J Korean Diabetes.
2015 Dec;16(4):260-268. 10.4093/jkd.2015.16.4.260.
Recent Advances for Anti-Obesity Agents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea. ironeat@gmail.com
- KMID: 2173852
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2015.16.4.260
Abstract
- Obesity is one of the most significant risk factor for diabetes, cardiovascular disease, malignancy and other chronic diseases. The obesity and its associated conditions is one of the most urgent health concerns worldwide. Lifestyle modifications comprising diet modification, exercise, and behavior therapy are basic to the treatment for obesity. However, it has become apparent that lifestyle modifications alone will not be enough for many patients with obesity. Therefore, apractical approach includes consideration of pharmacotherapeutic options. Until 2012, orlistat was the only approved medication for long-term obesity management. In 2012, lorcaserin and phentermine/topiramate were approved by the USA Food and Drug Administration as new anti-obesity drugs, and in 2014, two additional medications were added, naltrexone/bupropion and liraglutide. This review discusses the different pharmacotherapeutic options for the treatment of obesity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Haslam DW, James WP. Obesity. Lancet. 2005; 366:1197–209.
Article2. Haslam D. Obesity: a medical history. Obes Rev. 2007; 8(Suppl 1):S31–6.
Article3. World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic: report of a WHO Consultation. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO;2000.4. World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Available from:. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/. (cited 2015 Nov 8).5. Kim CS, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim NH, Kim JH, Lim S, Choi SH, Song KH, Won JC, Kim DJ, Cha BY. Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Prevalence, awareness, and management of obesity in Korea: data from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (1998–2011). Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:35–43.
Article6. Tsigos C, Hainer V, Basdevant A, Finer N, Fried M, Mathus-Vliegen E, Micic D, Maislos M, Roman G, Schutz Y, Toplak H, Zahorska-Markiewicz B. Obesity Management Task Force of the European Association for the Study of Obesity. Management of obesity in adults: European clinical practice guidelines. Obes Facts. 2008; 1:106–16.
Article7. James WP. The epidemiology of obesity: the size of the problem. J Intern Med. 2008; 263:336–52.
Article8. Plodkowski RA, St Jeor ST. Medical nutrition therapy for the treatment of obesity. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2003; 32:935–65.
Article9. Hensrud DD. Pharmacotherapy for obesity. Med Clin North Am. 2000; 84:463–76.
Article10. Bassett J. International Diabetes Institute; World Health Organization; Regional Office for the Western Pacific; International Association for the Study of Obesity; International Obesity Task Force. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. St Leonards, Australia: Health Communications Australia;2000.11. Connolly HM, Crary JL, McGoon MD, Hensrud DD, Edwards BS, Edwards WD, Schaff HV. Valvular heart disease associated with fenfluramine-phentermine. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:581–8.
Article12. James WP, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal LF, Maggioni AP, Torp-Pedersen C, Sharma AM, Shepherd GM, Rode RA, Renz CL. SCOUT Investigators. Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:905–17.
Article13. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Treatment guideline of obesity 2012. Seoul: Korean Society for the Study of Obesity;2012.14. Vetter ML, Faulconbridge LF, Webb VL, Wadden TA. Behavioral and pharmacologic therapies for obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010; 6:578–88.
Article15. National Institutes of Health. The Practical Guide; identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults. Bethesda (MD): National Institutes of Health;2000.16. Bray GA, Ryan DH. Medical therapy for the patient with obesity. Circulation. 2012; 125:1695–703.
Article18. Torgerson JS, Hauptman J, Boldrin MN, Sjöström L. XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study: a randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:155–61.19. Rucker D, Padwal R, Li SK, Curioni C, Lau DC. Long term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight: updated metaanalysis. BMJ. 2007; 335:1194–9.
Article20. Thomsen WJ, Grottick AJ, Menzaghi F, Reyes-Saldana H, Espitia S, Yuskin D, Whelan K, Martin M, Morgan M, Chen W, Al-Shamma H, Smith B, Chalmers D, Behan D. Lorcaserin, a novel selective human 5-hydroxytryptamine2C agonist: in vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008; 325:577–87.
Article21. Lam DD, Przydzial MJ, Ridley SH, Yeo GS, Rochford JJ, O'Rahilly S, Heisler LK. Serotonin 5-HT2C receptor agonist promotes hypophagia via downstream activation of melanocortin 4 receptors. Endocrinology. 2008; 149:1323–8.
Article22. Weissman NJ, Tighe JF Jr, Gottdiener JS, Gwynne JT. An assessment of heart-valve abnormalities in obese patients taking dexfenfluramine, sustained-release dexfenfluramine, or placebo. Sustained-Release Dexfenfluramine Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:725–32.23. Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Anderson CM, Sanchez M, Chuang E, Stubbe S, Bays H, Shanahan WR. Behavioral Modification and Lorcaserin for Overweight and Obesity Management (BLOOM) Study Group. Multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of lorcaserin for weight management. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:245–56.
Article24. Fidler MC, Sanchez M, Raether B, Weissman NJ, Smith SR, Shanahan WR, Anderson CM. BLOSSOM Clinical Trial Group. A one-year randomized trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in obese and overweight adults: the BLOSSOM trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:3067–77.
Article25. O'Neil PM, Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Fidler MC, Sanchez M, Zhang J, Raether B, Anderson CM, Shanahan WR. Randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in type 2 diabetes mellitus: the BLOOM-DM study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012; 20:1426–36.26. Astrup A, Toubro S. Topiramate: a new potential pharmacological treatment for obesity. Obes Res. 2004; 12(Suppl):167S–73S.
Article27. Allison DB, Gadde KM, Garvey WT, Peterson CA, Schwiers ML, Najarian T, Tam PY, Troupin B, Day WW. Controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: a randomized controlled trial (EQUIP). Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012; 20:330–42.
Article28. Gadde KM, Allison DB, Ryan DH, Peterson CA, Troupin B, Schwiers ML, Day WW. Effects of low-dose, controlled-release, phentermine plus topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011; 377:1341–52.
Article29. Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, Gadde KM, Allison DB, Peterson CA, Schwiers M, Day WW, Bowden CH. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012; 95:297–308.
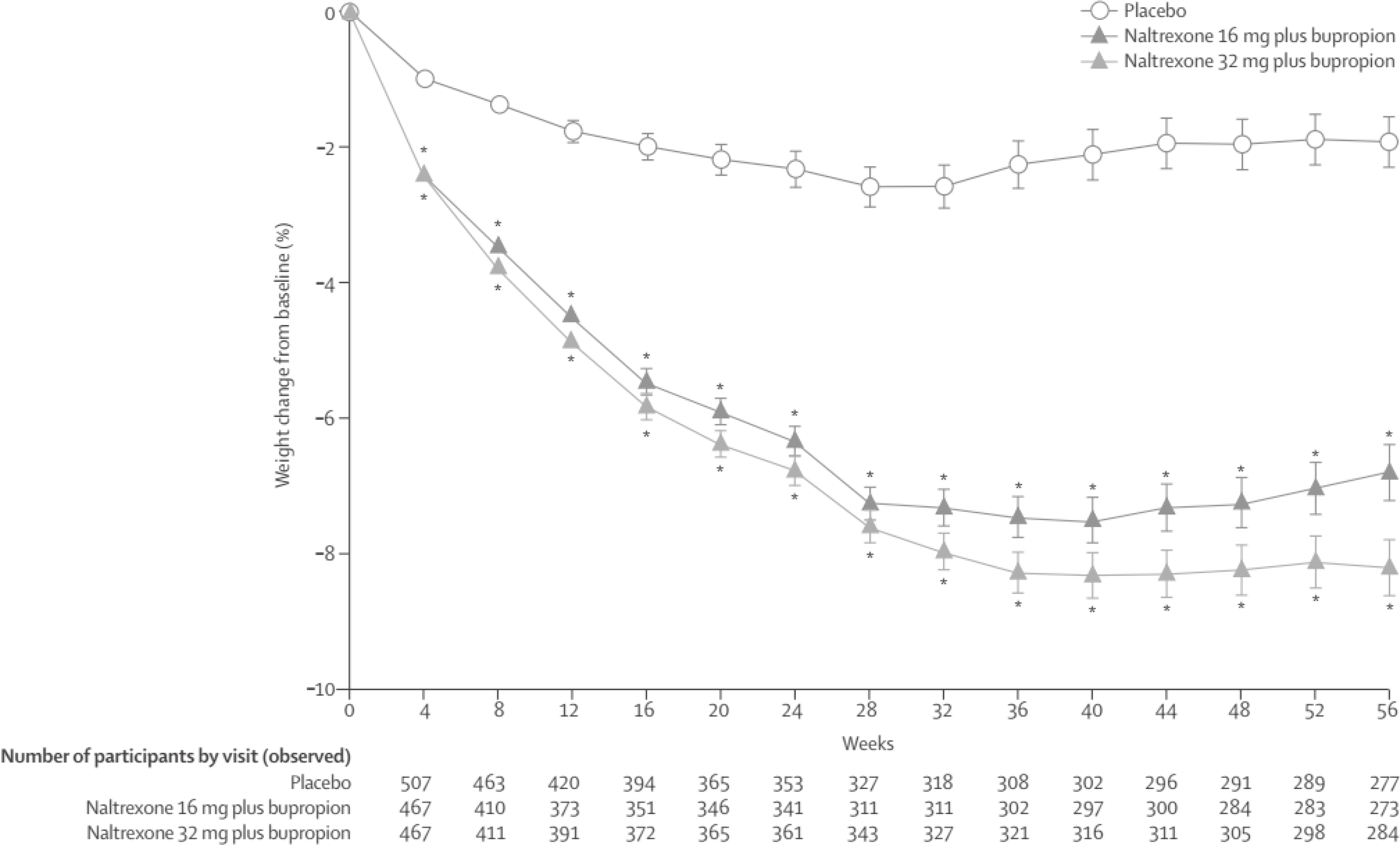
Article30. Ornellas T, Chavez B. Naltrexone SR/Bupropion SR (Contrave): a new approach to weight loss in obese adults. P T. 2011; 36:255–62.31. Greenway FL, Fujioka K, Plodkowski RA, Mudaliar S, Guttadauria M, Erickson J, Kim DD, Dunayevich E. COR-I Study Group. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010; 376:595–605.
Article32. Apovian CM, Aronne L, Rubino D, Still C, Wyatt H, Burns C, Kim D, Dunayevich E. COR-II Study Group. A randomized, phase 3 trial of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related risk factors (COR-II).33. Astrup A, Carraro R, Finer N, Harper A, Kunesova M, Lean ME, Niskanen L, Rasmussen MF, Rissanen A, Rössner S, Savolainen MJ, Van Gaal L. NN8022–1807 Investigators. Safety, tolerability and sustained weight loss over 2 years with the once-daily human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012; 36:843–54.
Article34. Wadden TA, Hollander P, Klein S, Niswender K, Woo V, Hale PM, Aronne L. NN8022–1923 Investigators. Weight maintenance and additional weight loss with liraglutide after low-calorie-diet-induced weight loss: the SCALE Maintenance randomized study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2013; 37:1443–51.
Article