Ann Dermatol.
2010 Feb;22(1):114-118. 10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.114.
Identification of Cutaneous Mycobacterium massiliense Infections Associated with Repeated Surgical Procedures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. resina20@cnuh.co.kr
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Korean Institute of Tuberculosis, Korean National Tuberculosis Association, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2172055
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.114
Abstract
- Mycobacterium massiliense, an emerging pathogen that is increasingly reported as a causative agent in infections occurring during medical procedures, is difficult to be identified using conventional methods. Here we report the case of a cutaneous M. massiliense infection that was associated with repeated surgical procedures and that was identified via a comparative sequence analysis of rpoB and hsp65. The patient showed a substantial response to treatment with a combination of antimicrobial therapies consisting of clarithromycin, amikacin, and cefoxitin for 6 months.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
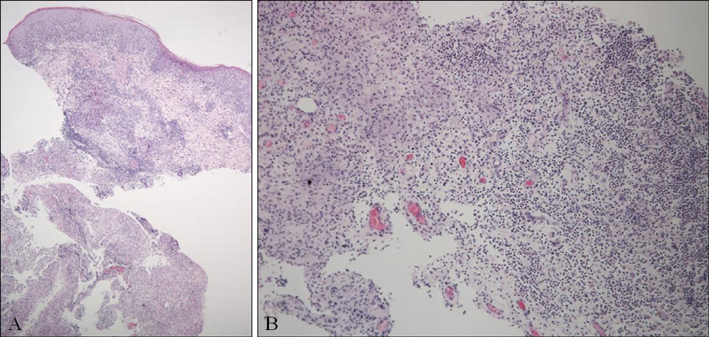
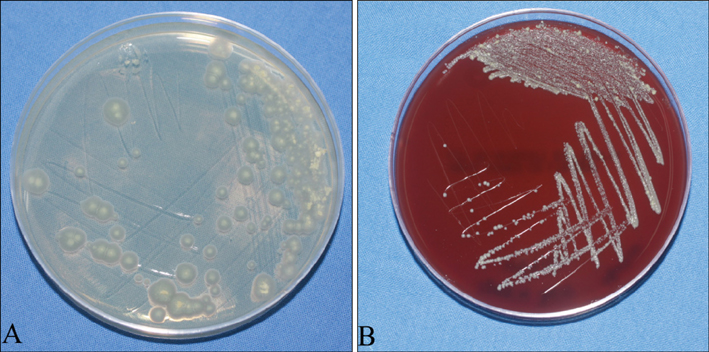
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cutaneous Mycobacterium massiliense Infection of the Sole of the Feet
Mi Young Jung, Jae Hyoung Lee, Cho Rok Kim, Hyun Je Kim, Won Jung Koh, Chang Suk Ki, Joo Heung Lee, Jun Mo Yang, Dong Youn Lee
Ann Dermatol. 2014;26(1):92-95. doi: 10.5021/ad.2014.26.1.92.
Reference
-
1. Adekambi T, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Greub G, Gevaudan MJ, La Scola B, Raoult D, et al. Amoebal coculture of "Mycobacterium massiliense" sp. nov. from the sputum of a patient with hemoptoic pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:5493–5501.
Article2. Brown-Elliott BA, Wallace RJ Jr. Clinical and taxonomic status of pathogenic nonpigmented or late-pigmenting Rapidly growing mycobacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002. 15:716–746.
Article3. Kwon YH, Lee GY, Kim WS, Kim KJ. A case of skin and soft tissue infection caused by Mycobacterium abscessus. Ann Dermatol. 2009. 21:84–87.
Article4. Kim HS, Park HJ, Lee JY, Cho BK. Mycobacterium fortuitum infection caused by a nerve block. Ann Dermatol. 2007. 19:9–12.
Article5. Cardoso AM, Martins de Sousa E, Viana-Niero C, Bonfim de Bortoli F, Pereira das Neves ZC, Leao SC, et al. Emergence of nosocomial Mycobacterium massiliense infection in Goias, Brazil. Microbes Infect. 2008. 10:1552–1557.
Article6. Kim BJ, Lee SH, Lyu MA, Kim SJ, Bai GH, Chae GT, et al. Identification of mycobacterial species by comparative sequence analysis of the RNA polymerase gene (rpoB). J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:1714–1720.
Article7. Kim H, Kim SH, Shim TS, Kim MN, Bai GH, Park YG, et al. PCR restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis (PRA)-algorithm targeting 644 bp Heat Shock Protein 65 (hsp65) gene for differentiation of Mycobacterium spp. J Microbiol Methods. 2005. 62:199–209.
Article8. Kim HY, Yun YJ, Park CG, Lee DH, Cho YK, Park BJ, et al. Outbreak of Mycobacterium massiliense infection associated with intramuscular injections. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:3127–3130.
Article9. Kim HY, Kook Y, Yun YJ, Park CG, Lee NY, Shim TS, et al. Proportions of Mycobacterium massiliense and Mycobacterium bolletii strains among Korean Mycobacterium chelonae-Mycobacterium abscessus group isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. 46:3384–3390.
Article10. Simmon KE, Pounder JI, Greene JN, Walsh F, Anderson CM, Cohen S, et al. Identification of an emerging pathogen, Mycobacterium massiliense, by rpoB sequencing of clinical isolates collected in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:1978–1980.
Article11. Springer B, Stockman L, Teschner K, Roberts GD, Bottger EC. Two-laboratory collaborative study on identification of mycobacteria: molecular versus phenotypic methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. 34:296–303.
Article12. Tortoli E, Gabini R, Galanti I, Mariottini A. Lethal Mycobacterium massiliense sepsis, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008. 14:984–985.13. Viana-Niero C, Lima KV, Lopes ML, Rabello MC, Marsola LR, Brilhante VC, et al. Molecular characterization of Mycobacterium massiliense and Mycobacterium bolletii in isolates collected from outbreaks of infections after laparoscopic surgeries and cosmetic procedures. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. 46:850–855.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Skin and Soft Tissue Infection by Mycobacterium massiliense
- Cutaneous Mycobacterium massiliense Infection Associated with Acupuncture
- Mycobacterium massiliense Infection after Liposuction
- A Case of Mycobacterium massiliense Infection Presenting as Pneumonia Resistant to Antibiotics in an Immunocompetent Host
- A Fatal Case of Acute Respiratory Failure Caused by Mycobacterium massiliense