Infect Chemother.
2012 Oct;44(5):391-394. 10.3947/ic.2012.44.5.391.
Herpes Zoster Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in a HIV-infected Patient: Case Report and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. yhj822@medimail.co.kr
- KMID: 2170386
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2012.44.5.391
Abstract
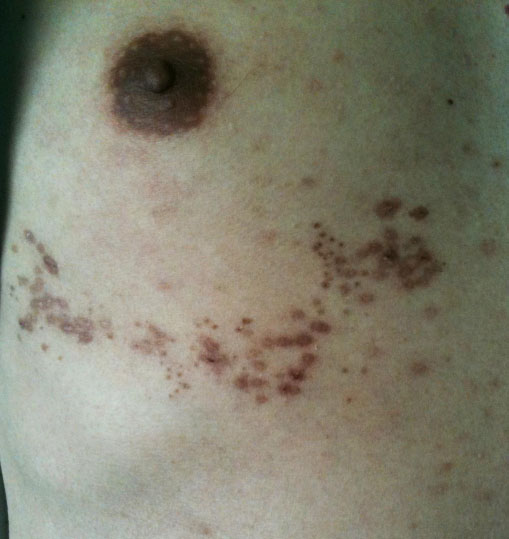
- According to current evidence, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients who have undergone treatment with antiretroviral therapy are at greater risk of developing herpes zoster, not when they are severely immunocompromised, but, paradoxically, when their immune system is recovering. This is a manifestation of the immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). Here we report on a case of IRIS, presented as herpes zoster in a HIV-infected patient after undergoing highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. French MA, Lenzo N, John M, Mallal SA, McKinnon EJ, James IR, Price P, Felxman JP, Tay-Kearney ML. Immune restoration disease after the treatment of immunodeficient HIV-infected patients with highly active antiretroviral therapy. HIV Med. 2000. 1:107–115.
Article2. Espinosa E, Peña-Jiménez A, Ormsby CE, Vega-Barrientos R, Reyes-Terán G. Later onset of herpes zoster-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. HIV Med. 2009. 10:454–457.
Article3. Harpaz R, Ortega-Sanchez IR, Seward JF. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of herpes zoster: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008. 57:1–30. Quiz CE2-4.4. Bower M, Nelson M, Young AM, Thirlwell C, Newsom-Davis T, Mandalia S, Dhillon T, Holmes P, Gazzard BG, Stebbing J. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome associated with Kaposi's sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:5224–5228.
Article5. Lawn SD, Bekker LG, Miller RF. Immune reconstitution disease associated with mycobacterial infections in HIV-infected individuals receiving antiretrovirals. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005. 5:361–373.
Article6. Tsang CS, Samaranayake LP. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after highly active antiretroviral therapy: a review. Oral Dis. 2010. 16:248–256.
Article7. Müller M, Wandel S, Colebunders R, Attia S, Furrer H, Egger M. IeDEA Southern and Central Africa. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in patients starting antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010. 10:251–261.
Article8. Gebo KA, Kalyani R, Moore RD, Polydefkis MJ. The incidence of, risk factors for, and sequelae of herpes zoster among HIV patients in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005. 40:169–174.
Article9. Lawn SD, Wood R. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010. 10:833–834.
Article10. Michailidis C, Pozniak AL, Mandalia S, Basnayake S, Nelson MR, Gazzard BG. Clinical characteristics of IRIS syndrome in patients with HIV and tuberculosis. Antivir Ther. 2005. 10:417–422.
Article11. Ratnam I, Chiu C, Kandala NB, Easterbrook PJ. Incidence and risk factors for immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in an ethnically diverse HIV type 1-infected cohort. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42:418–427.
Article12. Martínez E, Gatell J, Morán Y, Aznar E, Buira E, Guelar A, Mallolas J, Soriano E. High incidence of herpes zoster in patients with AIDS soon after therapy with protease inhibitors. Clin Infect Dis. 1998. 27:1510–1513.
Article13. Domingo P, Torres OH, Ris J, Vazquez G. Herpes zoster as an immune reconstitution disease after initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy in patients with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infection. Am J Med. 2001. 110:605–609.
Article14. Rodgers S, Leslie KS. Skin infection in HIV-infected individuals in the era of HAART. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011. 24:124–129.15. Srikantiah P, Walusimbi MN, Kayanja HK, Mayanja-Kizza H, Mugerwa RD, Lin R, Charlebois ED, Boom WH, Whalen CC, Havlir DV. Early virological response of zidovudine/lamivudine/abacavir for patients co-infected with HIV and tuberculosis in Uganda. AIDS. 2007. 21:1972–1974.
Article16. Shelburne SA, Visnegarwala F, Darcourt J, Graviss EA, Giordano TP, White AC Jr, Hamill RJ. Incidence and risk factors for immune reconstitution syndrome during highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS. 2005. 19:399–406.
Article17. Bucy RP, Hockett RD, Derdeyn CA, Saag MS, Squires K, Sillers M, Mitsuyasu RT, Kilby JM. Initial increase in blood CD4(+) lymphocytes after HIV antiretroviral therapy reflects redistribution from lymphoid tissues. J Clin Invest. 1999. 103:1391–1398.
Article18. Feller L, Wood NH, Lemmer J. Herpes zoster infection as an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-seropositive subjects: a review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007. 104:455–460.
Article19. Lidhoo P, Unemori P, Leslie KS, Maurer T. Disseminated herpes zoster with increased CD4 counts in 3 HIV-infected patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009. 61:345–347.
Article20. Shelburne SA 3rd, Hamill RJ, Rodriguez-Barradas MC, Greengerg SB, Atmar RL, Musher DW, Gathe JC Jr, Visnegarwala F, Trautner BW. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: emergence of a unique syndrome during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Medicine (Baltimore). 2002. 81:213–227.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Presenting as Cutaneous Miliary Tuberculosis in an HIV-Infected Patient
- Molluscum Contagiosum as a Skin Manifestation of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in an AIDS Patient Who Is Receiving HAART
- A Case of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in Recurrent Herpes Zoster
- Treatment and Prevention of Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Patients
- Paradoxical Cryptococcal Meningitis Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in a Patient with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: Matching Clinical Findings with MRI Findings