Ewha Med J.
2013 Sep;36(2):149-152. 10.12771/emj.2013.36.2.149.
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Presenting Variceal Bleeding in Patient with Systemic Anaerobic Bacterial Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. junghk@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2171252
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2013.36.2.149
Abstract
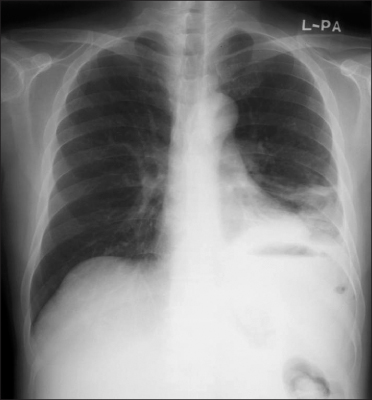
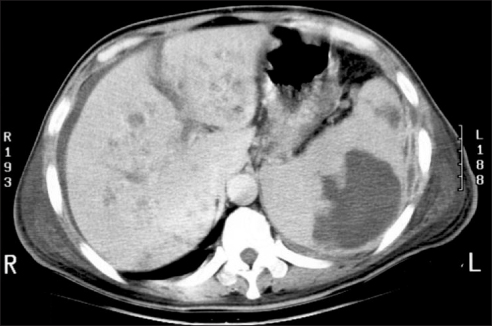
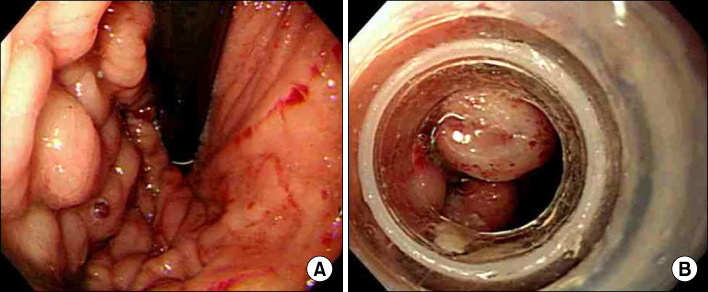
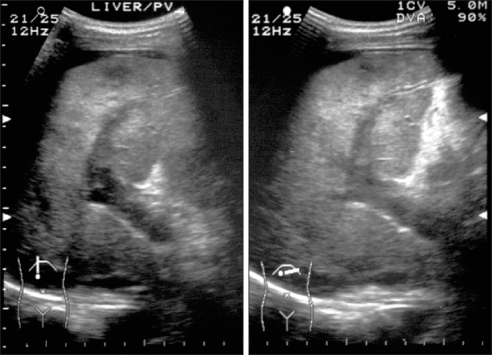
- Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is characterized by raised levels of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), in association with thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia. Development of APS is related with idiopathic origin, autoimmune disease, malignancy and, on rare occasions, infection. However, in secondary APS combined with bacterial infections, aPL is usually shown with low titer and rarely associated with thrombotic events. A 52-year-old male was admitted due to pneumonia and multiple hepatosplenic abscesses. He had been treated with proper antibiotics, but he presented ascites and sudden variceal bleeding because of portal vein thrombosis. The bleeding was controlled by endoscopic variceal ligation. Acute portal vein thrombosis was successfully managed by low molecular weight heparin and hepatosplenic abscesses were completely resolved by antibiotics. This case suggests that systemic bacterial infection in immunocompetent patients possibly develops into secondary APS.
MeSH Terms
-
Abscess
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Antiphospholipid Syndrome*
Ascites
Bacterial Infections*
Esophageal and Gastric Varices*
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage*
Heparin, Low-Molecular-Weight
Humans
Ligation
Male
Middle Aged
Pneumonia
Portal Vein
Thrombocytopenia
Venous Thrombosis
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Heparin, Low-Molecular-Weight
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levine JS, Branch W, Rauch J. The antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:752–763.2. Harel M, Aron-Maor A, Sherer Y, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y. The infectious etiology of the antiphospholipid syndrome:links between infection and autoimmunity. Immunobiology. 2005; 210:743–747.3. Sthoeger ZM, Fogel M, Smirov A, Ergas D, Lurie Y, Bass DD, et al. Anticardiolipin autoantibodies in serum samples and cryoglobulins of patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000; 59:483–486.4. Baid S, Pascual M, Williams WW Jr, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Johnson SM, Collins B, et al. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy associated with anticardiolipin antibodies in hepatitis C-positive renal allograft recipients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:146–153.5. Bloom EJ, Abrams DI, Rodgers G. Lupus anticoagulant in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1986; 256:491–493.6. Himoto T, Yoneyama H, Kurokohchi K, Mori H, Inukai M, Masugata H, et al. Clinical relevance of antibodies to cardiolipin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Clin Lab Anal. 2012; 26:342–348.7. Kiser KL, Badowski ME. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pharmacotherapy. 2010; 30:1292–1302.8. Blank M, Asherson RA, Cervera R, Shoenfeld Y. Antiphospholipid syndrome infectious origin. J Clin Immunol. 2004; 24:12–23.9. Blank M, Krause I, Fridkin M, Keller N, Kopolovic J, Goldberg I, et al. Bacterial induction of autoantibodies to beta2-glycoprotein-I accounts for the infectious etiology of antiphospholipid syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2002; 109:797–804.10. Martin E, Winn R, Nugent K. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome in a community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection: A review of pathogenesis with a case for molecular mimicry. Autoimmun Rev. 2011; 10:181–188.11. Blank M, Shoenfeld Y. Beta-2-glycoprotein-I, infections, antiphospholipid syndrome and therapeutic considerations. Clin Immunol. 2004; 112:190–199.12. Gropp K, Weber N, Reuter M, Micklisch S, Kopka I, Hallström T, et al. 2-glycoprotein I, the major target in antiphospholipid syndrome, is a special human complement regulator. Blood. 2011; 118:2774–2783.13. Hirohata Y, Murata A, Abe S, Otsuki M. Portal vein thrombosis associated with antiphospholipid syndrome. J Gastroenterol. 2001; 36:574–578.14. Plemmons RM, Dooley DP, Longfield RN. Septic thrombophlebitis of the portal vein (pylephlebitis): diagnosis and management in the modern era. Clin Infect Dis. 1995; 21:1114–1120.15. Bjornson HS, Hill EO. Bacteroidaceae in thromboembolic disease: effects of cell wall components on blood coagulation in vivo and in vitro. Infect Immun. 1973; 8:911–918.16. Bjornson HS. Activation of Hageman factor by lipopolysaccharides of Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides vulgatus, and Fusobacterium mortiferum. Rev Infect Dis. 1984; 6:Suppl 1. S30–S33.17. Liappis AP, Roberts AD, Schwartz AM, Simon GL. Thrombosis and infection: a case of transient anti-cardiolipin antibody associated with pylephlebitis. Am J Med Sci. 2003; 325:365–368.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Secondary AntiphospholipidSyndrome Presenting as Livedo Reticularis
- A patient with chorea associated with hyperthyroidism and primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- Flank ulcer in a patient with primary antiphospholipid syndrome
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome Associated with Adenocarcinoma
- Recurrent Systemic Embolizetion Caused by Aortic Thrombus in Antiphospholipid Antibody syndrome: A Case Report