Healthc Inform Res.
2016 Apr;22(2):95-100. 10.4258/hir.2016.22.2.95.
Comparison of Predictive Models for the Early Diagnosis of Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Technology and Engineering, Qom University, Qom, Iran.
- 2Department of Health Services Management and Organizations, Institute of Health Policy and Management, Erasmus University Rotterdam, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. info.mahdavi@gmail.com
- KMID: 2166941
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2016.22.2.95
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This study develops neural network models to improve the prediction of diabetes using clinical and lifestyle characteristics. Prediction models were developed using a combination of approaches and concepts.
METHODS
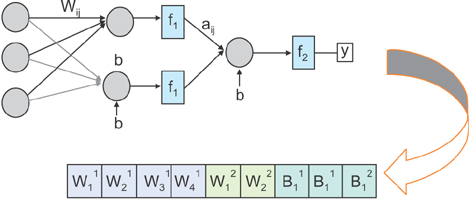
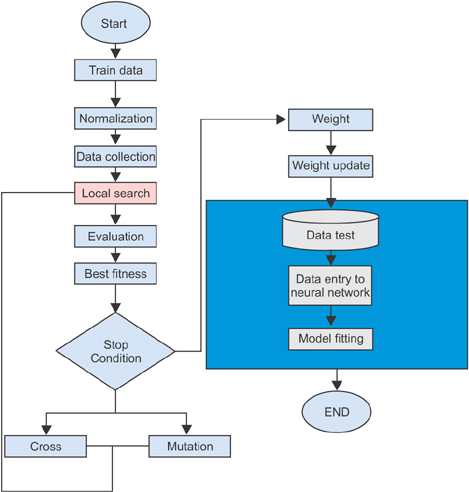
We used memetic algorithms to update weights and to improve prediction accuracy of models. In the first step, the optimum amount for neural network parameters such as momentum rate, transfer function, and error function were obtained through trial and error and based on the results of previous studies. In the second step, optimum parameters were applied to memetic algorithms in order to improve the accuracy of prediction. This preliminary analysis showed that the accuracy of neural networks is 88%. In the third step, the accuracy of neural network models was improved using a memetic algorithm and resulted model was compared with a logistic regression model using a confusion matrix and receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC).
RESULTS
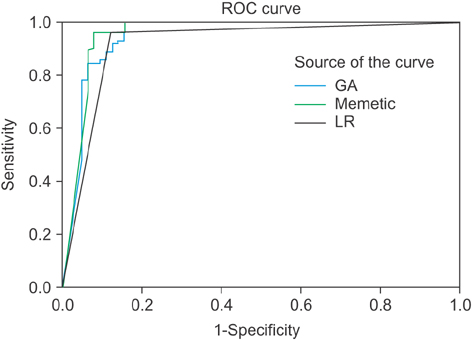
The memetic algorithm improved the accuracy from 88.0% to 93.2%. We also found that memetic algorithm had a higher accuracy than the model from the genetic algorithm and a regression model. Among models, the regression model has the least accuracy. For the memetic algorithm model the amount of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and ROC are 96.2, 95.3, 93.8, 92.4, and 0.958 respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study provide a basis to design a Decision Support System for risk management and planning of care for individuals at risk of diabetes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 6th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation;2013.2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Fact Sheet: national estimates and general information on diabetes and prediabetes in the United States, 2011 [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2011. cited at 2016 Mar 1. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2011.pdf.3. Pei E, Li J, Lu C, Xu J, Tang T, Ye M, et al. Effects of lipids and lipoproteins on diabetic foot in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Complicat. 2014; 28(4):559–564.
Article4. Zaugg SD, Dogbey G, Collins K, Reynolds S, Batista C, Brannan G, et al. Diabetes numeracy and blood glucose control: association with type of diabetes and source of care. Clin Diabetes. 2014; 32(4):152–157.
Article5. Nielsen DS, Krych L, Buschard K, Hansen CH, Hansen AK. Beyond genetics: Influence of dietary factors and gut microbiota on type 1 diabetes. FEBS Lett. 2014; 588(22):4234–4243.
Article6. Manzella D, Grella R, Abbatecola AM, Paolisso G. Repaglinide administration improves brachial reactivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28(2):366–371.
Article7. Zhuo X, Zhang P, Barker L, Albright A, Thompson TJ, Gregg E. The lifetime cost of diabetes and its implications for diabetes prevention. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37(9):2557–2564.
Article8. Chavey A, Ah Kioon MD, Bailbe D, Movassat J, Portha B. Maternal diabetes, programming of beta-cell disorders and intergenerational risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2014; 40(5):323–330.
Article9. Mohan D, Raj D, Shanthirani CS, Datta M, Unwin NC, Kapur A, et al. Awareness and knowledge of diabetes in Chennai: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES-9]. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005; 53:283–287.10. Hadaegh F, Bozorgmanesh MR, Ghasemi A, Harati H, Saadat N, Azizi F. High prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes and abnormal glucose tolerance in the Iranian urban population: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. BMC Public Health. 2008; 8:176.
Article11. Ofman JJ, Badamgarav E, Henning JM, Knight K, Gano AD Jr, Levan RK, et al. Does disease management improve clinical and economic outcomes in patients with chronic diseases? A systematic review. Am J Med. 2004; 117(3):182–192.
Article12. Baan CA, Ruige JB, Stolk RP, Witteman JC, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, et al. Performance of a predictive model to identify undiagnosed diabetes in a health care setting. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22(2):213–219.
Article13. Asche C, LaFleur J, Conner C. A review of diabetes treatment adherence and the association with clinical and economic outcomes. Clin Ther. 2011; 33(1):74–109.
Article14. Billings J, Blunt I, Steventon A, Georghiou T, Lewis G, Bardsley M. Development of a predictive model to identify inpatients at risk of re-admission within 30 days of discharge (PARR-30). BMJ Open. 2012; 2(4):e001667.15. Gray AR, MacDonell SG. A comparison of techniques for developing predictive models of software metrics. Inf Softw Technol. 1997; 39(6):425–437.
Article16. Narasingarao MR, Sridhar GR, Madhu K, Rao AA. A clinical decision support system using multi-layer perceptron neural network to predict quality of life in diabetes. J Assoc Physicians India. 2010; 4(1):127–133.17. Karan O, Bayraktar C, Gumuskaya H, Karlik B. Diagnosing diabetes using neural networks on small mobile devices. Expert Syst Appl. 2012; 39(1):54–60.
Article18. Kang JO, Chung SH, Suh YM. Prediction of hospital charges for the cancer patients with data mining techniques. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 2009; 15(1):13–23.
Article19. Tahmasebi P, Hezarkhani A. A hybrid neural networksfuzzy logic-genetic algorithm for grade estimation. Comput Geosci. 2012; 42:18–27.
Article20. Mahmoudabadi H, Izadi M, Menhaj MB. A hybrid method for grade estimation using genetic algorithm and neural networks. Comput Geosci. 2009; 13(1):91–101.
Article21. Cho SB. Fusion of neural networks with fuzzy logic and genetic algorithm. Integr Comput Aided Eng. 2002; 9(4):363–372.
Article22. Smith AD, Bolam JP. The neural network of the basal ganglia as revealed by the study of synaptic connections of identified neurones. Trends Neurosci. 1990; 13(7):259–265.
Article23. Wang C, Li L, Wang L, Ping Z, Flory MT, Wang G, et al. Evaluating the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus using artificial neural network: an effective classification approach. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 100(1):111–118.
Article