Ann Surg Treat Res.
2015 Apr;88(4):215-221. 10.4174/astr.2015.88.4.215.
The effect of long Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy in gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes and body mass index < 35 kg/m2: preliminary results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bckimgs@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2167019
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2015.88.4.215
Abstract
- PURPOSE
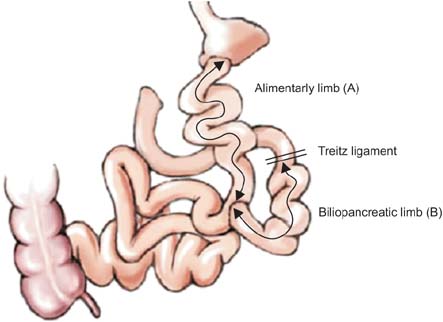
We applied a long Roux-en-Y (RY) gastrojejunostomy (bypassed jejunum over 100 cm) as a reconstruction method for diabetes control to gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes and body mass index (BMI) < 35 kg/m2. The effect of this procedure on diabetes control was assessed.
METHODS
We prospectively performed modified RY gastrojejunostmy after curative radical distal gastrectomy. Thirty patients had completed a 1-year follow-up. Patients were followed concerning their diabetic status. The factors included in the investigation were length of bypassed jejunum, BMI and its reduction ratio, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting blood glucose, and duration of diabetes. Diabetic status after surgery was assessed in three categories: remission, improvement, and stationary. In evaluation of surgical effects on diabetes control, remission and improvement groups were regarded as effective groups, while stationary was regarded as an ineffective group.
RESULTS
At postoperative one year, statistical significance was observed in the mean BMI and HbA1c. Diabetes control was achieved in 50% of the patients (remission, 30%; improvement, 20%). BMI reduction ratio, preoperative HbA1c, and duration of diabetes were correlated to the status of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The preoperative HbA1c was the most influential predictor in diabetic control.
CONCLUSION
The effect of long RY gastrojejunostomy after gastrectomy for diabetes control could be contentious but an applicable reconstruction method for diabetes control in gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes and BMI < 35 kg/m2. Diabetes remission is expected to be higher in patients with greater BMI reduction, short duration of diabetes, and lower preoperative HbA1c.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1577–1585.2. Shukla AP, Ahn SM, Patel RT, Rosenbaum MW, Rubino F. Surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes: the surgeon perspective. Endocrine. 2011; 40:151–161.3. Dixon JB, Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Rubino F. International Diabetes Federation Taskforce on Epidemiology and Prevention. Bariatric surgery: an IDF statement for obese Type 2 diabetes. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2011; 55:367–382.4. Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004; 292:1724–1737.5. Chiellini C, Rubino F, Castagneto M, Nanni G, Mingrone G. The effect of biliopancreatic diversion on type 2 diabetes i n pat ients wit h BMI <35 kg/m2. Diabetologia. 2009; 52:1027–1030.6. Lee WJ, Hur KY, Lakadawala M, Kasama K, Wong SK, Lee YC. Gastrointestinal metabolic surgery for the treatment of diabetic patients: a multi-institutional international study. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:45–51.7. Shimizu H, Timratana P, Schauer PR, Rogula T. Review of metabolic surgery for type 2 diabetes in patients with a BMI <35kg/m(2). J Obes. 2012; 2012:147256.8. Lanzarini E, Csendes A, Gutierrez L, Cuevas P, Lembach H, Molina JC, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with mild obesity: preliminary results of surgical treatment. Obes Surg. 2013; 23:234–240.9. DePaul a, Macedo AL, Rassi N, Machado CA, Schraibman V, Silva LQ, et al. Laparoscopic treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus for patients with a body mass index less than 35. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:706–716.10. Lee WJ, Ser KH, Chong K, Lee YC, Chen SC, Tsou JJ, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for diabetes treatment in nonmorbidly obese patients: efficacy and change of insulin secretion. Surgery. 2010; 147:664–669.11. Lee WJ, Chong K, Ser KH, Lee YC, Chen SC, Chen JC, et al. Gastric bypass vs sleeve gastrectomy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Surg. 2011; 146:143–148.12. Rubino F, Marescaux J. Effect of duodenaljejunal exclusion in a non-obese animal model of type 2 diabetes: a new perspective for an old disease. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:1–11.13. Cohen RV, Schiavon CA, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Rubino F. Duodenal-jejunal bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with body mass index of 22-34 kg/m2: a report of 2 cases. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2007; 3:195–197.14. Ramos AC, Galvao Neto MP, de Souza YM, Galvao M, Murakami AH, Silva AC, et al. Laparoscopic duodenal-jejunal exclusion in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with BMI<30 kg/m2 (LBMI). Obes Surg. 2009; 19:307–312.15. Ferzli GS, Dominique E, Ciaglia M, Bluth MH, Gonzalez A, Fingerhut A. Clinical improvement after duodenojejunal bypass for nonobese type 2 diabetes despite minimal improvement in glycemic homeostasis. World J Surg. 2009; 33:972–979.16. Geloneze B, Geloneze SR, Fiori C, Stabe C, Tambascia MA, Chaim EA, et al. Surgery for nonobese type 2 diabetic patients: an interventional study with duodenaljejunal exclusion. Obes Surg. 2009; 19:1077–1083.17. Boza C, Munoz R, Salinas J, Gamboa C, Klaassen J, Escalona A, et al. Safety and efficacy of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus in nonseverely obese patients. Obes Surg. 2011; 21:1330–1336.18. Huang CK, Shabbir A, Lo CH, Tai CM, Chen YS, Houng JY. Laparoscopic Rouxen-Y gastric bypass for the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus in Chinese patients with body mass index of 25-35. Obes Surg. 2011; 21:1344–1349.19. Kim WS, Kim JW, Ahn CW, Choi SH. Resolution of type 2 diabetes after gastrectomy for gastric cancer with long limb Roux-en Y reconstruction: a prospective pilot study. J Korean Surg Soc. 2013; 84:88–93.20. Shah SS, Todkar JS, Shah PS, Cummings DE. Diabetes remission and reduced cardiovascular risk after gastric bypass in Asian Indians with body mass index <35 kg/m(2). Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010; 6:332–338.21. Kim JW, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ, Choi SH, Noh SH. Outcome after gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:49–54.22. Lee W, Ahn SH, Lee JH, Park DJ, Lee HJ, Kim HH, et al. Comparative study of diabetes mellitus resolution according to reconstruction type after gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with diabetes mellitus. Obes Surg. 2012; 22:1238–1243.23. Lanzarini E, Csendes A, Lembach H, Molina J, Gutierrez L, Silva J. Evolution of type 2 diabetes mellitus in non morbid obese gastrectomized patients with Roux en-Y reconstruction: retrospective study. World J Surg. 2010; 34:2098–2102.24. Yang J, Li C, Liu H, Gu H, Chen P, Liu B. Effects of subtotal gastrectomy and Rouxen-Y gastrojejunostomy on the clinical outcome of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Surg Res. 2010; 164:e67–e71.25. Saeidi N, Meoli L, Nestoridi E, Gupta NK, Kvas S, Kucharczyk J, et al. Reprogramming of intestinal glucose metabolism and glycemic control in rats after gastric bypass. Science. 2013; 341:406–410.26. Mari A, Manco M, Guidone C, Nanni G, Castagneto M, Mingrone G, et al. Restoration of normal glucose tolerance in severely obese patients after biliopancreatic diversion: role of insulin sensitivity and beta cell function. Diabetologia. 2006; 49:2136–2143.27. Knop FK. Resolution of type 2 diabetes fol low i ng g ast r ic by pass surger y: involvement of gut-derived glucagon and glucagonotropic signalling? Diabetologia. 2009; 52:2270–2276.28. Schauer PR, Burguera B, Ikramuddin S, Cottam D, Gourash W, Hamad G, et al. Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en Y gastric bypass on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 2003; 238:467–484.29. Hall TC, Pellen MG, Sedman PC, Jain PK. Preoperative factors predicting remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus after Rouxen-Y gastric bypass surgery for obesity. Obes Surg. 2010; 20:1245–1250.30. Torquati A, Lutfi R, Abumrad N, Richards WO. Is Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery the most effective treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus in morbidly obese patients? J Gastrointest Surg. 2005; 9:1112–1116.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Resolution of type 2 diabetes after gastrectomy for gastric cancer with long limb Roux-en Y reconstruction: a prospective pilot study
- Roux Stasis Syndrome in Conventional Roux-en-Y Gastrojejunostomy and Uncut Roux-en-Y Gastrojejunostomy after Subtotal Gastrectomy
- Comparison of Changes in Body Weight and Serum Lipid Profile after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass between Non-obese Patients and Obese Patients
- A Clinical Study of the Uncut Roux-en-Y Gastrojejunostomy Using a Short Roux Limb after Subtotal Gastrectomy
- Influence of gastrectomy for stomach cancer on type 2 diabetes mellitus for patients with a body mass index less than 30 kg/m2