Clin Endosc.
2016 Jan;49(1):76-80. 10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.76.
Two Cases of Stress Cardiomyopathy during Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. H00095@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2166553
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.76
Abstract
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is considered a relatively safe procedure. However, the procedure and the materials used in EGD with conscious sedation can cause stress to the patient. Adverse events during EGD have been reported, represented by cardiopulmonary complications. To date, five cases have reported worldwide to be associated with gastrointestinal endoscopy. Stress cardiomyopathy (SCMP) is a reversible cardiomyopathy that typically occurs in postmenopausal women due to stress and may resolve within a few weeks. SCMP resembles acute myocardial infarction but differs in terms of treatment and prognosis. Here, we describe two cases of SCMP with shock during EGD with conscious sedation.
MeSH Terms
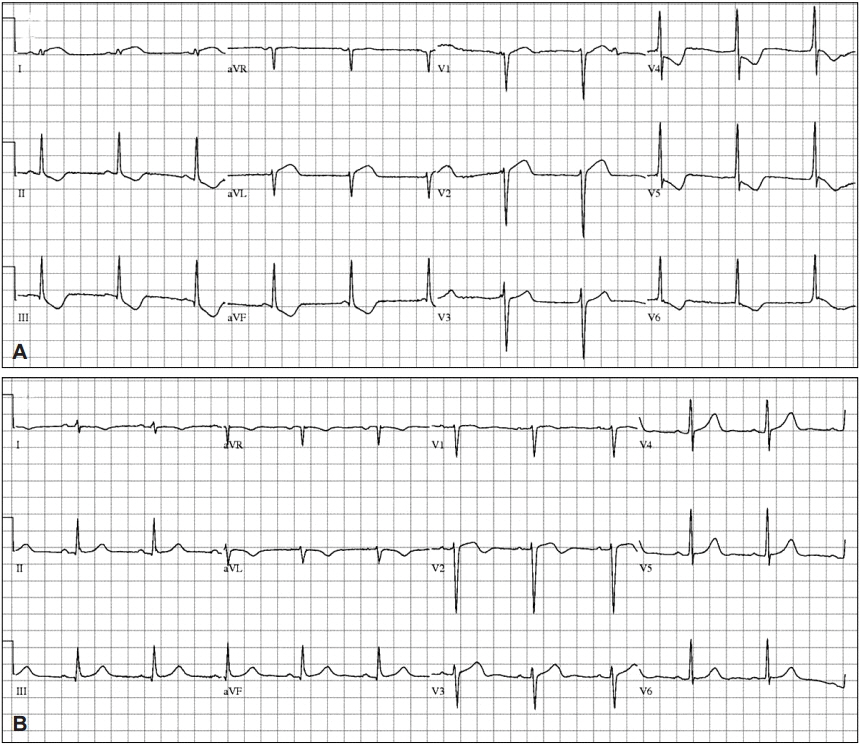
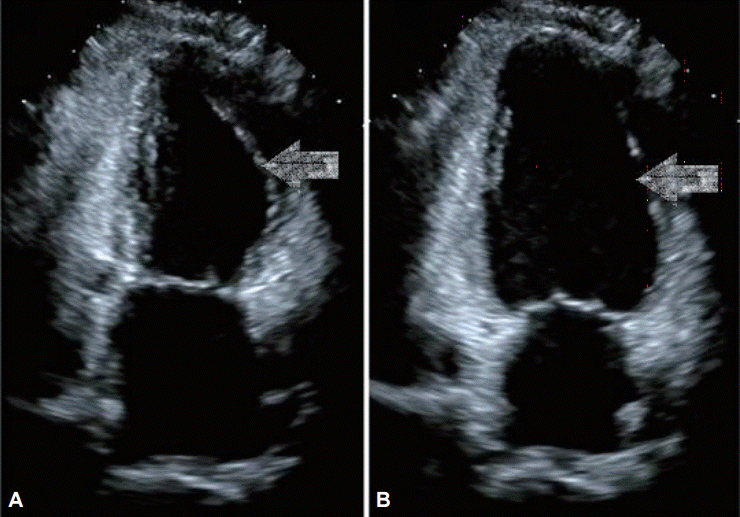
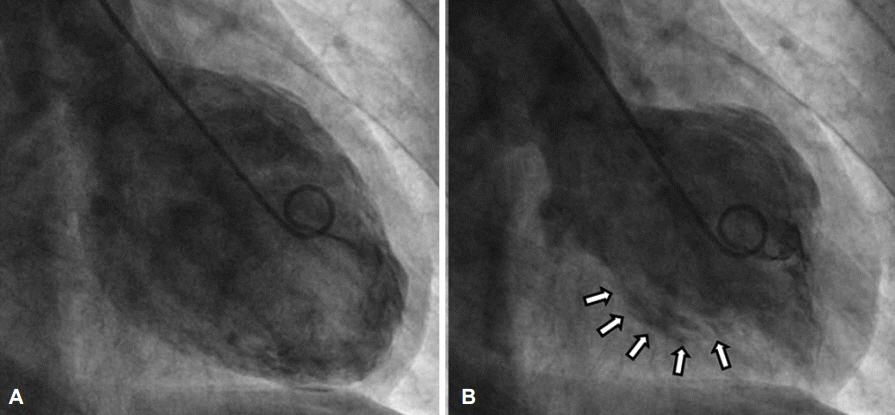
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Bradycardia, Hypotension, and Midventricular Takotsubo Syndrome during Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
John E. Madias
Clin Endosc. 2016;49(3):308-309. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.034.
Reference
-
1. Waring JP, Baron TH, Hirota WK, et al. Guidelines for conscious sedation and monitoring during gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:317–322.
Article2. Kim SR, Nakashima K, Nishiuchi S, et al. A case of takotsubo cardiomyopathy with ventricular fibrillation after gastroenterological endoscopy. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2011; 4:73–78.
Article3. Kawai S, Kitabatake A, Tomoike H; Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Group. Guidelines for diagnosis of takotsubo (ampulla) cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2007; 71:990–992.
Article4. Bybee KA, Prasad A. Stress-related cardiomyopathy syndromes. Circulation. 2008; 118:397–409.
Article5. Gianni M, Dentali F, Grandi AM, Sumner G, Hiralal R, Lonn E. Apical ballooning syndrome or takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a systematic review. Eur Heart J. 2006; 27:1523–1529.
Article6. Park JH, Kang SJ, Song JK, et al. Left ventricular apical ballooning due to severe physical stress in patients admitted to the medical ICU. Chest. 2005; 128:296–302.
Article7. Madhavan M, Prasad A. Proposed Mayo Clinic criteria for the diagnosis of Tako-Tsubo cardiomyopathy and long-term prognosis. Herz. 2010; 35:240–243.
Article8. Sharkey SW, Windenburg DC, Lesser JR, et al. Natural history and expansive clinical profile of stress (tako-tsubo) cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55:333–341.
Article9. Akashi R, Oogushi M, Yoshida M, et al. A case report of “takotsubo”type cardiomyophaty during upper digestive endoscopy. Gastroenterol Endosc. 2003; 45:253–260.10. Kaneko E, Harada H, Kasugai T, Ogoshi K, Tanba H. Complications from gastrointestinal endoscopy procedure from 1998 to 2002. Gastroenterol Endosc. 2004; 46:54–61.11. Bell GD, Bown S, Morden A, Coady T, Logan RF. Prevention of hypoxaemia during upper-gastrointestinal endoscopy by means of oxygen via nasal cannulae. Lancet. 1987; 1:1022–1024.
Article12. Vargo JJ, Zuccaro G Jr, Dumot JA, Conwell DL, Morrow JB, Shay SS. Automated graphic assessment of respiratory activity is superior to pulse oximetry and visual assessment for the detection of early respiratory depression during therapeutic upper endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:826–831.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stress Cardiomyopathy due to Misuse of Transdermal Fentanyl Patches in an Elderly Patient
- A case of stress-induced cardiomyopathy with an "inverted Takotsubo" contractile pattern
- Recurrent fetal postpartum stress induced cardiomyopathy after normal vaginal delivery
- Left Ventricular Thrombus Associated with Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: A Cardioembolic Cause of Cerebral Infarction
- Stress-induced cardiomyopathy during ophthalmologic surgery: A case report