Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Dec;39(6):1042-1046. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.1042.
Leg Weakness Caused by Bilateral Piriformis Syndrome: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. rusl98@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2165634
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.1042
Abstract
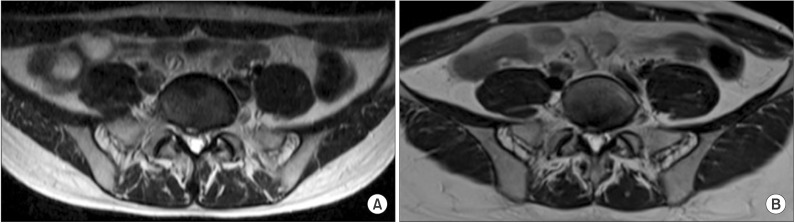
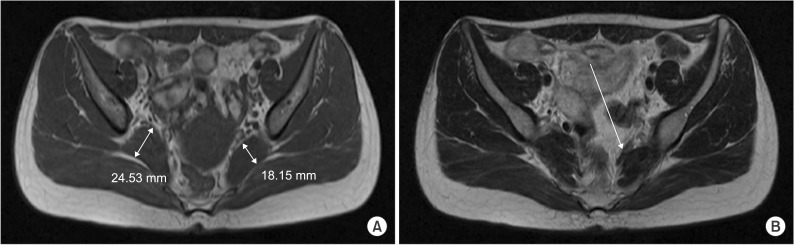
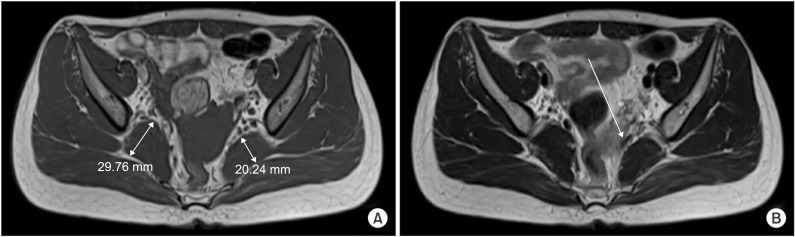
- Piriformis syndrome (PS) is an uncommon neuromuscular disorder caused by the piriformis muscle (PM) compressing the sciatic nerve (SN). The main symptom of PS is sciatica, which worsens with certain triggering conditions. Because the pathophysiology is poorly understood, there are no definite diagnostic and therapeutic choices for PS. This case report presents a young woman who mainly complained of bilateral leg weakness. Electromyography revealed bilateral sciatic neuropathy and magnetic resonance imaging confirmed structural lesions causing entrapment of the bilateral SNs. After a laborious diagnosis of bilateral PS, she underwent PM releasing surgery. Few PS cases present with bilateral symptoms and leg weakness. Therefore, in such cases, a high level of suspicion is necessary for accurate and prompt diagnosis and treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hopayian K, Song F, Riera R, Sambandan S. The clinical features of the piriformis syndrome: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19:2095–2109. PMID: 20596735.
Article2. Michel F, Decavel P, Toussirot E, Tatu L, Aleton E, Monnier G, et al. Piriformis muscle syndrome: diagnostic criteria and treatment of a monocentric series of 250 patients. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2013; 56:371–383. PMID: 23684470.3. Michel F, Decavel P, Toussirot E, Tatu L, Aleton E, Monnier G, et al. The piriformis muscle syndrome: an exploration of anatomical context, pathophysiological hypotheses and diagnostic criteria. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2013; 56:300–311. PMID: 23684469.
Article4. Rossi P, Cardinali P, Serrao M, Parisi L, Bianco F, De Bac S. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in piriformis syndrome: a case report. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:519–521. PMID: 11295014.
Article5. Woodson C, Bandy WD, Curis D, Baldwin D. Relationship of isokinetic peak torque with work and power for ankle plantar flexion and dorsiflexion. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1995; 22:113–115. PMID: 8535468.
Article6. Uchio Y, Nishikawa U, Ochi M, Shu N, Takata K. Bilateral piriformis syndrome after total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998; 117:177–179. PMID: 9521528.
Article7. Al-Al-Shaikh M, Michel F, Parratte B, Kastler B, Vidal C, Aubry S. An MRI evaluation of changes in piriformis muscle morphology induced by botulinum toxin injections in the treatment of piriformis syndrome. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015; 96:37–43. PMID: 24703886.
Article8. Benson ER, Schutzer SF. Posttraumatic piriformis syndrome: diagnosis and results of operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:941–949. PMID: 10428125.9. Jenkins DB. Hollinshead's functional anatomy of the limbs and back. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2009. p. 294–306.10. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts MJ. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;2002. p. 713–776.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Caudal Steroid Injection for Treatment of Piriformis Syndrome
- Piriformis Syndrome (Sciatic Nerve Entrapment) Associated With Type C Sciatic Nerve Variation: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
- Accessory Belly of the Piriformis Muscle as a Cause of Piriformis Syndrome: a Case Report with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Neurography Imaging Findings
- Piriformis Syndrome: A Case Report
- Piriformis syndrome: a case report