Education as Prescription for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Compliance and Efficacy in Clinical Practice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jaehyeon@skku.edu
- 2Department of Dietetics, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2174371
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.452
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Diabetes self-management education has an important role in diabetes management. The efficacy of education has been proven in several randomized trials. However, the status of diabetes education programs in real Korean clinical practice has not yet been evaluated in terms of patient compliance with the education prescription.
METHODS
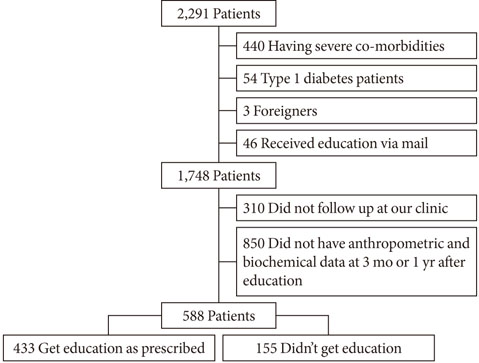
We retrospectively analyzed clinical and laboratory data from all patients who were ordered to undergo diabetes education during 2009 at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea (n=2,291). After excluding ineligible subjects, 588 patients were included in the analysis.
RESULTS
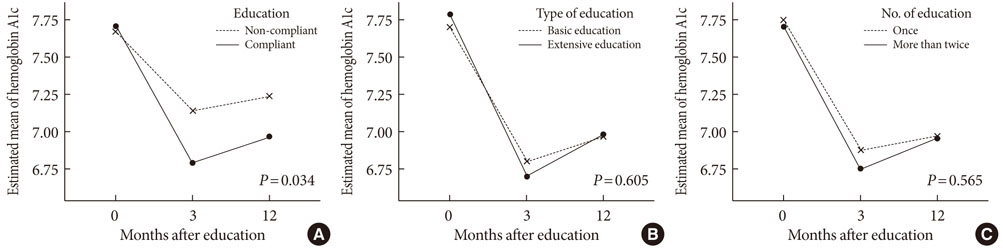
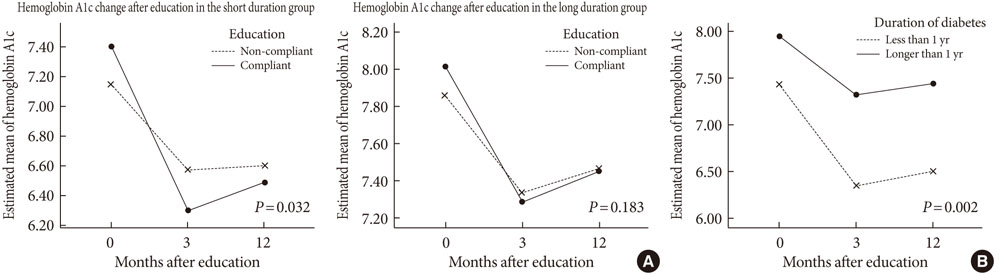
Among the 588 patients, 433 received education. The overall compliance rate was 73.6%, which was significantly higher in the subjects with a short duration or living in a rural area compared to those with a long duration (85.0% vs. 65.1%, respectively; P<0.001) or living in an urban area (78.2% vs. 70.4%, respectively; P=0.037). The hemoglobin A1c decreased greater in the compliant group (from 7.84+/-1.54 at baseline to 6.79+/-1.06 at 3 months and 6.97+/-1.20 at 12 months after prescription in the compliant group vs. from 7.74+/-1.25 to 7.14+/-1.02 and 7.24+/-1.24 in the non-compliant group; P=0.001). The decrease in hemoglobin A1c was greater in the subjects with a short duration (P=0.032).
CONCLUSION
In our study a large percent of patients refuse to get education despite having a prescription from their physician. This refusal rate was higher in the patients with long-standing diabetes or in urban residence. Furthermore, education was more effective in patients with a short duration of diabetes in clinical practice.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The Effectiveness of Multidisciplinary Team-Based Education in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Jong Ho Kim, Yun Jeong Nam, Won Jin Kim, Kyung Ah Lee, A Ran Baek, Jung Nam Park, Jin Mi Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Sang Soo Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2018;19(2):119-133. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2018.19.2.119.Diabetes Camp as Continuing Education for Diabetes Self-Management in Middle-Aged and Elderly People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
So Young Park, Sun Young Kim, Hye Mi Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Kang-Hee Sim, Sang-Man Jin
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(2):99-112. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.99.Management Status of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in Korea: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee, Hyang Mi Jang, Young Na, Hee Sun Choi, Yeon Hee Lee, Yang Gyo Kang, Na Rae Kim, Jeong Rim Lee, Bok Rye Song, Kang Hee Sim
J Korean Diabetes. 2022;23(1):64-75. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2022.23.1.64.
Reference
-
1. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011. 35:303–308.2. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2011. Diabetes Care. 2011. 34:Suppl 1. S11–S61.3. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:1577–1589.4. The relationship of glycemic exposure (HbA1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes. 1995. 44:968–983.5. Gillett M, Dallosso HM, Dixon S, Brennan A, Carey ME, Campbell MJ, Heller S, Khunti K, Skinner TC, Davies MJ. Delivering the diabetes education and self management for ongoing and newly diagnosed (DESMOND) programme for people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: cost effectiveness analysis. BMJ. 2010. 341:c4093.6. Ko SH, Park SA, Cho JH, Shin KM, Lee SH, Song KH, Park YM, Ahn YB. Influence of the duration of diabetes on the outcome of a diabetes self-management education program. Diabetes Metab J. 2012. 36:222–229.7. Noh JH, Kim SK, Cho YJ, Nam HU, Kim IJ, Jeong IK, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Ahn YH, Bae HY, Jang HC. Current status of diabetes management in elderly Koreans with diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 77:Suppl 1. S71–S75.8. Park SW, Kim DJ, Min KW, Baik SH, Choi KM, Park IB, Park JH, Son HS, Ahn CW, Oh JY, Lee J, Chung CH, Kim J, Kim H. Current status of diabetes management in Korea using National Health Insurance database. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2007. 31:362–367.9. Lee JR, Kim SA, Yoo JW, Kang YK. The present status of diabetes education and the role recognition as a diabetes educator of nurses in Korea. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 77:Suppl 1. S199–S204.10. Oh JA, Kim HS, Yoon KH, Choi ES. A telephone-delivered intervention to improve glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients. Yonsei Med J. 2003. 44:1–8.11. Scain SF, dos Santos BL, Friedman R, Gross JL. Type 2 diabetic patients attending a nurse educator have improved metabolic control. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 77:399–404.12. Norris SL, Engelgau MM, Narayan KM. Effectiveness of self-management training in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care. 2001. 24:561–587.13. Funnell MM, Brown TL, Childs BP, Haas LB, Hosey GM, Jensen B, Maryniuk M, Peyrot M, Piette JD, Reader D, Siminerio LM, Weinger K, Weiss MA. National standards for diabetes self-management education. Diabetes Care. 2012. 35:Suppl 1. S101–S108.14. Winkleby MA, Jatulis DE, Frank E, Fortmann SP. Socioeconomic status and health: how education, income, and occupation contribute to risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Am J Public Health. 1992. 82:816–820.15. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). JAMA. 1999. 281:2005–2012.16. Choi MJ, Yoo SH, Kim KR, Bae YM, Ahn SH, Kim SS, Min SA, Choi JS, Lee SE, Moon YJ, Rhee EJ, Park CY, Lee WY, Oh KW, Park SW, Kim SW. Effect on glycemic, blood pressure, and lipid control according to education types. Diabetes Metab J. 2011. 35:580–586.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Development of Exercise Therapy Protocol Applied to an Efficacy Expectation Promoting Program in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Effect of Diabetes Education Program on Glycemic Control and Self Management for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- A Study on the Relationship of Self Care Behavioral Compliance and Perceived Self-Efficacy in Type II Diabetic Patient
- A Study on Perceived Self-efficacy in Non-insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- The Effects of Planned Exercise Program on Metabolism, Cardiopulmonary Function and Exercise Compliance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients