Blood Res.
2014 Mar;49(1):61-64. 10.5045/br.2014.49.1.61.
A case of oxaliplatin-induced immune-mediated thrombocytopenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. doh@cha.ac.kr
- 2Platelet & Neutrophil Immunology Laboratory, Blood Center of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA.
- KMID: 2172825
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2014.49.1.61
Abstract
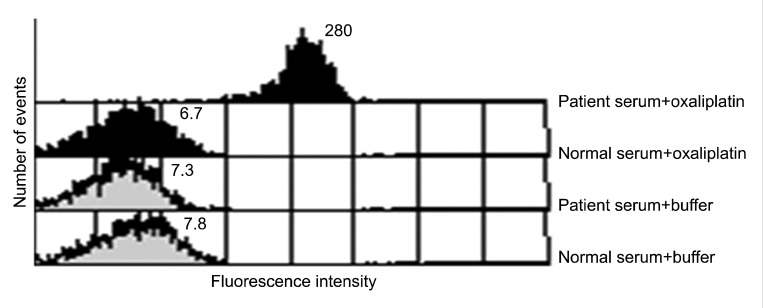
- Oxaliplatin is a platinum compound used in patients with gastrointestinal malignancies. It is known to evoke a drug-induced immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, which has not been reported in Korea. We describe a 53-year-old man who developed oxaliplatin-induced immune-mediated thrombocytopenia during chemotherapy for colon cancer. Oxaliplatin-dependent IgG platelet antibodies were detected in his serum on flow cytometry. He was treated with immunoglobulin and corticosteroids without any complications. Physicians should consider oxaliplatin-induced immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, when a sudden, isolated thrombocytopenia develops during chemotherapy with oxaliplatin.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jardim DL, Rodrigues CA, Novis YA, Rocha VG, Hoff PM. Oxaliplatin-related thrombocytopenia. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:1937–1942. PMID: 22534771.
Article2. Taleghani BM, Meyer O, Fontana S, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced immune pancytopenia. Transfusion. 2005; 45:704–708. PMID: 15847658.
Article3. Curtis BR, Kaliszewski J, Marques MB, et al. Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia resulting from sensitivity to oxaliplatin. Am J Hematol. 2006; 81:193–198. PMID: 16493620.
Article4. Overman MJ, Maru DM, Charnsangavej C, et al. Oxaliplatin-mediated increase in spleen size as a biomarker for the development of hepatic sinusoidal injury. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:2549–2555. PMID: 20406923.
Article5. Desrame J, Broustet H, Darodes de Tailly P, Girard D, Saissy JM. Oxaliplatin-induced haemolytic anaemia. Lancet. 1999; 354:1179–1180. PMID: 10513718.
Article6. Earle CC, Chen WY, Ryan DP, Mayer RJ. Oxaliplatin-induced Evan's syndrome. Br J Cancer. 2001; 84:441. PMID: 11161414.
Article7. Dahabreh I, Tsoutsos G, Tseligas D, Janinis D. Hemolytic uremic syndrome following the infusion of oxaliplatin: case report. BMC Clin Pharmacol. 2006; 6:5. PMID: 16968538.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Oxaliplatin-Induced Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia: A Case Report
- Drug-induced immune-mediated thrombocytopenia due to bevacizumab-FOLFOX therapy: a case report
- Naproxen-induced Immune Thrombocytopenia: A case report
- A Case of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura Associated with Scrub Typhus
- Thrombosis and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 vaccines: vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia