Ann Dermatol.
2009 Feb;21(1):78-80. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.78.
A Case of Acquired Smooth Muscle Hamartoma on the Sole
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. skindoctor@paran.com
- KMID: 2172074
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.78
Abstract
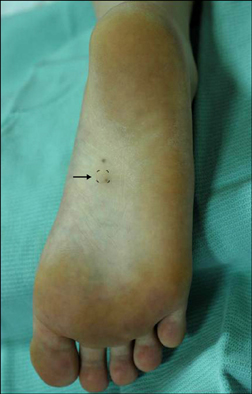
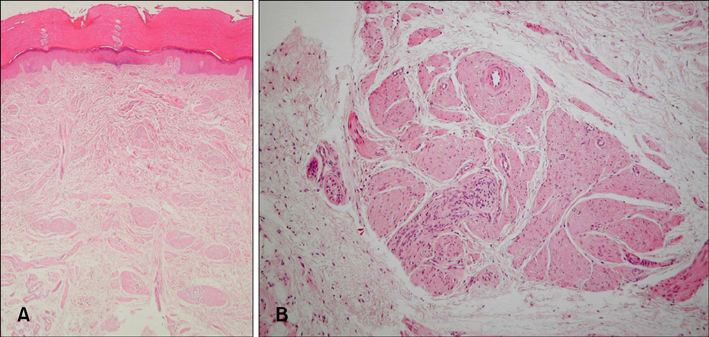
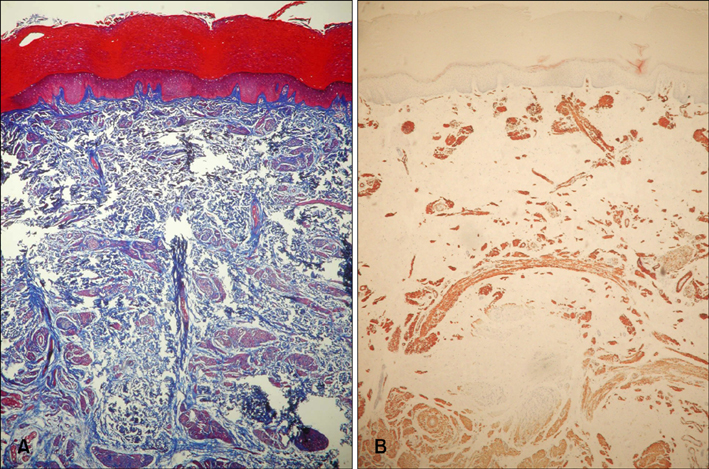
- A smooth muscle hamartoma is a benign proliferation of smooth muscle bundles within the dermis. It arises from smooth muscle cells that are located in arrector pili muscles, dartos muscles, vascular smooth muscles, muscularis mammillae and the areolae. Acquired smooth muscle hamartoma (ASMH) is rare, with only 10 such cases having been reported in the English medical literature to date. Most of these cases of ASMH were shown to have originated from arrector pili and dartos muscles. Only one case was reported to have originated from vascular smooth muscle cells. A 21 year-old woman presented with a tender pigmented nodule, with numbness, on the sole of her foot, and this lesion had developed over the previous 18 months. The lesion showed no hyperpigmentation or hypertrichosis, and the biopsies demonstrated increased smooth muscle bundles in the dermis, and especially around the blood vessels. Moreover, the specimens stained positive with Masson trichrome stain and alpha-smooth-muscle actin antibodies, thus supporting our diagnosis of ASMH of the foot sole. Herein, we report on a rare case of ASMH on the foot sole, and this lesion originated from vascular smooth muscle cells. This type of case has not been previously described in the English medical literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wong RC, Solomon AR. Acquired dermal smooth-muscle hamartoma. Cutis. 1985. 35:369–370.2. ul Bari A, Rahman SB. Acquired smooth muscle hamartoma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006. 72:178.
Article3. van Kooten EO, Hage JJ, Meinhardt W, Horenblas S, Mooi WJ. Acquired smooth-muscle hamartoma of the scrotum: a histological simulator? J Cutan Pathol. 2004. 31:388–392.
Article4. Quinn TR, Young RH. Smooth-muscle hamartoma of the tunica dartos of the scrotum: report of a case. J Cutan Pathol. 1997. 24:322–326.
Article5. Hsiao GH, Chen JS. Acquired genital smooth-muscle hamartoma. A case report. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995. 17:67–70.
Article6. Semerci B, Ilbey O, Yurtseven O. Acquired penoscrotal smooth muscle hamartoma. J Urol. 1997. 158:885–886.
Article7. Oiso N, Fukai K, Ishii M, Hayashi T, Uda H, Imanishi M. A case of acquired smooth muscle hamartoma of the scrotum. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005. 30:523–524.
Article8. Kwon KS, Lee CW, Seo KH, Park JH, Oh CK, Jang HS, et al. Acquired vulvar smooth muscle hamartoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Dermatol. 2000. 27:56–59.
Article9. Morales-Callaghan A, Vila JB, Cardenal EA, Bernier MA, Fraile HA, Miranda-Romero A. Acquired cutaneous smooth muscle hamartoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005. 19:142–143.
Article10. Darling TN, Kamino H, Murray JC. Acquired cutaneous smooth muscle hamartoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993. 28:844–845.
Article11. Ryu HJ, Kim G, Song HJ, Oh CH. A case of acquired cutaneous smooth muscle hamartoma. Ann Dermatol. 2002. 14:161–163.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acquired Smooth Muscle Hamartoma on the Sole
- A Case of Acquired Cutaneous Smooth Muscle Hamartoma
- A Case of Aquired Smooth Muscle Hamartoma with Follicular Spotted Appearance
- A Case of Becker's Nevus Associated with Smooth Muscle Hamartoma
- A case of smooth muscle hamartoma associated with Becker's nevus