Ann Dermatol.
2011 Dec;23(Suppl 3):S404-S407. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S404.
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Sorafenib and Tosufloxacin in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jheo@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dermatology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2171884
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S404
Abstract
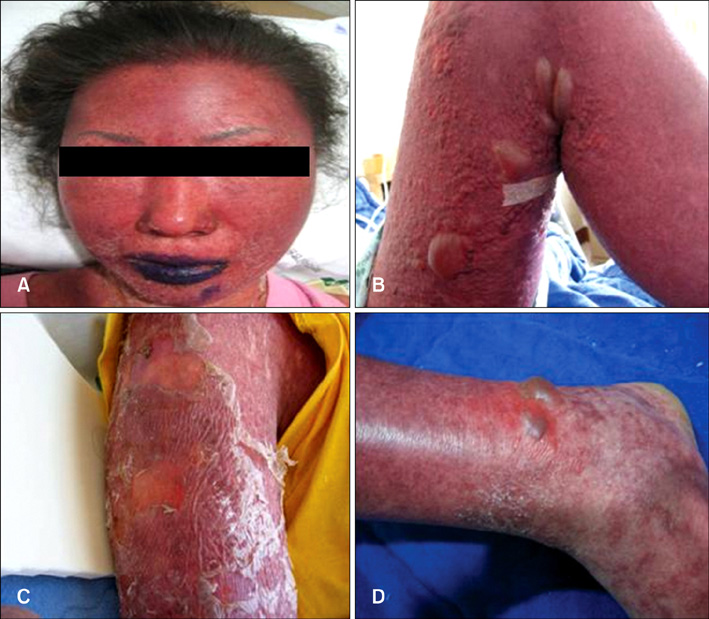
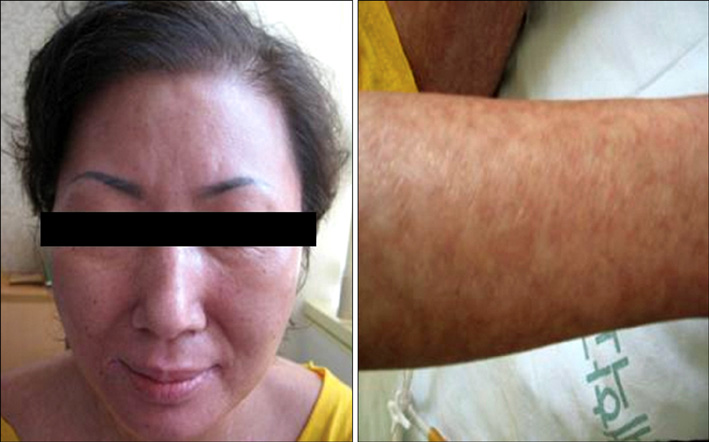
- This is the first case report to describe a 44-year-old woman with a history of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who developed toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) clinically after taking 400 mg sorafenib (Nexavar(R), BAY 43-9006) and tosufloxacin orally once per day. Both sorafenib and tosufloxacin were eventually discontinued, and the TEN resolved with corticosteroids and supportive treatment. Clinical physicians should be aware of this possible complication so that early interventions can be made.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994. 331:1272–1285.
Article2. Roujeau JC, Chosidow O, Saiag P, Guillaume JC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell syndrome). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990. 23:1039–1058.
Article3. Lyell A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (the scalded skin syndrome): a reappraisal. Br J Dermatol. 1979. 100:69–86.
Article4. Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol. 1993. 129:92–96.
Article5. Parsons JM. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Int J Dermatol. 1992. 31:749–768.
Article6. Becker DS. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Lancet. 1998. 351:1417–1420.
Article7. Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Rzany B, Stern RS, Anderson T, et al. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med. 1995. 333:1600–1607.
Article8. Guillaume JC, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Penso D, Touraine R. The culprit drugs in 87 cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome). Arch Dermatol. 1987. 123:1166–1170.
Article9. French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens Johnson syndrome: our current understanding. Allergol Int. 2006. 55:9–16.
Article10. Villada G, Roujeau JC, Clérici T, Bourgault I, Revuz J. Immunopathology of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Keratinocytes, HLA-DR expression, Langerhans cells, and mononuclear cells: an immunopathologic study of five cases. Arch Dermatol. 1992. 128:50–53.
Article11. Correia O, Delgado L, Ramos JP, Resende C, Torrinha JA. Cutaneous T-cell recruitment in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Further evidence of CD8+ lymphocyte involvement. Arch Dermatol. 1993. 129:466–468.
Article12. Nassif A, Bensussan A, Dorothée G, Mami-Chouaib F, Bachot N, Bagot M, et al. Drug specific cytotoxic T-cells in the skin lesions of a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. 118:728–733.
Article13. Chung WH, Hung SI, Hong HS, Hsih MS, Yang LC, Ho HC, et al. Medical genetics: a marker for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Nature. 2004. 428:486.14. van der Meer JB, Schuttelaar ML, Toth GG, Kardaun SH, Beerthuizen G, de Jong MC, et al. Successful dexamethasone pulse therapy in a toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) patient featuring recurrent TEN to oxazepam. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001. 26:654–656.
Article15. Khoo AK, Foo CL. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a burns centre: a 6-year review. Burns. 1996. 22:275–278.
Article16. Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Wolkenstein P. SCORTEN: a severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. 115:149–153.
Article17. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. SHARP Investigators Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:378–390.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Carbamazepine- Induced- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Due to Contact of Paraquat(Gramoxone(R))
- A Case of Complete Vaginal Ostruction Following Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Review of Literatures
- T Cell Mediated Drug Hypersensitivity: Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis