Cancer Res Treat.
2012 Jun;44(2):121-126.
Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biology, Shiraz University College of Sciences, Shiraz, Iran. msaadat41@yahoo.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Apolipoprotein E (APOE, MIM: 107741) has three functionally distinct isoforms of the protein (E2, E3, and E4), encoded by corresponding alleles epsilon2, epsilon3, and epsilon4, which have been well described. Findings from previous studies investigating association between APOE polymorphisms and breast cancer risk have been inconsistent. The present meta-analysis was conducted in order to investigate association of APOE polymorphisms with risk of breast cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Several electronic databases were used for identification of studies containing information on APOE polymorphisms and breast cancer risk published up to January 2012. We identified 10 eligible studies, including 3,835 subjects (2008 patients, and 1,827 healthy controls), that reported on polymorphisms of APOE and risk of breast cancer. Summary odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained using a fixed and random-effects models.
RESULTS
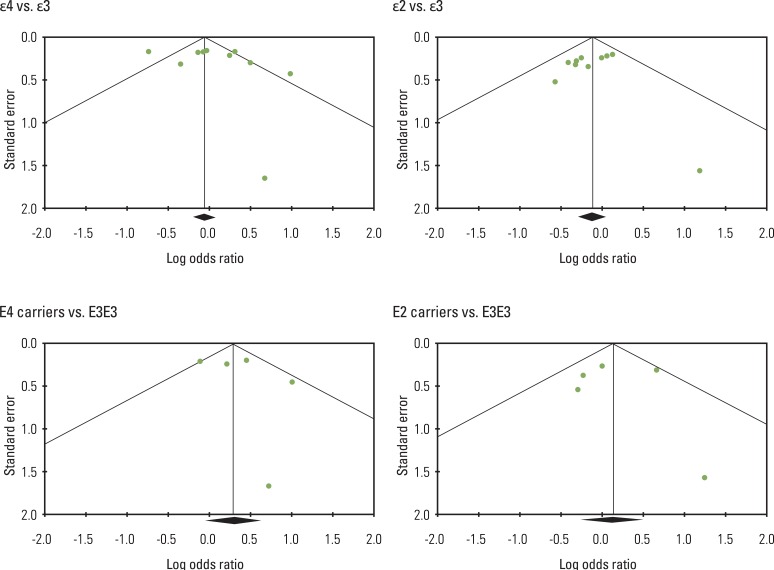
Among studies reported from Asia, an association of the epsilon4 allele with increased risk of breast cancer, in comparison with the epsilon3 allele, was observed (OR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.19 to 2.04; p=0.001). It should be noted that allele epsilon2 showed no association with breast cancer risk. Among Caucasians, neither the epsilon4 (OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.83 to 1.17; p=0.917) nor the epsilon2 (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.17; p=0.514) allele showed an association with susceptibility to breast cancer, when compared with the epsilon3 allele. Carriers of the epsilon4 allele (E4E4, E4E3, and E4E2 genotypes), in comparison with the E3E3 genotype, showed an association with elevated risk of breast cancer only among Asians (OR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.23 to 2.47; p=0.002). No publication bias was detected.
CONCLUSION
This meta-analysis suggest that the APOEepsilon4 allele is a low-penetrant risk factor for development of breast cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weisgraber KH, Rall SC Jr, Mahley RW. Human E apoprotein heterogeneity. Cysteine-arginine interchanges in the amino acid sequence of the apo-E isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1981; 256:9077–9083. PMID: 7263700.
Article2. Rall SC Jr, Weisgraber KH, Innerarity TL, Mahley RW. Structural basis for receptor binding heterogeneity of apolipoprotein E from type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982; 79:4696–4700. PMID: 6289314.
Article3. Moysich KB, Freudenheim JL, Baker JA, Ambrosone CB, Bowman ED, Schisterman EF, et al. Apolipoprotein E genetic polymorphism, serum lipoproteins, and breast cancer risk. Mol Carcinog. 2000; 27:2–9. PMID: 10642431.
Article4. Niemi M, Kervinen K, Kiviniemi H, Lukkarinen O, Kyllönen AP, Apaja-Sarkkinen M, et al. Apolipoprotein E phenotype, cholesterol and breast and prostate cancer. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2000; 54:938–939. PMID: 11076992.
Article5. Yaylim I, Bozkurt N, Yilmaz H, Isbir T, Isik N, Arikan S. The apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele is not a risk factor for Turkish breast cancer patients. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2003; 146:86–87. PMID: 14499704.6. Menzel HJ, Sarmanova J, Soucek P, Berberich R, Grünewald K, Haun M, et al. Association of NQO1 polymorphism with spontaneous breast cancer in two independent populations. Br J Cancer. 2004; 90:1989–1994. PMID: 15138483.
Article7. Chang NW, Chen DR, Wu CT, Aouizerat BE, Chen FN, Hung SJ, et al. Influences of apolipoprotein E polymorphism on the risk for breast cancer and HER2/neu status in Taiwan. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005; 90:257–261. PMID: 15830139.
Article8. Chang SJ, Hou MF, Tsai SM, Kao JT, Wu SH, Hou LA, et al. Association between the apolipoprotein E genotypes and breast cancer patients in Taiwanese. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006; 98:109–113. PMID: 16752225.
Article9. Surekha D, Vishnupriya S, Sailaja K, Nageswara Rao D, Raghunadharao D. Influence of apolipoprotein e gene polymorphism on the risk for breast cancer. Int J Hum Genet. 2008; 8:277–282.
Article10. Porrata-Doria T, Matta JL, Acevedo SF. Apolipoprotein E allelic frequency altered in women with early-onset breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2010; 4:43–48. PMID: 20697532.
Article11. Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959; 22:719–748. PMID: 13655060.12. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:177–188. PMID: 3802833.
Article13. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634. PMID: 9310563.
Article14. Niu W, Qi Y, Qian Y, Gao P, Zhu D. The relationship between apolipoprotein E epsilon2/epsilon3/epsilon4 polymorphisms and hypertension: a meta-analysis of six studies comprising 1812 cases and 1762 controls. Hypertens Res. 2009; 32:1060–1066. PMID: 19816504.15. Bennet AM, Di Angelantonio E, Ye Z, Wensley F, Dahlin A, Ahlbom A, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E genotypes with lipid levels and coronary risk. JAMA. 2007; 298:1300–1311. PMID: 17878422.
Article16. Carroll KK, Braden LM, Bell JA, Kalamegham R. Fat and cancer. Cancer. 1986; 58(8 Suppl):1818–1825. PMID: 3756806.
Article17. Agurs-Collins T, Kim KS, Dunston GM, Adams-Campbell LL. Plasma lipid alterations in African-American women with breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1998; 124:186–190. PMID: 9619745.
Article18. Takatani O, Okumoto T, Kosano H. Genesis of breast cancer in Japanese: a possible relationship between sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and serum lipid components. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1991; 18(Suppl 1):S27–S29. PMID: 1873554.
Article20. Kiyohara C, Takayama K, Nakanishi Y. Association of genetic polymorphisms in the base excision repair pathway with lung cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 2006; 54:267–283. PMID: 16982113.
Article21. Saadat M. Genetic polymorphisms of glutathione S-transferase T1 (GSTT1) and susceptibility to gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Sci. 2006; 97:505–509. PMID: 16734729.
Article22. Saadat M, Ansari-Lari M. Genetic polymorphism of glutathione S-transferase T1, M1 and asthma, a meta-analysis of the literature. Pak J Biol Sci. 2007; 10:4183–4189. PMID: 19086569.
Article23. Saadat M, Ansari-Lari M. Polymorphism of XRCC1 (at codon 399) and susceptibility to breast cancer, a meta-analysis of the literatures. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 115:137–144. PMID: 18481169.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Apolipoprotein E Polymorphism in Patients with Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease
- Discrepancy in Genotyping of Apolipoprotein E between Allele-Specific PCR and Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer or Sequencing
- Polymorphisms of Apolipoprotein B and Apolipoprotein E in Hypobetalipoproteinemic Korean
- Comparison of Two Real-Time PCR Assays for Apolipoprotein E Genotyping
- An Association Study of Apolipoprotein E Gene Polymorphism and Cataracts