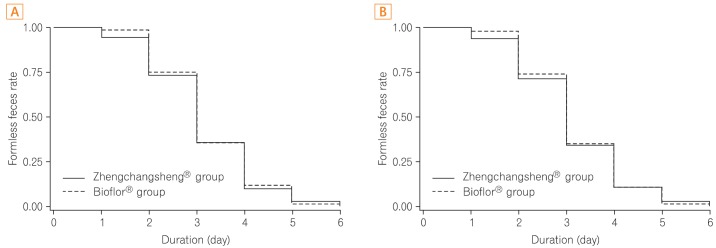
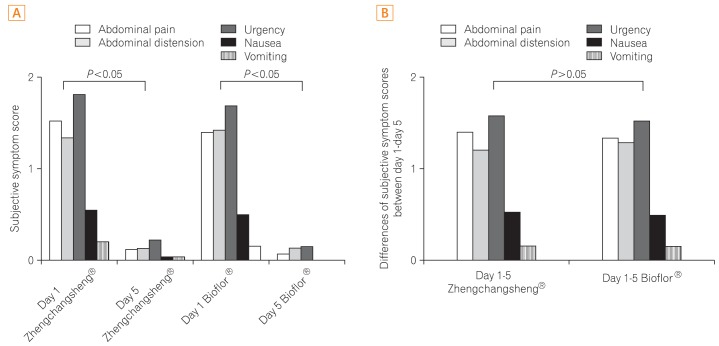
Of the 158 full analysis set (FAS) patient population, 151 patients comprised the per protocol (PP) analysis. The rates of recovered to formed feces in the Bacillus and Saccharomyces groups were 91.0% vs. 95.0% in the FAS (P=0.326) and 90.5% vs. 96.1% in the PP analysis (P=0.169), respectively. The mean duration of diarrhea changing to formed feces was 3.15+/-1.10 days in the Bacillus group and 3.22+/-1.01 in the Saccharomyces group (P=0.695, FAS). The frequency of defecation, subjective symptoms, and degree of severe diarrhea were improved in both groups, however, there were no statistically significant differences between the 2 groups. Analysis of the 95% confidence intervals for the differences in the rate of recovery to formed feces between the 2 groups met the criteria for non-inferiority of Bacillus compared to Saccharomyces. No significant adverse events were observed during the study period.
CONCLUSIONS
Zhengchangsheng(R) is not inferior to Bioflor(R) in therapeutic efficacy and is a safe and useful therapeutic agent for the treatment of diarrhea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. de Vrese M, Marteau PR. Probiotics and prebiotics: effects on diarrhea. J Nutr. 2007; 137:803S–811S. PMID: 17311979.2. Eizaguirre I, Urkia NG, Asensio AB, et al. Probiotic supplementation reduces the risk of bacterial translocation in experimental short bowel syndrome. J Pediatr Surg. 2002; 37:699–702. PMID: 11987081.
Article3. Billoo AG, Memon MA, Khaskheli SA, et al. Role of a probiotic (Saccharomyces boulardii) in management and prevention of diarrhoea. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:4557–4560. PMID: 16874872.
Article4. Whorwell PJ, Altringer L, Morel J, et al. Efficacy of an encapsulated probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1581–1590. PMID: 16863564.
Article5. Oberhelman RA, Gilman RH, Sheen P, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of Lactobacillus GG to prevent diarrhea in undernourished Peruvian children. J Pediatr. 1999; 134:15–20. PMID: 9880443.
Article6. Dendukuri N, Costa V, McGregor M, Brophy JM. Probiotic therapy for the prevention and treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: a systematic review. CMAJ. 2005; 173:167–170. PMID: 16027434.
Article7. McFarland LV. Meta-analysis of probiotics for the prevention of traveler's diarrhea. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2007; 5:97–105. PMID: 17298915.
Article8. Rolfe RD. The role of probiotic cultures in the control of gastrointestinal health. J Nutr. 2000; 130:396S–402S. PMID: 10721914.
Article9. Gaon D, Garcia H, Winter L, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus strains and Saccharomyces boulardii on persistent diarrhea in children. Medicina (B Aires). 2003; 63:293–298. PMID: 14518142.10. Bleichner G, Blehaut H, Mentec H, Moyse D. Saccharomyces boulardii prevents diarrhea in critically ill tube-fed patients. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 1997; 23:517–523. PMID: 9201523.
Article11. Htwe K, Yee KS, Tin M, Vandenplas Y. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii in the treatment of acute watery diarrhea in Myanmar children: a randomized controlled study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008; 78:214–216. PMID: 18256417.
Article13. Conway PL, Gorbach SL, Goldin BR. Survival of lactic acid bacteria in the human stomach and adhesion to intestinal cells. J Dairy Sci. 1987; 70:1–12. PMID: 3106442.
Article14. Goldin BR, Gorbach SL, Saxelin M, Barakat S, Gualtieri L, Salminen S. Survival of Lactobacillus species (strain GG) in human gastrointestinal tract. Dig Dis Sci. 1992; 37:121–128. PMID: 1728516.
Article15. Castagliuolo I, LaMont JT, Nikulasson ST, Pothoulakis C. Saccharomyces boulardii protease inhibits Clostridium difficile toxin A effects in the rat ileum. Infect Immun. 1996; 64:5225–5232. PMID: 8945570.
Article16. Castagliuolo I, Riegler MF, Valenick L, LaMont JT, Pothoulakis C. Saccharomyces boulardii protease inhibits the effects of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B in human colonic mucosa. Infect Immun. 1999; 67:302–307. PMID: 9864230.
Article17. Pothoulakis C, Kelly CP, Joshi MA, et al. Saccharomyces boulardii inhibits Clostridium difficile toxin A binding and enterotoxicity in rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1993; 104:1108–1115. PMID: 8462799.
Article18. Fukushima Y, Kawata Y, Hara H, Terada A, Mitsuoka T. Effect of a probiotic formula on intestinal immunoglobulin A production in healthy children. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998; 42:39–44. PMID: 9706796.
Article19. Malin M, Suomalainen H, Saxelin M, Isolauri E. Promotion of IgA immune response in patients with Crohn's disease by oral bacteriotherapy with Lactobacillus GG. Ann Nutr Metab. 1996; 40:137–145. PMID: 8862696.
Article20. Kaila M, Isolauri E, Soppi E, Virtanen E, Laine S, Arvilommi H. Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human Lactobacillus strain. Pediatr Res. 1992; 32:141–144. PMID: 1324462.
Article21. de Boer AS, Priest F, Diderichsen B. On the industrial use of Bacillus licheniformis: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1994; 40:595–598.
Article22. Rowland I. Probiotics and benefits to human health--the evidence in favour. Environ Microbiol. 1999; 1:375–376. PMID: 11207755.
Article23. Kim JY, Bae EA, Han MJ, Kim DH. Inhibitory activity of Bacillus licheniformis AJ on the growth of diarrheal pathogens. Biomol Ther. 1999; 7:385–389.24. Kim Y, Cho JY, Kuk JH, et al. Identification and antimicrobial activity of phenylacetic acid produced by Bacillus licheniformis isolated from fermented soybean, Chungkook-Jang. Curr Microbiol. 2004; 48:312–317. PMID: 15057459.
Article25. Nijland R, Hall MJ, Burgess JG. Dispersal of biofilms by secreted, matrix degrading, bacterial DNase. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e15668. PMID: 21179489.
Article26. McFarland LV. Meta-analysis of probiotics for the prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhea and the treatment of Clostridium difficile disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:812–822. PMID: 16635227.
Article27. Ki Cha B, Mun Jung S, Hwan Choi C, et al. The effect of a multispecies probiotic mixture on the symptoms and fecal microbiota in diarrhea-dominant irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012; 46:220–227. PMID: 22157240.
Article28. Zhong YQ, Zhu J, Guo JN, et al. A randomized and case-control clinical study on trimebutine maleate in treating functional dyspepsia coexisting with diarrhea-dominant irritable bowel syndrome. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2007; 46:899–902. PMID: 18261269.29. O'Sullivan MA, O'Morain CA. Bacterial supplementation in the irritable bowel syndrome. A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Dig Liver Dis. 2000; 32:294–301. PMID: 11515626.30. Kim YG, Moon JT, Lee KM, Chon NR, Park H. The effects of probiotics on symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006; 47:413–419. PMID: 16809947.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prophylactic efficacy of probiotics on travelers' diarrhea: an adaptive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- A Case of Bacillus licheniformis Bacteremia Associated with Bronchoscopy
- The Effects of Probiotics on Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Efficacy of Levofloxacin and Rifaximin based Quadruple Therapy in Helicobacter pylori Associated Gastroduodenal Disease: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial
- Effect of Probiotics on Intestinal Infections