Ann Dermatol.
2015 Aug;27(4):450-451. 10.5021/ad.2015.27.4.450.
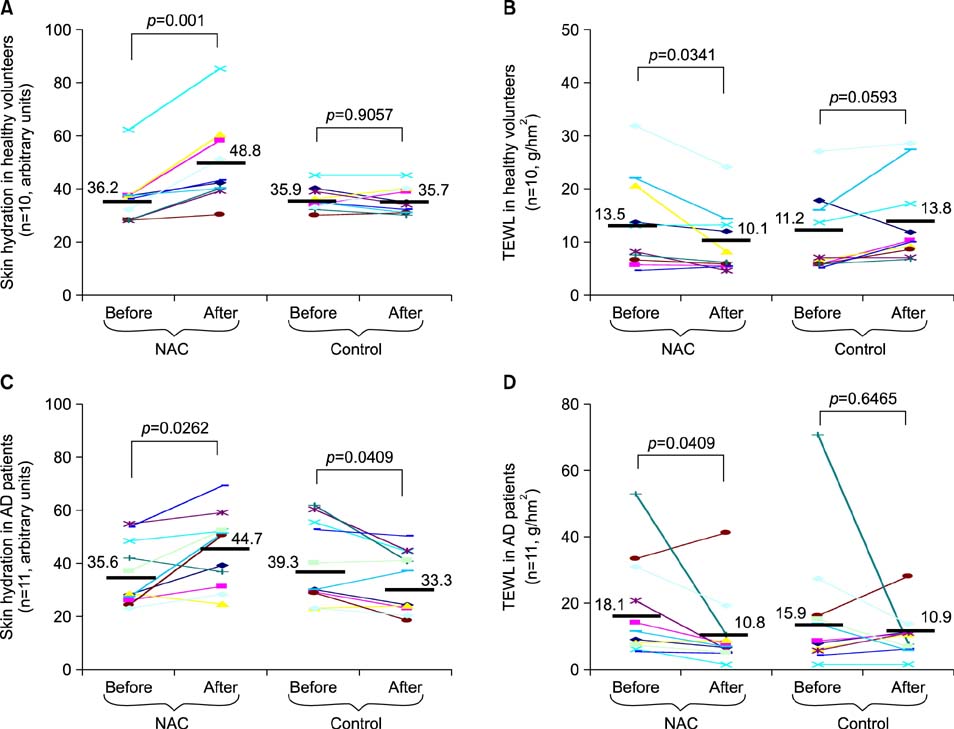
Effects of Topical N-Acetylcysteine on Skin Hydration/Transepidermal Water Loss in Healthy Volunteers and Atopic Dermatitis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Kagawa, Japan. kozo@kms.ac.jp
- KMID: 2171506
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.4.450
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Werner Y. The water content of the stratum corneum in patients with atopic dermatitis. Measurement with the Corneometer CM 420. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986; 66:281–284.2. Werner Y, Lindberg M. Transepidermal water loss in dry and clinically normal skin in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985; 65:102–105.3. Vélez A, Moreno JC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with N-acetylcysteine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002; 46:469–470.
Article4. Redondo P, Bauzá A. Topical N-acetylcysteine for lamellar ichthyosis. Lancet. 1999; 354:1880.
Article5. Nakai K, Yoneda K, Hosokawa Y, Moriue T, Presland RB, Fallon PG, et al. Reduced expression of epidermal growth factor receptor, E-cadherin, and occludin in the skin of flaky tail mice is due to filaggrin and loricrin deficiencies. Am J Pathol. 2012; 181:969–977.
Article6. Tokura Y. Extrinsic and intrinsic types of atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. 2010; 58:1–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction in the Scalp, Nails, and Lips in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- The Correlation between SCORAD Index and Instrumental Assessment in Evaluation of Atopic Dermatitis Severity
- The Effects of Humidifier Generating Nano-sized Water Particles on Skin Hydration and Transepidermal Water Loss of the Normal Human Skin
- Comparison of Transepidermal Water Loss, Capacitance and pH Values in the Skin between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Atopic Dermatitis Patients
- Effectiveness of Topical Chia Seed Oil on Pruritus of End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Patients and Healthy Volunteers