Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Jun;39(3):477-481. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.3.477.
Churg-Strauss Syndrome as an Unusual Cause of Dysphagia: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. lafolia@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2165652
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.3.477
Abstract
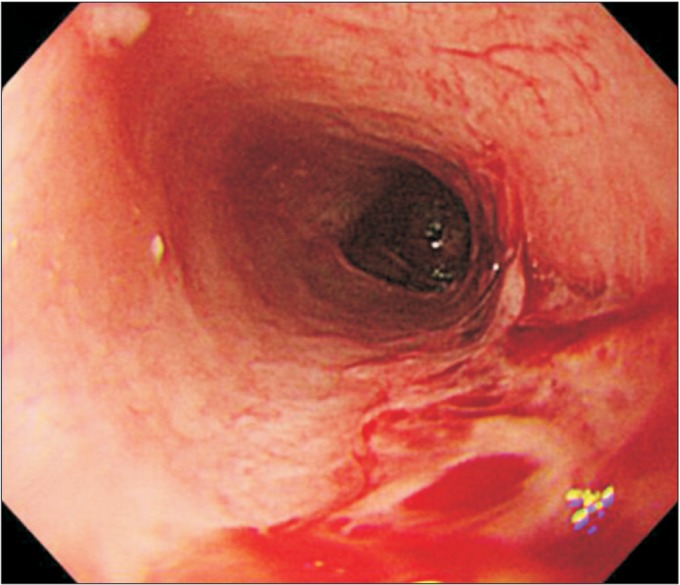
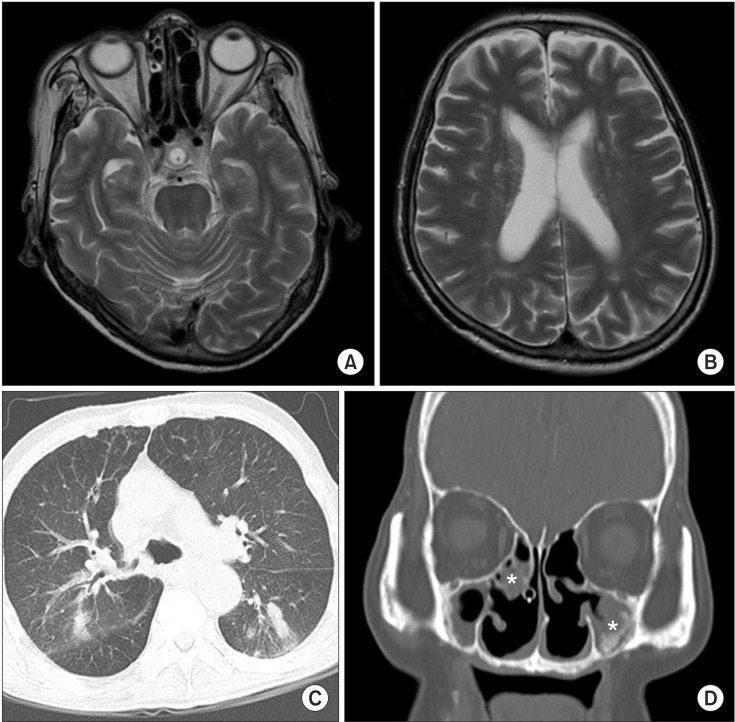
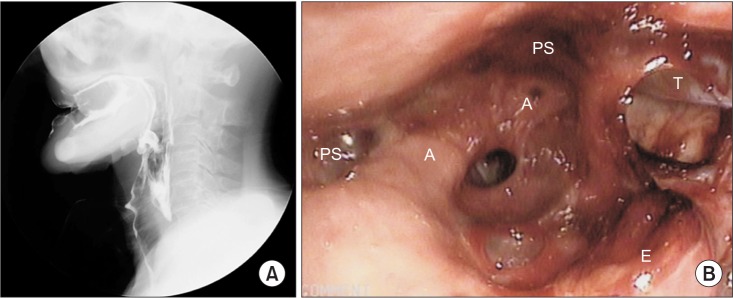
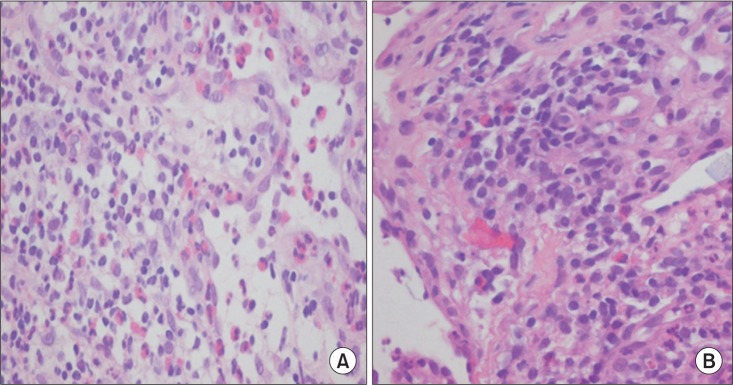
- Systemic vasculitis is a rare disease, and the diagnosis is very difficult when patient shows atypical symptoms. We experienced an unusual case of dysphagia caused by Churg-Strauss syndrome with lower cranial nerve involvement. A 74-year-old man, with a past history of sinusitis, asthma, and hearing deficiency, was admitted to our department for evaluation of dysphagia. He also complained of recurrent bleeding of nasal cavities and esophagus. Brain magnetic resonance imaging did not show definite abnormality, and electrophysiologic findings were suggestive of mononeuritis multiplex. Dysphagia had not improved after conventional therapy. Biopsy of the nasal cavity showed extravascular eosinophilic infiltration. All these findings suggested a rare form of Churg-Strauss syndrome involving multiple lower cranial nerves. Dysphagia improved after steroid therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Palmer JB, Monahan DM, Matsuo K. Rehabilitation of patients with swallowing disorders. In : Braddom RL, editor. Physical medicine & rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2011. p. 581–600.2. Armani M, Spinazzi M, Andrigo C, Fassina A, Mantovan M, Tavolato B. Severe dysphagia in lower cranial nerve involvement as the initial symptom of Wegener's granulomatosis. J Neurol Sci. 2007; 263:187–190. PMID: 17658554.
Article3. Miller PG, Santini C, Freed MJ. Dysphagia in a patient with Wegener's granulomatosis: case report. Dysphagia. 2001; 16:136–139. PMID: 11305224.
Article4. Buhaescu I, Williams A, Yood R. Rare manifestations of Churg-Strauss syndrome: coronary artery vasospasm, temporal artery vasculitis, and reversible monocular blindness-a case report. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28:231–233. PMID: 19034601.
Article5. Tsuda H, Ishikawa H, Majima T, Sawada U, Mizutani T. Isolated oculomotor nerve palsy in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Intern Med. 2005; 44:638–640. PMID: 16020896.
Article6. Mori A, Hira K, Hatano T, Okuma Y, Kubo S, Hirano K, et al. Bilateral facial nerve palsy due to otitis media associated with myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody. Am J Med Sci. 2013; 346:240–243. PMID: 23470272.
Article7. Mazzantini M, Fattori B, Matteucci F, Gaeta P, Ursino F. Neuro-laryngeal involvement in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1998; 255:302–306. PMID: 9693926.
Article8. Shimada T, Sasaki R, Ii Y, Taniguchi A, Ueda Y, Tomimoto H. A case of Churg-Strauss syndrome presenting with lower cranial neuropathy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2012; 52:507–510. PMID: 22849995.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Chrug-Strauss Syndrome Complicated with Intestinal Perforation
- A case of Churg-Strauss syndrome that underwent endoscopic sinus surgery under total intravenous anesthesia: A case report
- A Case of Churg-Strauss Syndrome with Endomyocardial Fibrosis
- A Case of Churg-Strauss Syndrome Presenting Umbilicated Ulcerative Papules
- An atypical case of Churg-Strauss syndrome without asthma