Infect Chemother.
2011 Jun;43(3):245-250. 10.3947/ic.2011.43.3.245.
Serial Testing of T-SPOT.TB Assays with Anti-Tuberculosis Therapy in Patients with Extrapulmonay Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimsunghanmd@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2170345
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2011.43.3.245
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
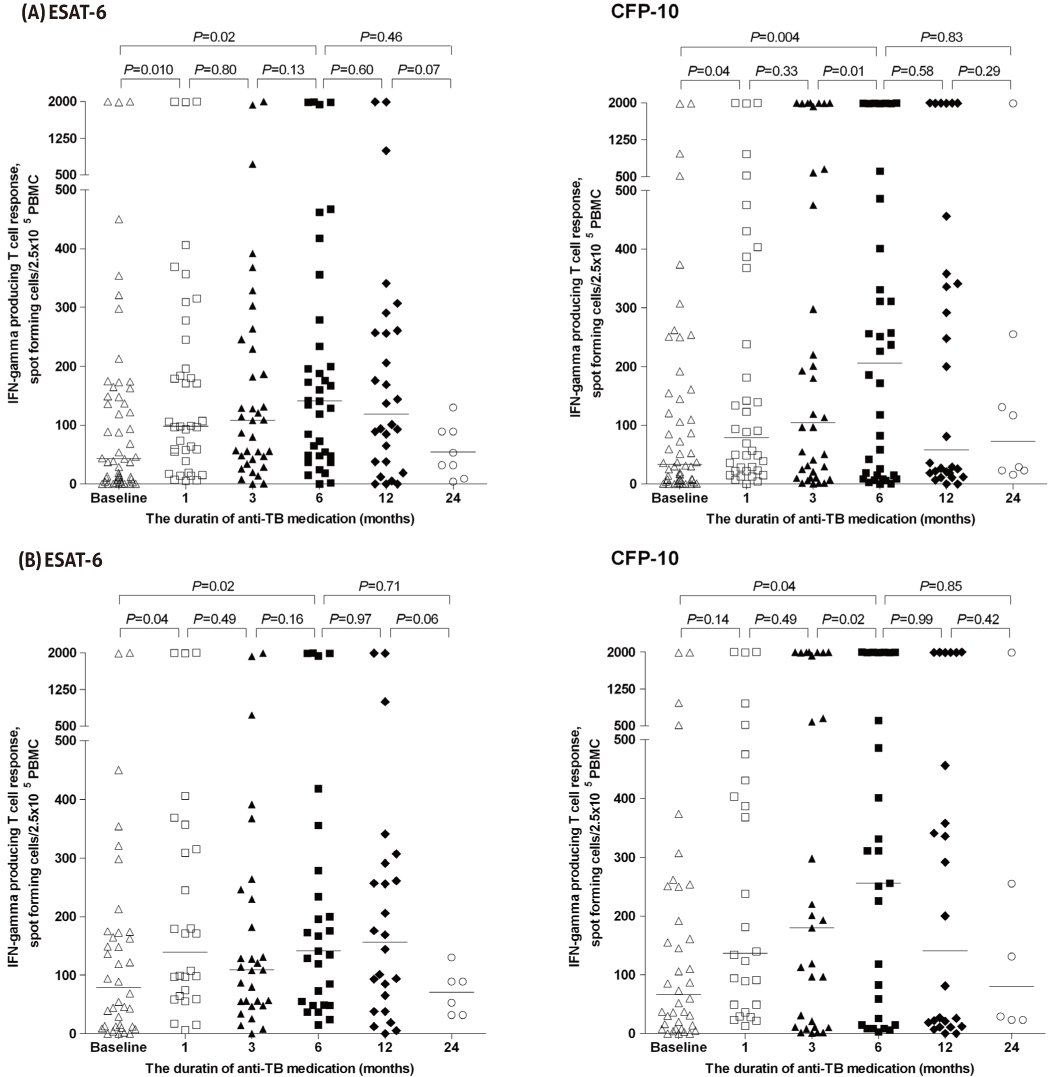
Limited data are available for the clinical utility of serial interferon-gamma producing T-cell response after initiation of treatment in patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis (TB). We studied the serial TB-specific antigen T-cell responses measured using the T-SPOT.TB assay during the course of therapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We prospectively enrolled adult patients who were newly diagnosed with active extrapulmonary TB over a 24-month period. All patients were given standard anti-TB treatment. Blood samples were obtained for T-SPOT.TB at diagnosis, as well as 1-, 3-, 6-, and 12-months after initiating anti-TB therapy.
RESULTS
A total of 52 patients with extrapulmonary TB (38 confirmed and 14 probable TB) were included in the final analysis. All patients had clinical and radiologic improvement after treatment and cured. T-SPOT.TB was positive for 90% at diagnosis, 100% at 1-, 3-, and 6-months, and 93% at 12-months after initiation of anti-TB therapy. There was no significant difference in median T-cell response between early secreting antigenic target-6 (ESAT-6) and culture filtrate protein-10 (CFP-10) at all time points. Median T-cell response steadily increased up to 6 months and then decreased.
CONCLUSIONS
T-SPOT.TB assay remained positive after successful anti-TB treatment in most patients with extrapulmonary TB. Our data suggests that serial T-SPOT.TB has limited clinical utility as a surrogate marker of treatment response in patients with extrapulmonary TB.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tuberculosis profile: Republic of Korea. World Health Organization. Accessed 28 March 2011. Available at: http://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=%2FWHO_HQ%2FSTB_TME%2FPublic%2FTBCountryProfile&ISO2=KR&outtype=html.2. Pai M, Riley LW, Colford JM Jr. Interferon-gamma assays in the immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004. 4:761–776.
Article3. Kim SH, Choi SJ, Kim HB, Kim NJ, Oh MD, Choe KW. Diagnostic usefulness of a T-cell based assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Arch Intern Med. 2007. 167:2255–2259.
Article4. Kim SH, Song KH, Choi SJ, Kim HB, Kim NJ, Oh MD, Choe KW. Diagnostic usefulness of a T-cell-based assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis in immunocompromised patients. Am J Med. 2009. 122:189–195.
Article5. Doherty TM, Demissie A, Olobo J, Wolday D, Britton S, Eguale T, Ravn P, Andersen P. Immune responses to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigen ESAT-6 signal subclinical infection among contacts of tuberculosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. 40:704–706.
Article6. Vordermeier HM, Chambers MA, Cockle PJ, Whelan AO, Simmons J, Hewinson RG. Correlation of ESAT-6-specific gamma interferon production with pathology in cattle following Mycobacterium bovis BCG vaccination against experimental bovine tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 2002. 70:3026–3032.
Article7. Lee SW, Lee CT, Yim JJ. Serial interferon-gamma release assays during treatment of active tuberculosis in young adults. BMC Infect Dis. 2010. 10:300.
Article8. Pai M, Joshi R, Bandyopadhyay M, Narang P, Dogra S, Taksande B, Kalantri S. Sensitivity of a whole-blood interferon-gamma assay among patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and variations in T-cell responses during antituberculosis treatment. Infection. 2007. 35:98–103.
Article9. Aiken AM, Hill PC, Fox A, McAdam KP, Jackson-Sillah D, Lugos MD, Donkor SA, Adegbola RA, Brookes RH. Reversion of the ELISPOT test after treatment in Gambian tuberculosis cases. BMC Infect Dis. 2006. 6:66.
Article10. Kobashi Y, Mouri K, Yagi S, Obase Y, Miyashita N, Oka M. Transitional changes in T-cell responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens during treatment. J Infect. 2009. 58:197–204.
Article11. Katiyar SK, Sampath A, Bihari S, Mamtani M, Kulkarni H. Use of the QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube test to monitor treatment efficacy in active pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008. 12:1146–1152.12. Carrara S, Vincenti D, Petrosillo N, Amicosante M, Girardi E, Goletti D. Use of a T cell-based assay for monitoring efficacy of antituberculosis therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 38:754–756.
Article13. Chee CB, KhinMar KW, Gan SH, Barkham TM, Koh CK, Shen L, Wang YT. Tuberculosis treatment effect on T-cell interferon-gamma responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens. Eur Respir J. 2010. 36:355–361.
Article14. Dheda K, Pooran A, Pai M, Miller RF, Lesley K, Booth HL, Scott GM, Akbar AN, Zumla A, Rook GA. Interpretation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen-specific IFN-gamma release assays (T-SPOT.TB) and factors that may modulate test results. J Infect. 2007. 55:169–173.
Article15. Domínguez J, De Souza-Galváo M, Ruiz-Manzano J, Latorre I, Prat C, Lacoma A, Milà C, Jiménez MA, Blanco S, Maldonado J, Altet N, Ausina V. T-cell responses to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens in active tuberculosis patients at the beginning, during, and after antituberculosis treatment. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009. 63:43–51.
Article16. Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, Daley CL, Etkind SC, Friedman LN, Fujiwara P, Grzemska M, Hopewell PC, Iseman MD, Jasmer RM, Koppaka V, Menzies RI, O'Brien RJ, Reves RR, Reichman LB, Simone PM, Starke JR, Vernon AA. American Thoracic Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Infectious Diseases Society. American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003. 167:603–662.
Article17. Liebeschuetz S, Bamber S, Ewer K, Deeks J, Pathan AA, Lalvani A. Diagnosis of tuberculosis in South African children with a T-cell-based assay: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2004. 364:2196–2203.
Article18. Kim SH, Cho OH, Park SJ, Ye BD, Sung H, Kim MN, Lee SO, Choi SH, Woo JH, Kim YS. Diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis by T-cell-based assays on peripheral blood and peritoneal fluid mononuclear cells. J Infect. 2009. 59:409–415.
Article19. Cho OH, Park SJ, Park KH, Chong YP, Sung H, Kim MN, Lee SO, Choi SH, Woo JH, Kim YS, Kim SH. Diagnostic usefulness of a T-cell-based assay for osteoarticular tuberculosis. J Infect. 2010. 61:228–234.
Article20. Kim SH, Cho OH, Park SJ, Lee EM, Kim MN, Lee SO, Choi SH, Kim YS, Woo JH, Lee SA, Kang JK. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis by T cell-based assays on peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid mononuclear cells. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. 50:1349–1358.
Article21. Lalvani A, Nagvenkar P, Udwadia Z, Pathan AA, Wilkinson KA, Shastri JS, Ewer K, Hill AV, Mehta A, Rodrigues C. Enumeration of T cells specific for RD1-encoded antigens suggests a high prevalence of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in healthy urban Indians. J Infect Dis. 2001. 183:469–477.
Article22. Adetifa IM, Ota MO, Walther B, Hammond AS, Lugos MD, Jeffries DJ, Donkor SA, Adegbola RA, Hill PC. Decay kinetics of an interferon gamma release assay with anti-tuberculosis therapy in newly diagnosed tuberculosis cases. PLoS One. 2010. 5:e12502.
Article23. Pathan AA, Wilkinson KA, Klenerman P, McShane H, Davidson RN, Pasvol G, Hill AV, Lalvani A. Direct ex vivo analysis of antigen-specific IFN-gamma-secreting CD4 T cells in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected individuals: associations with clinical disease state and effect of treatment. J Immunol. 2001. 167:5217–5225.
Article24. Herrmann JL, Belloy M, Porcher R, Simonney N, Aboutaam R, Lebourgeois M, Gaudelus J, De Losangeles L, Chadelat K, Scheinmann P, Beydon N, Fauroux B, Bingen M, Terki M, Barraud D, Cruaud P, Offredo C, Ferroni A, Berche P, Moissenet D, Vuthien H, Doit C, Bingen E, Lagrange PH. Temporal dynamics of interferon gamma responses in children evaluated for tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2009. 4:e4130.
Article25. Nicol MP, Pienaar D, Wood K, Eley B, Wilkinson RJ, Henderson H, Smith L, Samodien S, Beatty D. Enzyme-linked immunospot assay responses to early secretory antigenic target 6, culture filtrate protein 10, and purified protein derivative among children with tuberculosis: implications for diagnosis and monitoring of therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. 40:1301–1308.
Article26. Cheng SL, Wang HC, Yang PC. Paradoxical response during anti-tuberculosis treatment in HIV-negative patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007. 11:1290–1295.27. van Zyl-Smit RN, Pai M, Peprah K, Meldau R, Kieck J, Juritz J, Badri M, Zumla A, Sechi LA, Bateman ED, Dheda K. Within-subject variability and boosting of T-cell interferon-gamma responses after tuberculin skin testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. 180:49–58.
Article28. Naseer A, Naqvi S, Kampmann B. Evidence for boosting Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific IFN-gamma responses at 6 weeks following tuberculin skin testing. Eur Respir J. 2007. 29:1282–1283.
Article29. Igari H, Watanabe A, Sato T. Booster phenomenon of QuantiFERON-TB Gold after prior intradermal PPD injection. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007. 11:788–791.30. Vilaplana C, Ruiz-Manzano J, Gil O, Cuchillo F, Montané E, Singh M, Spallek R, Ausina V, Cardona PJ. The tuberculin skin test increases the responses measured by T cell interferon-gamma release assays. Scand J Immunol. 2008. 67:610–617.
Article31. Richeldi L, Ewer K, Losi M, Roversi P, Fabbri LM, Lalvani A. Repeated tuberculin testing does not induce false positive ELISPOT results. Thorax. 2006. 61:180.
Article32. Leyten EM, Prins C, Bossink AW, Thijsen S, Ottenhoff TH, van Dissel JT, Arend SM. Effect of tuberculin skin testing on a Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific interferon-gamma assay. Eur Respir J. 2007. 29:1212–1216.
Article33. Nguyen M, Perry S, Parsonnet J. QuantiFERON-TB predicts tuberculin skin test boosting in U.S. foreign-born. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2005. 9:985–991.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Qualitative and quantitative results of interferon-γ release assays for monitoring the response to anti-tuberculosis treatment
- Clinical Utility of Two Interferon-gamma Release Assays on Pleural Fluid for the Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleurisy
- Discordance between Tuberculin Skin Test and Interferon-gamma Release Assays for Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Infection in Korean Children
- Interferon-gamma Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay in Patients with Tuberculosis and Healthy Adults
- Evolution of Interferon-Gamma Release Assay Results and Submillisievert Chest CT Findings among Close Contacts of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients