J Bone Metab.
2015 May;22(2):77-81. 10.11005/jbm.2015.22.2.77.
Oral Bisphosphonate and Risk of Esophageal Cancer: A Nationwide Claim Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hjchoi@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2170091
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.2.77
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Epidemiology studies suggest that oral bisphosphonate may increase the risk of esophageal cancer. The present study aimed to investigate the association between exposure of oral bisphosphonate and risk of esophageal cancer.
METHODS
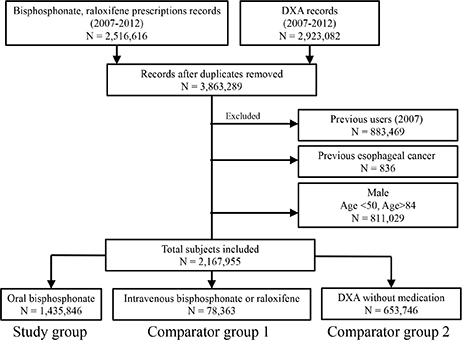
Using the nationwide medical claim database in South Korea, 2,167,955 subjects, who initiated osteoporosis treatment (oral bisphosphonate, intravenous bisphosphonate or raloxifene) or performed dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) between 2008 and 2012, were analyzed. Diagnosis of esophageal cancer was estimated from medical claim database. Standardized incidence ratio (SIR) was estimated by comparing with incidence in the general population. Cox proportional hazards modeling was used to investigate age-adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) of esophageal cancer.
RESULTS
The present study included oral bisphosphonate group (N=1,435,846), comparator group 1 (intravenous bisphosphonate or raloxifene, N=78,363) and comparator group 2 (DXA, N=653,746). Mean age was 65.6+/-8.8 years and mean observation duration was 30.9+/-17.7 months. During 5,503,688 patient-years, 205 esophageal cancer incidences were observed. The annual incidence of esophageal cancer was 3.88, 4.21, and 3.30 for oral bisphosphonate group, comparator group 1 and comparator group 2, respectively. SIR of esophageal cancer was 1.24, 1.38, and 1.40 for oral bisphosphonate group, comparator group 1 and comparator group 2, respectively. Esophageal cancer risk of oral bisphosphonate group was not significantly different from comparator group 1 and comparator group 2 (aHR 0.87; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.39-1.98 and aHR 0.94; 95% CI 0.68-1.30, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
The use of oral bisphosphonate was not associated with increased risk of esophageal cancer in real clinical practice using large scale nationwide database.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Characteristics of Patients Diagnosed with Osteoporosis in South Korea: Results from the National Claim Registry
Hyun Koo Yoon, Young-Kyun Lee, Yong-Chan Ha
J Bone Metab. 2017;24(1):59-63. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2017.24.1.59.Association Between Body Mass Index and the Incidence of Laryngeal Cancer
Chan-Eui Hong, Young-Hoon Joo, Jin Kook Kim, Jae Hoon Cho
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2024;67(8):447-451. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2023.00829.
Reference
-
1. Shin CS, Choi HJ, Kim MJ, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of osteoporosis in Korea: a community-based cohort study with lumbar spine and hip bone mineral density. Bone. 2010; 47:378–387.
Article2. Shin CS, Kim MJ, Shim SM, et al. The prevalence and risk factors of vertebral fractures in Korea. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012; 30:183–192.
Article3. Lee YK, Ha YC, Choi HJ, et al. Bisphosphonate use and subsequent hip fracture in South Korea. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24:2887–2892.
Article4. Chung DJ, Choi HJ, Chung YS, et al. The prevalence and risk factors of vertebral fractures in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013; 31:161–168.
Article5. Wysowski DK. Reports of esophageal cancer with oral bisphosphonate use. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:89–90.
Article6. Green J, Czanner G, Reeves G, et al. Oral bisphosphonates and risk of cancer of oesophagus, stomach, and colorectum: case-control analysis within a UK primary care cohort. BMJ. 2010; 341:c4444.
Article7. Cardwell CR, Abnet CC, Cantwell MM, et al. Exposure to oral bisphosphonates and risk of esophageal cancer. JAMA. 2010; 304:657–663.
Article8. Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Exposure to bisphosphonates and risk of gastrointestinal cancers: series of nested case-control studies with QResearch and CPRD data. BMJ. 2013; 346:f114.
Article9. Kim SH, Ko YB, Lee YK, et al. National utilization of calcium supplements in patients with osteoporotic hip fracture in Korea. J Bone Metab. 2013; 20:99–103.
Article10. Seo GH, Lee YK, Ha YC. Risk of hip fractures in men with alpha-blockers: a nationwide study base on claim registry. J Bone Metab. 2015; 22:29–32.
Article11. Park C, Jang S, Lee A, et al. Incidence and mortality after proximal humerus fractures over 50 years of age in South Korea: national claim data from 2008 to 2012. J Bone Metab. 2015; 22:17–21.
Article12. Choi HJ, Park C, Lee YK, et al. Risk of fractures in subjects with antihypertensive medications: A nationwide claim study. Int J Cardiol. 2015; 184:62–67.
Article13. Choi HJ, Shin CS, Ha YC, et al. Burden of osteoporosis in adults in Korea: a national health insurance database study. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012; 30:54–58.
Article14. Ha YC, Lee YK, Lim YT, et al. Physicians' attitudes to contemporary issues on osteoporosis management in Korea. J Bone Metab. 2014; 21:143–149.
Article15. Kong SY, Kim DY, Han EJ, et al. Effects of a 'drug holiday' on bone mineral density and bone turnover marker during bisphosphonate therapy. J Bone Metab. 2013; 20:31–35.
Article16. Wright E, Schofield PT, Seed P, et al. Bisphosphonates and risk of upper gastrointestinal cancer--a case control study using the General Practice Research Database (GPRD). PLoS One. 2012; 7:e47616.17. Vestergaard P. Occurrence of gastrointestinal cancer in users of bisphosphonates and other antiresorptive drugs against osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2011; 89:434–441.
Article18. Sun K, Liu JM, Sun HX, et al. Bisphosphonate treatment and risk of esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24:279–286.
Article19. Oh YH, Yoon C, Park SM. Bisphosphonate use and gastrointestinal tract cancer risk: meta-analysis of observational studies. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:5779–5788.
Article20. Ho YF, Lin JT, Wu CY. Oral bisphosphonates and risk of esophageal cancer: a dose-intensity analysis in a nationwide population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012; 21:993–995.
Article21. Lee WY, Sun LM, Lin MC, et al. A higher dosage of oral alendronate will increase the subsequent cancer risk of osteoporosis patients in Taiwan: a population-based cohort study. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e53032.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Esophageal Cancer in Korea: Epidemiology and Treatment Patterns
- Current Trends in the Epidemiology and Treatment of Esophageal Cancer in South Korea
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Korean Woman with Osteoporosis Treated with Oral Bisphosphonate: Case Report
- Clinical feature and treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of jaw about oral bisphosphonate administrated patients: case reports
- Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis in a Patient with Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia