Clin Endosc.
2015 Jul;48(4):345-347. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.345.
Could Transgastric Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Aspiration Alone Be Effective for the Treatment of Pancreatic Abscesses?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. kth@wonkwang.ac.kr
- 2GI Endoscopy Center, National Cancer Center of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia.
- KMID: 1964281
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.345
Abstract
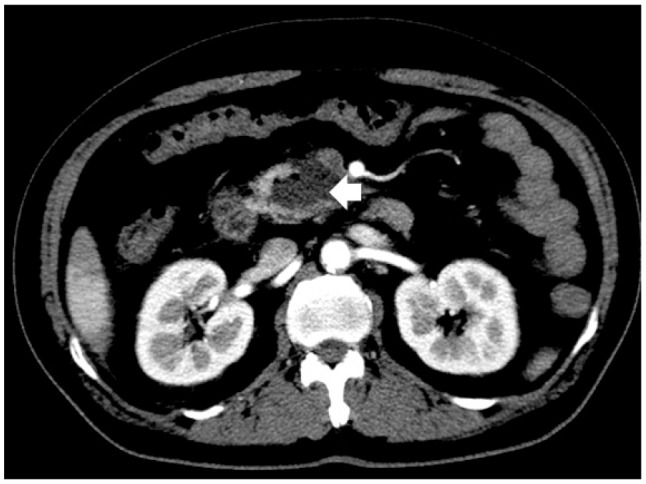
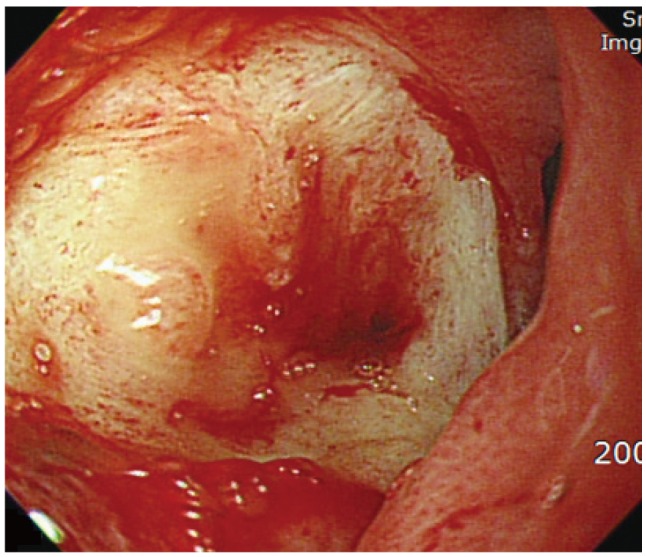
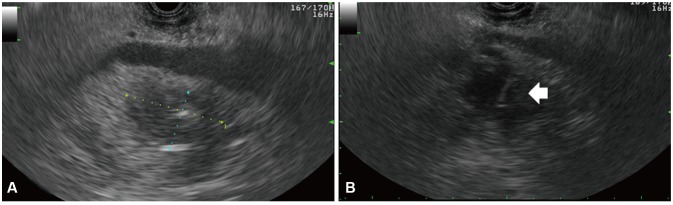
- Drainage of pancreatic abscesses is required for effective control of sepsis. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided endoscopic drainage is less invasive than surgery and prevents local complications related to percutaneous drainage. Endoscopic drainage with stent placement in the uncinate process of the pancreas is a technically difficult procedure. We report a case of pancreatic abscess treated by repeated EUS-guided aspiration and intravenous antibiotics without an indwelling drainage catheter or surgical intervention.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baillie J. Pancreatic pseudocysts (part I). Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:873–879. PMID: 15173808.
Article2. Varadarajulu S, Lopes TL, Wilcox CM, Drelichman ER, Kilgore ML, Christein JD. EUS versus surgical cyst-gastrostomy for management of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:649–655. PMID: 18547566.
Article3. Piraka C, Shah RJ, Fukami N, Chathadi KV, Chen YK. EUS-guided transesophageal, transgastric, and transcolonic drainage of intra-abdominal fluid collections and abscesses. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:786–792. PMID: 19577742.
Article4. Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Frequency of complications during EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections in 148 consecutive patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26:1504–1508. PMID: 21575060.
Article5. Jenssen C, Dietrich CF. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy and trucut biopsy in gastroenterology: an overview. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2009; 23:743–759. PMID: 19744637.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Transgastric Drainage of an Intra-Abdominal Abscess following Gastrectomy
- Role of Repeated Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Inconclusive Initial Cytology Result
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Cystic Pancreatic Lesions
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Transgastric Puncture and Drainage of an Adrenal Abscess in an Immunosuppressed Patient
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Direct Intervention for Solid Pancreatic Tumors