Infect Chemother.
2012 Oct;44(5):386-390. 10.3947/ic.2012.44.5.386.
A Case of Mixed Malaria Infection with Severe Hemolytic Anemia after Travel to Angola
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. joonsup.yeom@gmail.com
- 3Division of Malaria and Parasitic Diseases, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Osong, Korea.
- KMID: 2170385
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2012.44.5.386
Abstract
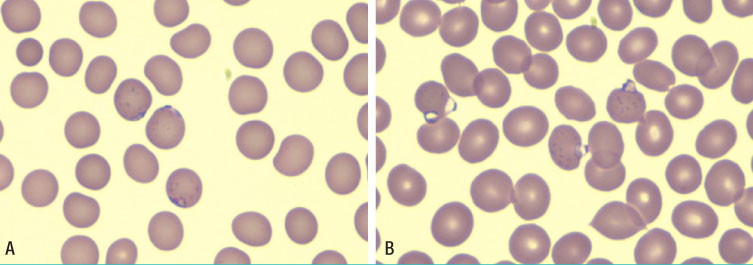
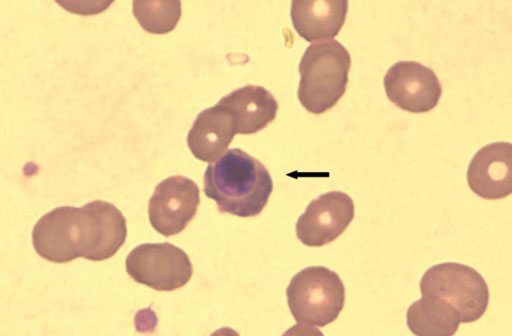
- In Korea, Plasmodium vivax (P. vivax) is the most common agent of malaria infection. However, as travel to regions where malaria is endemic increases, so do the numbers of Plasmodium falciparum and mixed infections. P. falciparum predominates, while P. vivax is rare in west-central Africa. We report on a case of mixed malaria infection with severe hemolytic anemia caused by P. falciparum and P. vivax in a 38-year-old man after traveling to Angola. A diagnosis of P. falciparum malaria was made by microscopic examination. However, both P. vivax and P. falciparum were detected by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). As a radical cure P. vivax, the patient was treated with mefloquine, artemether, and primaquine. Both P. falciparum and P. vivax had disappeared from peripheral blood by admission day 4, however, low grade fever and headache persisted, and his hemoglobin and hematocrit levels were depleted. A peripheral blood smear was negative for both P. vivax and P. falciparum; however, a direct anti-globulin test and anti-nuclear antibody test were positive, suggesting immune hemolytic anemia. After conservative treatment, which included a transfusion with packed red blood cells (RBC), his symptoms and signs showed improvement and laboratory findings were normalized.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Mixed Infection with Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium ovale in a Returned Traveller: the First Case in Korea
Gayeon Kim, Hyo-Lim Hong, So Yeon Kim, Hye Ryun Lee, Dong Geun Kim, Seungman Park, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Bum Sik Chin, YeonJae Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(3):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e23.
Reference
-
1. Korea Center for disease control & prevention. 2009 Malaria. Accessed 11 February 2012. Available at: http://www.cdc.go.kr.2. Mehlotra RK, Lorry K, Kastens W, Miller SM, Alpers MP, Bockarie M, Kazura JW, Zimmerman PA. Random distribution of mixed species malaria infections in Papua New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000. 62:225–231.
Article3. Nathwani D, Badial R, Khaund RR, Douglas JG, Smith CC. Malaria in Aberdeen: an audit of 110 patients admitted between 1980-1991. Scott Med J. 1992. 37:106–110.
Article4. Krudsood S, Wilairatana P, Mason DP, Treeprasertsuk S, Singhasivanon P, Looareesuwan S. Hidden Plasmodium falciparum infections. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1999. 30:623–624.5. Lyn PC. Cerebral malaria and mixed falciparum-vivax infections. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1987. 16:310–312.6. Newton JA Jr, Schnepf GA, Wallace MR, Lobel HO, Kennedy CA, Oldfield EC 3rd. Malaria in US Marines returning from Somalia. JAMA. 1994. 272:397–399.
Article7. Inquérito de Indicadores de Malária em Angola 2011. Accessed 11 February 2012. Available at: http://www.measuredhs.com.8. Miller LH, Mason SJ, Dvorak JA, McGinniss MH, Rothman IK. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science. 1975. 189:561–563.
Article9. Mendes C, Dias F, Figueiredo J, Mora VG, Cano J, de Sousa B, do Rosário VE, Benito A, Berzosa P, Arez AP. Duffy negative antigen is no longer a barrier to Plasmodium vivax--molecular evidences from the African West Coast (Angola and Equatorial Guinea). PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011. 5:e1192. Epub 2011 Jun 21.10. Shin KS, Kim JS, Ryu SW, Suh IB, Lim CS. A case of Plasmodium vivax infection diagnosed after treatment of imported falciparum malaria. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2001. 21:360–364.11. Jeong AC, Ahn BJ, Choi CK, Yoon KS, Nam HW, Lee WJ, Lee JS. A case of mixed malarial infection wtih Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Korean J Infect Dis. 1998. 30:194–197.12. Kim JM, Yoo TH, Park CJ, Chi HS. A mixed cerebral infection of vivax and falciparum malaria. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2000. 20:263–267.13. Cooper RD, Waterson DG, Frances SP, Beebe NW, Pluess B, Sweeney AW. Malaria vectors of Papua New Guinea. Int J Parasitol. 2009. 39:1495–1501.
Article14. Alifrangis M, Lemnge MM, Moon R, Theisen M, Bygbjerg I, Ridley RG, Jakobsen PH. IgG reactivities against recombinant Rhoptry-Associated Protein-1 (rRAP-1) are associated with mixed Plasmodium infections and protection against disease in Tanzanian children. Parasitology. 1999. 119(Pt 4):337–342.
Article15. Drouin J, Rock G, Jolly EE. Plasmodium falciparum malaria mimicking autoimmune hemolytic anemia during pregnancy. Can Med Assoc J. 1985. 132:265–267.16. Facer CA, Bray RS, Brown J. Direct Coombs antiglobulin reactions in Gambian children with Plasmodium falciparum malaria. I. Incidence and class specificity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979. 35:119–127.17. Daniel Ribeiro CT, de Roquefeuil S, Druilhe P, Monjour L, Homberg JC, Gentilini M. Abnormal anti-single stranded (ss) DNA activity in sera from Plasmodium falciparum infected individuals. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984. 78:742–746.
Article18. Cho SE, Huh JW, Chung WS. Antinuclear Antibody Production in Patients with Malaria Infection. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2001. 21:385–389.19. Ashley EA, Touabi M, Ahrer M, Hutagalung R, Htun K, Luchavez J, Dureza C, Proux S, Leimanis M, Lwin MM, Koscalova A, Comte E, Hamade P, Page AL, Nosten F, Guerin PJ. Evaluation of three parasite lactate dehydrogenase-based rapid diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of falciparum and vivax malaria. Malar J. 2009. 8:241.
Article20. Okell LC, Ghani AC, Lyons E, Drakeley CJ. Submicroscopic infection in Plasmodium falciparum-endemic populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2009. 200:1509–1517.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Plasmodium vivax Malaria Associated with Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
- A mixed cerebral infection of vivax and falciparum malaria
- An Imported Case of Severe Falciparum Malaria with Prolonged Hemolytic Anemia Clinically Mimicking a Coinfection with Babesiosis
- Health advice for international travelers
- Severe Hemolytic Anemia following Anti-D Immunoglobulin Administration for Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Two-month-old Infants