Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Jun;86(6):289-294. 10.4174/astr.2014.86.6.289.
Higher incidence of gastroesophageal reflux disease after gastric wedge resections of gastric submucosal tumors located close to the gastroesophageal junction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. kjj@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2167105
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.86.6.289
Abstract
- PURPOSE
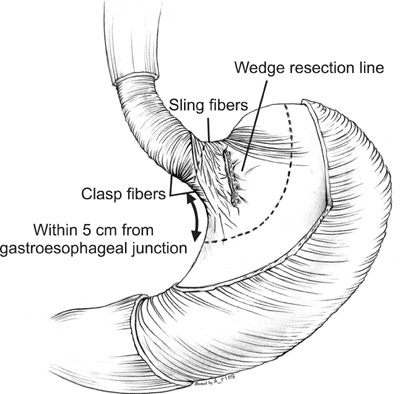
We hypothesized that gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) would be more prevalent after a gastric wedge resection of a submucosal tumor (SMT) located close to the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) than after a gastric wedge resection of an SMT at other locations because of the damage to the lower esophageal sphincter during surgery.
METHODS
Fifty-eight patients with gastric SMT who underwent open or laparoscopic gastric wedge resection between January 2000 and August 2012 at the Department of Surgery, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital were enrolled into this study. The patients were divided into 2 groups according to the location of the tumor, upper or lateral border of the tumor within 5 cm of the GEJ (GEJ < or = 5 cm group) and upper or lateral border of the tumor greater than 5 cm distal to the GEJ (GEJ > 5 cm group). The surgical records, clinicopathologic findings, postoperative GERD symptoms, postoperative use of acid suppressive medications and preoperative and postoperative endoscopic findings were retrospectively reviewed and compared between the 2 groups.
RESULTS
There was no difference in the frequency of the preoperative GERD symptoms between the 2 groups, whereas postoperative GERD symptoms and postoperative use of acid suppressive medications were more frequent in the GEJ < or = 5 cm group (P = 0.045 and P = 0.031). However, there were no differences in the follow-up endoscopic findings in terms of reflux esophagitis and Hill's grade between the 2 groups.
CONCLUSION
The incidence of GERD was higher after gastric wedge resection of SMTs located close to the GEJ. Hence, adequate care should be taken during the follow-up of these patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
IgG4-related Disease in the Stomach which Was Confused with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature
Ho Seok Seo, Yoon Ju Jung, Cho Hyun Park, Kyo Young Song, Eun Sun Jung
J Gastric Cancer. 2018;18(1):99-107. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2018.18.e8.
Reference
-
1. Buscaglia JM, Nagula S, Jayaraman V, Robbins DH, Vadada D, Gross SA, et al. Diagnostic yield and safety of jumbo biopsy forceps in patients with subepithelial lesions of the upper and lower GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:1147–1152.2. Papanikolaou IS, Triantafyllou K, Kourikou A, Rosch T. Endoscopic ultrasonography for gastric submucosal lesions. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 3:86–94.3. Mekky MA, Yamao K, Sawaki A, Mizuno N, Hara K, Nafeh MA, et al. Diagnostic utility of EUS-guided FNA in patients with gastric submucosal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:913–919.4. Karaca C, Turner BG, Cizginer S, Forcione D, Brugge W. Accuracy of EUS in the evaluation of small gastric subepithelial lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:722–727.5. Polkowski M, Gerke W, Jarosz D, Nasierowska-Guttmejer A, Rutkowski P, Nowecki ZI, et al. Diagnostic yield and safety of endoscopic ultrasound-guided trucut [corrected] biopsy in patients with gastric submucosal tumors: a prospective study. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:329–334.6. Tagaya N, Mikami H, Kogure H, Kubota K, Hosoya Y, Nagai H. Laparoscopic intragastric stapled resection of gastric submucosal tumors located near the esophagogastric junction. Surg Endosc. 2002; 16:177–179.7. Morinaga N, Sano A, Katayama K, Suzuki K, Kamisaka K, Asao T, et al. Laparoscopic transgastric tumor-everting resection of the gastric submucosal tumor located near the esophagogastric junction. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2004; 14:344–348.8. Uchikoshi F, Ito T, Nishida T, Kitagawa T, Endo S, Matsuda H. Laparoscopic intragastric resection of gastric stromal tumor located at the esophago-cardiac junction. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2004; 14:1–4.9. Granger SR, Rollins MD, Mulvihill SJ, Glasgow RE. Lessons learned from laparoscopic treatment of gastric and gastroesophageal junction stromal cell tumors. Surg Endosc. 2006; 20:1299–1304.10. Song KY, Kim SN, Park CH. Tailored-approach of laparoscopic wedge resection for treatment of submucosal tumor near the esophagogastric junction. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:2272–2276.11. Ke ZW, Chen DL, Cai JL, Zheng CZ. Extraluminal laparoscopic wedge-resection of submucosal tumors on the posterior wall of the gastric fundus close to the esophagocardiac junction. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2009; 19:741–744.12. Ke CW, Cai JL, Chen DL, Zheng CZ. Extraluminal laparoscopic wedge resection of gastric submucosal tumors: a retrospective review of 84 cases. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1962–1968.13. Shim JH, Lee HH, Yoo HM, Jeon HM, Park CH, Kim JG, et al. Intragastric approach for submucosal tumors located near the Z-line: a hybrid laparoscopic and endoscopic technique. J Surg Oncol. 2011; 104:312–315.14. Hara J, Nakajima K, Takahashi T, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Kurokawa Y, et al. Laparoscopic intragastric surgery revisited: its role for submucosal tumors adjacent to the esophagogastric junction. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2012; 22:251–254.15. Sakamoto Y, Sakaguchi Y, Akimoto H, Chinen Y, Kojo M, Sugiyama M, et al. Safe laparoscopic resection of a gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor close to the esophagogastric junction. Surg Today. 2012; 42:708–711.16. Kim HS, Kim MG, Kim BS, Lee IS, Lee S, Yook JH, et al. Laparoscopic surgery for submucosal tumor near the esophagogastric junction. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013; 23:225–230.17. Kong SH, Yang HK. Surgical treatment of gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Gastric Cancer. 2013; 13:3–18.18. Lee JS, Kim JJ, Park SM. Laparoscopic gastric wedge resection and prophylactic antireflux surgery for a submucosal tumor of gastroesophageal junction. J Gastric Cancer. 2011; 11:131–134.19. Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999; 45:172–180.20. Hill LD, Kozarek RA, Kraemer SJ, Aye RW, Mercer CD, Low DE, et al. The gastroesophageal flap valve: in vitro and in vivo observations. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:541–547.21. Coccolini F, Catena F, Ansaloni L, Lazzareschi D, Pinna AD. Esophagogastric junction gastrointestinal stromal tumor: resection vs enucleation. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:4374–4376.22. Langer C, Gunawan B, Schuler P, Huber W, Fuzesi L, Becker H. Prognostic factors influencing surgical management and outcome of gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br J Surg. 2003; 90:332–339.23. Kim JJ. Upper gastrointestinal cancer and reflux disease. J Gastric Cancer. 2013; 13:79–85.24. Kayaoglu HA. Correlation of the gastroesophageal flap valve grade with the surgery rate in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:801–807.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic Gastric Wedge Resection and Prophylactic Antireflux Surgery for a Submucosal Tumor of Gastroesophageal Junction
- Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer and Reflux Disease
- Relevance of Position and Movement of the Gastroesophageal Junction in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Relevance of Position and Movement of the Gastroesophageal Junction in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Author's Reply
- Reflux Following Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer