Clin Endosc.
2014 Jan;47(1):55-64.
Treatment of Dysplasia in Barrett Esophagus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, The Center of Advanced Therapeutic Endoscopy and Endoscopic Oncology, St. Michael's Hospital, University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine, Toronto, ON, Canada. norman.marcon@utoronto.ca
Abstract
- Barrett esophagus is recognized as a risk factor for the development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage with a 5-year survival rate of 15%. Most of these patients present de novo and are not part of a surveillance program. Endoscopic screening with improvement in recognition of early lesions may change this pattern. In the past, patients diagnosed with dysplasia and mucosal cancer were best managed by esophagectomy. Endoscopic techniques such as endoscopic mucosal resection and radiofrequency ablation have resulted in high curative rates and a shift away from esophagectomy. This pathway is supported by the literature review of esophagectomies performed for mucosal disease, as well as pathologists' interpretation of endoscopic mucosal specimens, which document the low risk of lymph node metastasis. The role of endoscopic therapy for superficial submucosal disease continues to be a challenge.
MeSH Terms
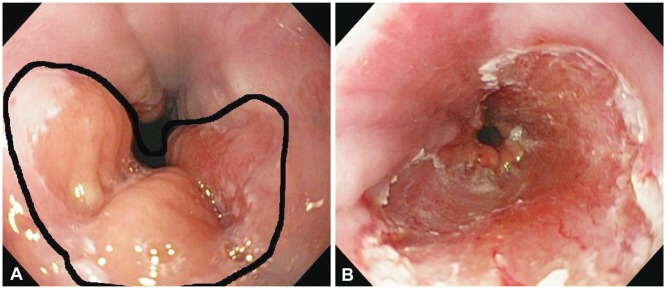
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010; 60:277–300. PMID: 20610543.
Article2. Zhang Y. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:5598–5606. PMID: 24039351.
Article3. Hvid-Jensen F, Pedersen L, Drewes AM, Sørensen HT, Funch-Jensen P. Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:1375–1383. PMID: 21995385.
Article4. Schnell TG, Sontag SJ, Chejfec G, et al. Long-term nonsurgical management of Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2001; 120:1607–1619. PMID: 11375943.
Article5. Bhat S, Coleman HG, Yousef F, et al. Risk of malignant progression in Barrett's esophagus patients: results from a large population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011; 103:1049–1057. PMID: 21680910.
Article6. Curvers WL, ten Kate FJ, Krishnadath KK, et al. Low-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: overdiagnosed and underestimated. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:1523–1530. PMID: 20461069.
Article7. Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM, Shaheen NJ. American Gastroenterological Association. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the management of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:e18–e52. PMID: 21376939.
Article8. Gordon LG, Mayne GC, Hirst NG, et al. Cost-effectiveness of endoscopic surveillance of non-dysplastic Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. Epub 2013 Sep 27. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.07.046.
Article9. Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, et al. The development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for Barrett's esophagus: the Prague C & M criteria. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:1392–1399. PMID: 17101315.10. Vieth M, Ell C, Gossner L, May A, Stolte M. Histological analysis of endoscopic resection specimens from 326 patients with Barrett's esophagus and early neoplasia. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:776–781. PMID: 15326572.
Article11. Dunbar KB, Spechler SJ. The risk of lymph-node metastases in patients with high-grade dysplasia or intramucosal carcinoma in Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:850–862. PMID: 22488081.
Article12. Kaneshiro DK, Post JC, Rybicki L, Rice TW, Goldblum JR. Clinical significance of the duplicated muscularis mucosae in Barrett esophagus-related superficial adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011; 35:697–700. PMID: 21490446.
Article13. Menon D, Stafinski T, Wu H, Lau D, Wong C. Endoscopic treatments for Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review of safety and effectiveness compared to esophagectomy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010; 10:111. PMID: 20875123.
Article14. Pech O, May A, Manner H, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. Epub 2013 Nov 20. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.11.006.
Article15. Ngamruengphong S, Wolfsen HC, Wallace MB. Survival of patients with superficial esophageal adenocarcinoma after endoscopic treatment vs surgery. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:1424–1429. PMID: 23735443.
Article16. Zehetner J, DeMeester SR, Hagen JA, et al. Endoscopic resection and ablation versus esophagectomy for high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; 141:39–47. PMID: 21055772.
Article17. Moss A, Bourke MJ, Hourigan LF, et al. Endoscopic resection for Barrett's high-grade dysplasia and early esophageal adenocarcinoma: an essential staging procedure with long-term therapeutic benefit. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:1276–1283. PMID: 20179694.
Article18. ASGE Technology Committee. Kantsevoy SV, Adler DG, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:11–18. PMID: 18577472.
Article19. Levine DS, Haggitt RC, Blount PL, Rabinovitch PS, Rusch VW, Reid BJ. An endoscopic biopsy protocol can differentiate high-grade dysplasia from early adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1993; 105:40–50. PMID: 8514061.
Article20. Namasivayam V, Wang KK, Prasad GA. Endoscopic mucosal resection in the management of esophageal neoplasia: current status and future directions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:743–754. PMID: 20541628.
Article21. Larghi A, Lightdale CJ, Memeo L, Bhagat G, Okpara N, Rotterdam H. EUS followed by EMR for staging of high-grade dysplasia and early cancer in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:16–23. PMID: 15990814.
Article22. Bhat YM, Furth EE, Brensinger CM, Ginsberg GG. Endoscopic resection with ligation using a multi-band mucosectomy system in Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal carcinoma. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2009; 2:323–330.
Article23. Wani S, Abrams J, Edmundowicz SA, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection results in change of histologic diagnosis in Barrett's esophagus patients with visible and flat neoplasia: a multicenter cohort study. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:1703–1709. PMID: 23633158.
Article24. Neuhaus H, Terheggen G, Rutz EM, Vieth M, Schumacher B. Endoscopic submucosal dissection plus radiofrequency ablation of neoplastic Barrett's esophagus. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:1105–1113. PMID: 22968641.
Article25. Pech O, May A, Günter E, Gossner L, Ell C. The impact of endoscopic ultrasound and computed tomography on the TNM staging of early cancer in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:2223–2229. PMID: 17032186.
Article26. Buskens CJ, Westerterp M, Lagarde SM, Bergman JJ, ten Kate FJ, van Lanschot JJ. Prediction of appropriateness of local endoscopic treatment for high-grade dysplasia and early adenocarcinoma by EUS and histopathologic features. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:703–710. PMID: 15557945.
Article27. Keswani RN, Early DS, Edmundowicz SA, et al. Routine positron emission tomography does not alter nodal staging in patients undergoing EUS-guided FNA for esophageal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:1210–1217. PMID: 19012886.
Article28. Conio M, Repici A, Cestari R, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection for high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal carcinoma in Barrett's esophagus: an Italian experience. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:6650–6655. PMID: 16425359.
Article29. Lopes CV, Hela M, Pesenti C, et al. Circumferential endoscopic resection of Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia or early adenocarcinoma. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:820–824. PMID: 17294308.
Article30. Nijhawan PK, Wang KK. Endoscopic mucosal resection for lesions with endoscopic features suggestive of malignancy and high-grade dysplasia within Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:328–332. PMID: 10968845.
Article31. Chung A, Bourke MJ, Hourigan LF, et al. Complete Barrett's excision by stepwise endoscopic resection in short-segment disease: long term outcomes and predictors of stricture. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:1025–1032. PMID: 22068701.
Article32. Chennat J, Konda VJ, Ross AS, et al. Complete Barrett's eradication endoscopic mucosal resection: an effective treatment modality for high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal carcinoma: an American single-center experience. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:2684–2692. PMID: 19690526.33. Peters FP, Krishnadath KK, Rygiel AM, et al. Stepwise radical endoscopic resection of the complete Barrett's esophagus with early neoplasia successfully eradicates pre-existing genetic abnormalities. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1853–1861. PMID: 17509033.
Article34. Pouw RE, Seewald S, Gondrie JJ, et al. Stepwise radical endoscopic resection for eradication of Barrett's oesophagus with early neoplasia in a cohort of 169 patients. Gut. 2010; 59:1169–1177. PMID: 20525701.
Article35. Soehendra N, Seewald S, Groth S, et al. Use of modified multiband ligator facilitates circumferential EMR in Barrett's esophagus (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:847–852. PMID: 16650552.
Article36. Sato H, Inoue H, Kobayashi Y, et al. Control of severe strictures after circumferential endoscopic submucosal dissection for esophageal carcinoma: oral steroid therapy with balloon dilation or balloon dilation alone. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:250–257. PMID: 23453294.
Article37. Hashimoto S, Kobayashi M, Takeuchi M, Sato Y, Narisawa R, Aoyagi Y. The efficacy of endoscopic triamcinolone injection for the prevention of esophageal stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1389–1393. PMID: 22136782.
Article38. Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, Nakayama T, et al. Management of esophageal stricture after complete circular endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011; 11:46. PMID: 21542926.
Article39. Deprez PH, Piessevaux H, Aouattah T, Yeung RC, Sempoux C, Jouret-Mourin A. ESD in Barrett's esophagus high grade dysplasia and mucosal cancer: prospective comparison with CAP mucosectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:AB126.40. Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett's esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:2277–2288. PMID: 19474425.41. Shaheen NJ, Overholt BF, Sampliner RE, et al. Durability of radiofrequency ablation in Barrett's esophagus with dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:460–468. PMID: 21679712.42. Dulai PS, Pohl H, Levenick JM, Gordon SR, MacKenzie TA, Rothstein RI. Radiofrequency ablation for long- and ultralong-segment Barrett's esophagus: a comparative long-term follow-up study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:534–541. PMID: 23290719.
Article43. Hur C, Choi SE, Rubenstein JH, et al. The cost effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:567–575. PMID: 22626608.
Article44. Gray NA, Odze RD, Spechler SJ. Buried metaplasia after endoscopic ablation of Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:1899–1908. PMID: 21826111.
Article45. Phoa KN, Pouw RE, van Vilsteren FG, et al. Remission of Barrett's esophagus with early neoplasia 5 years after radiofrequency ablation with endoscopic resection: a Netherlands cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:96–104. PMID: 23542068.
Article46. Yuan J, Hernandez JC, Ratuapli SK, et al. Prevalence of buried Barrett's metaplasia in patients before and after radiofrequency ablation. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:993–997. PMID: 23108770.
Article47. Zhou C, Tsai TH, Lee HC, et al. Characterization of buried glands before and after radiofrequency ablation by using 3-dimensional optical coherence tomography (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:32–40. PMID: 22482920.
Article48. Bulsiewicz WJ, Kim HP, Dellon ES, et al. Safety and efficacy of endoscopic mucosal therapy with radiofrequency ablation for patients with neoplastic Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:636–642. PMID: 23103824.
Article49. Overholt BF, Lightdale CJ, Wang KK, et al. Photodynamic therapy with porfimer sodium for ablation of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: international, partially blinded, randomized phase III trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:488–498. PMID: 16185958.
Article50. Overholt BF, Wang KK, Burdick JS, et al. Five-year efficacy and safety of photodynamic therapy with Photofrin in Barrett's high-grade dysplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:460–468. PMID: 17643436.
Article51. Dunn JM, Mackenzie GD, Banks MR, et al. A randomised controlled trial of ALA vs. Photofrin photodynamic therapy for high-grade dysplasia arising in Barrett's oesophagus. Lasers Med Sci. 2013; 28:707–715. PMID: 22699800.
Article52. Ertan A, Zaheer I, Correa AM, Thosani N, Blackmon SH. Photodynamic therapy vs radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's dysplasia: efficacy, safety and cost-comparison. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:7106–7113. PMID: 24222954.53. Gosain S, Mercer K, Twaddell WS, Uradomo L, Greenwald BD. Liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy in Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia: long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:260–265. PMID: 23622979.
Article54. Fitzgerald RC, di Pietro M, Ragunath K, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 2014; 63:7–42. PMID: 24165758.
Article55. Bennett C, Vakil N, Bergman J, et al. Consensus statements for management of Barrett's dysplasia and early-stage esophageal adenocarcinoma, based on a Delphi process. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:336–346. PMID: 22537613.56. Gupta M, Iyer PG, Lutzke L, et al. Recurrence of esophageal intestinal metaplasia after endoscopic mucosal resection and radiofrequency ablation of Barrett's esophagus: results from a US Multicenter Consortium. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:79–86. PMID: 23499759.
Article57. Haidry RJ, Dunn JM, Butt MA, et al. Radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic mucosal resection for dysplastic barrett's esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma: outcomes of the UK National Halo RFA Registry. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:87–95. PMID: 23542069.
Article58. Diaz-Cervantes E, De-la-Torre-Bravo A, Spechler SJ, et al. Banding without resection (endoscopic mucosal ligation) as a novel approach for the ablation of short-segment Barrett's epithelium: results of a pilot study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1640–1645. PMID: 17488252.
Article59. Raftopoulos SC, Efthymiou M, May G, Marcon N. Dysplastic Barrett's esophagus in cirrhosis: a treatment dilemma. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:1724–1726. PMID: 21897417.
Article60. Wani S, Falk GW, Post J, et al. Risk factors for progression of low-grade dysplasia in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:1179–1186. PMID: 21723218.
Article61. Badreddine RJ, Prasad GA, Lewis JT, et al. Depth of submucosal invasion does not predict lymph node metastasis and survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:248–253. PMID: 19948247.
Article62. Gockel I, Sgourakis G, Lyros O, et al. Risk of lymph node metastasis in submucosal esophageal cancer: a review of surgically resected patients. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 5:371–384. PMID: 21651355.
Article63. Nentwich MF, von Loga K, Reeh M, et al. Depth of submucosal tumor infiltration and its relevance in lymphatic metastasis formation for T1b squamous cell and adenocarcinomas of the esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg. Epub 2013 Oct 4. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-013-2367-2.
Article64. Manner H, Pech O, Heldmann Y, et al. Efficacy, safety, and long-term results of endoscopic treatment for early stage adenocarcinoma of the esophagus with low-risk sm1 invasion. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:630–635. PMID: 23357492.
Article65. Alvarez Herrero L, Pouw RE, van Vilsteren FG, et al. Risk of lymph node metastasis associated with deeper invasion by early adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and cardia: study based on endoscopic resection specimens. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:1030–1036. PMID: 20960392.
Article66. Pech O, Behrens A, May A, et al. Long-term results and risk factor analysis for recurrence after curative endoscopic therapy in 349 patients with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and mucosal adenocarcinoma in Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 2008; 57:1200–1206. PMID: 18460553.
Article67. van Vilsteren FG, Alvarez Herrero L, Pouw RE, et al. Predictive factors for initial treatment response after circumferential radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus with early neoplasia: a prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:516–525. PMID: 23580412.
Article