Clin Endosc.
2014 Jan;47(1):115-118.
Extramedullary Plasmacytoma of the Pancreas Diagnosed Using Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Gastrointestinal Cancer Center, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea. mongmani@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Hemato-oncology, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
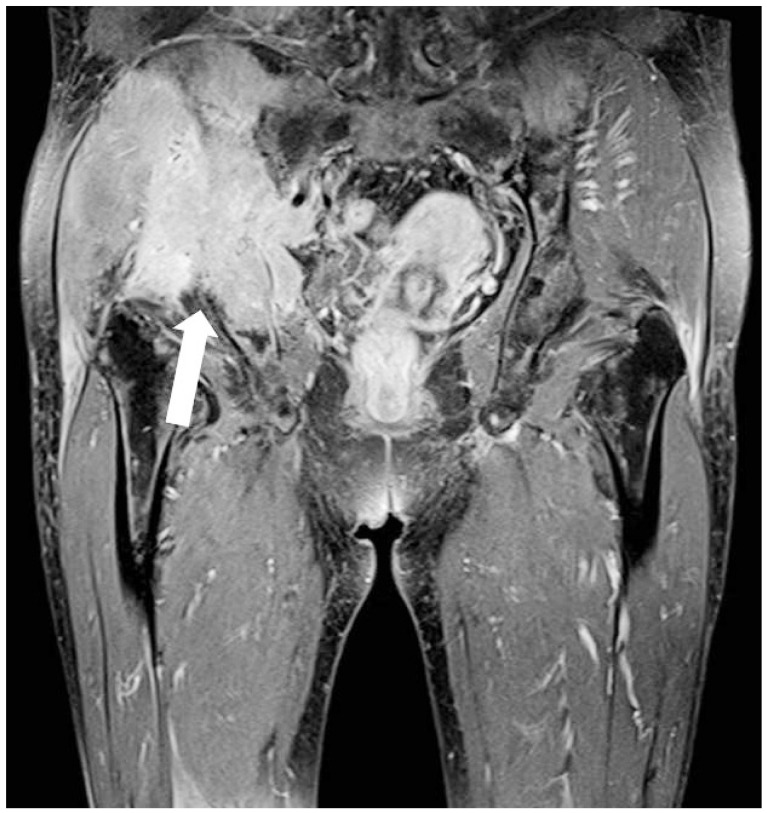
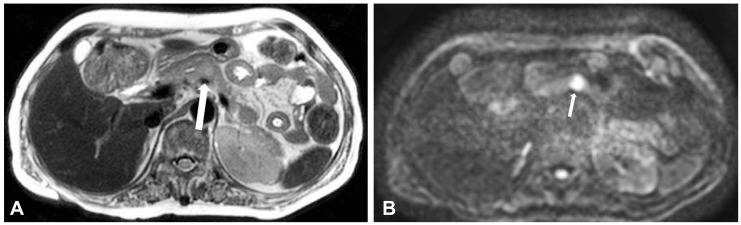
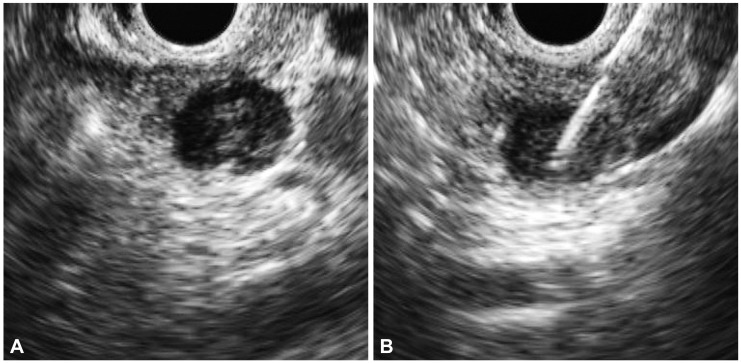
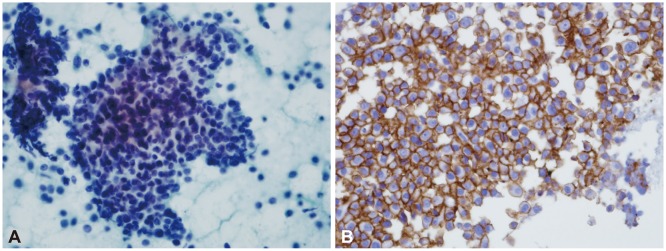
- Extramedullary plasmacytoma involves organs outside the bone marrow; however, involvement of the pancreas is rare. We recently experienced a case of extramedullary plasmacytoma of the pancreas that was diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). EUS-FNA, which has a high diagnostic accuracy and an excellent safety profile, is the modality of choice for establishing tissue diagnosis. We report a case of extramedullary plasmacytoma of the pancreas diagnosed using EUS-FNA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Soutar R, Lucraft H, Jackson G, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of solitary plasmacytoma of bone and solitary extramedullary plasmacytoma. Br J Haematol. 2004; 124:717–726. PMID: 15009059.
Article2. Dores GM, Landgren O, McGlynn KA, Curtis RE, Linet MS, Devesa SS. Plasmacytoma of bone, extramedullary plasmacytoma, and multiple myeloma: incidence and survival in the United States, 1992-2004. Br J Haematol. 2009; 144:86–94. PMID: 19016727.
Article3. Miljkovic' M, Senadhi V. Use of endoscopic ultrasound in diagnosing plasmacytoma of the pancreas. JOP. 2012; 13:26–29. PMID: 22233943.4. Bachar G, Goldstein D, Brown D, et al. Solitary extramedullary plasmacytoma of the head and neck: long-term outcome analysis of 68 cases. Head Neck. 2008; 30:1012–1019. PMID: 18327783.5. Schabel SI, Rogers CI, Rittenberg GM, Bubanj R. Extramedullary plasmacytoma. Radiology. 1978; 128:625–628. PMID: 674630.6. Fischer A, Suhrland MJ, Vogl SE. Myeloma of the head of the pancreas. A case report. Cancer. 1991; 67:681–683. PMID: 1985760.
Article7. Padda MS, Milless T, Adeniran AJ, Mahooti S, Aslanian HR. Pancreatic and gastric plasmacytoma presenting with obstructive jaundice, diagnosed with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2010; 4:410–415. PMID: 21060710.
Article8. Gupta P, Rice GD, Abraham K, Ghole V, Ketkar M. Extramedullary plasmacytoma of the pancreas and jejunum. Clin Imaging. 2009; 33:240–243. PMID: 19411034.
Article9. Eloubeidi MA, Tamhane A, Varadarajulu S, Wilcox CM. Frequency of major complications after EUS-guided FNA of solid pancreatic masses: a prospective evaluation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:622–629. PMID: 16564863.
Article10. Wiersema MJ, Vilmann P, Giovannini M, Chang KJ, Wiersema LM. Endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy: diagnostic accuracy and complication assessment. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:1087–1095. PMID: 9097990.
Article11. Katanuma A, Maguchi H, Hashigo S, et al. Tumor seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of cancer in the body of the pancreas. Endoscopy. 2012; 44(Suppl 2 UCTN):E160–E161. PMID: 22622721.
Article12. Micames C, Jowell PS, White R, et al. Lower frequency of peritoneal carcinomatosis in patients with pancreatic cancer diagnosed by EUS-guided FNA vs. percutaneous FNA. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:690–695. PMID: 14595302.
Article13. Artifon EL, Okawa L, Baba ER, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic plasmacytoma by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. Endoscopy. 2011; 43(Suppl 2 UCTN):E79–E80. PMID: 21425019.
Article14. Senadhi V, Dunbar K, Jagannath S. Diagnosis of a pancreatic plasmacytoma by endoscopic ultrasound with fine needle aspiration: a case report. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104(Suppl 3):S234–S235.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fine-Needle Biopsy: Should This Be the First Choice in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition?
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Cystic Pancreatic Lesions
- Performance Characteristics of a New Flexible Nitinol 19-Gauge Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Needle
- Review of the 2017 European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Guidelines for Endoscopic Ultrasound - Guided Sampling in Pancreaticobiliary Lesions
- Could Transgastric Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Aspiration Alone Be Effective for the Treatment of Pancreatic Abscesses?