Clin Endosc.
2014 Sep;47(5):469-472. 10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.469.
Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Severe Acute Pancreatitis Treated with Percutaneous Catheter Drainage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine and Medical Research Institute, Cheongju, Korea. smpark@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2165383
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.469
Abstract
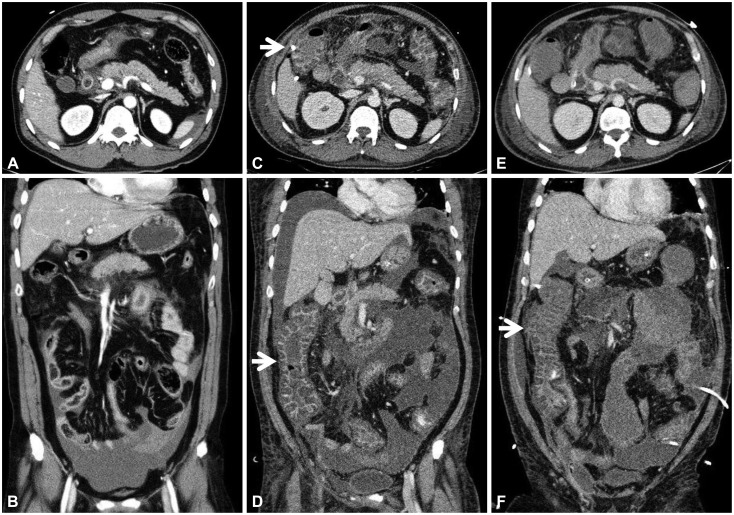
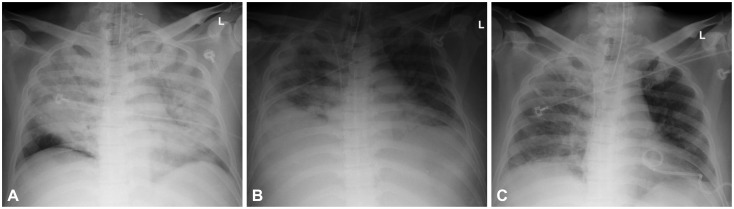
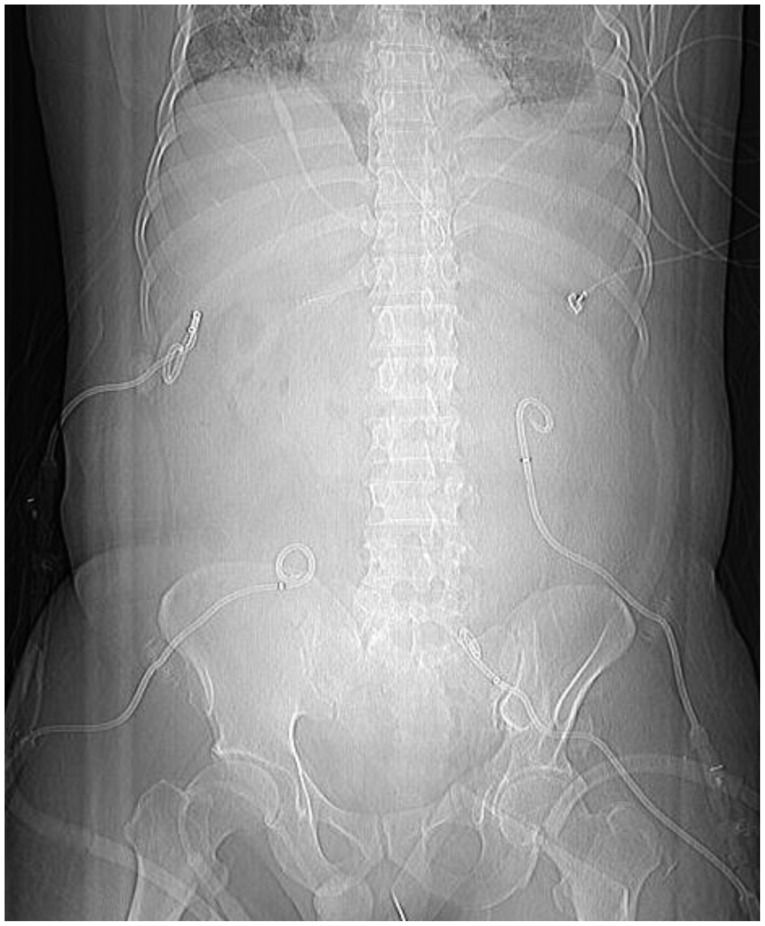
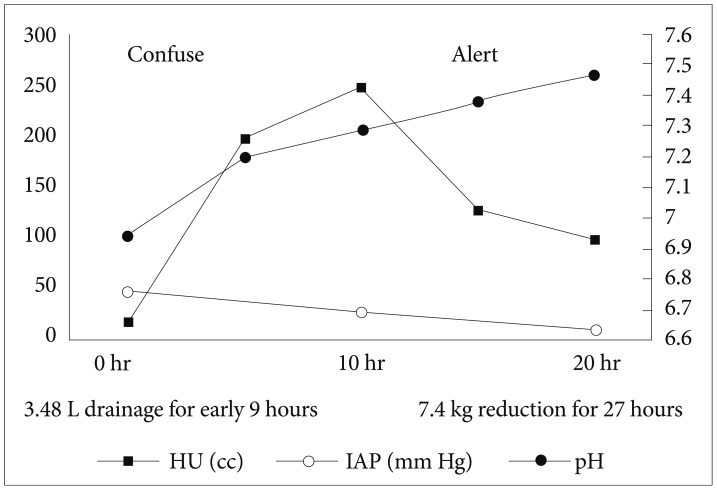
- Acute pancreatitis is one of the main causes of intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH). IAH contributes to multiple physiologic alterations and leads to the development of abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) that induces multiorgan failure. We report a case of ACS in a patient with severe acute pancreatitis. A 44-year-old man who was admitted in a drunk state was found to have severe acute pancreatitis. During management with fluid resuscitation in an intensive care unit, drowsy mentality, respiratory acidosis, shock requiring inotropes, and oliguria developed in the patient, with his abdomen tensely distended. With a presumptive diagnosis of ACS, abdominal decompression through percutaneous catheter drainage was performed immediately. The intraperitoneal pressure measured with a drainage catheter was 31 mm Hg. After abdominal decompression, the multiorgan failure was reversed. We present a case of ACS managed with percutaneous catheter decompression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Malbrain ML, Cheatham ML, Kirkpatrick A, et al. Results from the International Conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. I. Definitions. Intensive Care Med. 2006; 32:1722–1732. PMID: 16967294.
Article2. Malbrain ML, Chiumello D, Pelosi P, et al. Incidence and prognosis of intraabdominal hypertension in a mixed population of critically ill patients: a multiple-center epidemiological study. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:315–322. PMID: 15699833.
Article3. Cheatham ML, Malbrain ML, Kirkpatrick A, et al. Results from the International Conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. II. Recommendations. Intensive Care Med. 2007; 33:951–962. PMID: 17377769.
Article4. Gecelter G, Fahoum B, Gardezi S, Schein M. Abdominal compartment syndrome in severe acute pancreatitis: an indication for a decompressing laparotomy? Dig Surg. 2002; 19:402–404. PMID: 12435913.
Article5. Ke L, Ni HB, Sun JK, et al. Risk factors and outcome of intra-abdominal hypertension in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. World J Surg. 2012; 36:171–178. PMID: 21964817.
Article6. Mao EQ, Tang YQ, Fei J, et al. Fluid therapy for severe acute pancreatitis in acute response stage. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009; 122:169–173. PMID: 19187641.7. Mateĕjovic M, Novák I, Rokyta R Jr, Krouzecký A. Fluid resuscitation in conditions with disorders of capillary permeability. Cas Lek Cesk. 2002; 141:540–545. PMID: 12404957.8. Brown A, Baillargeon JD, Hughes MD, Banks PA. Can fluid resuscitation prevent pancreatic necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis? Pancreatology. 2002; 2:104–107. PMID: 12123089.
Article9. Forgács B, Foitzik T. Multiple organ failure in experimental pancreatitis. Magy Seb. 2000; 53:234–240. PMID: 11299487.10. Du XJ, Hu WM, Xia Q, et al. Hydroxyethyl starch resuscitation reduces the risk of intra-abdominal hypertension in severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2011; 40:1220–1225. PMID: 21775917.
Article11. Anand RJ, Ivatury RR. Surgical management of intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. Am Surg. 2011; 77(Suppl 1):S42–S45. PMID: 21944451.12. Radenkovic DV, Bajec D, Ivancevic N, et al. Decompressive laparotomy with temporary abdominal closure versus percutaneous puncture with placement of abdominal catheter in patients with abdominal compartment syndrome during acute pancreatitis: background and design of multicenter, randomised, controlled study. BMC Surg. 2010; 10:22. PMID: 20624281.
Article13. Malbrain ML. Different techniques to measure intra-abdominal pressure (IAP): time for a critical re-appraisal. Intensive Care Med. 2004; 30:357–371. PMID: 14730376.
Article14. Durand PY, Chanliau J, Gambéroni J, Hestin D, Kessler M. Measurement of hydrostatic intraperitoneal pressure: a necessary routine test in peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 1996; 16(Suppl 1):S84–S87. PMID: 8728169.
Article15. Al-Hwiesh A, Al-Mueilo S, Saeed I, Al-Muhanna FA. Intraperitoneal pressure and intra-abdominal pressure: are they the same? Perit Dial Int. 2011; 31:315–319. PMID: 21357935.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Drainage Through a Duodenal Fistula in a Patient with a Retroperitoneal Abscess that Developed after Acute Pancreatitis
- Comparison of Surgical Treatment with Percutaneous Catheter Drainage of a Pancreatic Pseudocyst
- Percutaneous catheter drainage of abdominal abscess associated with fistulas
- A case of acute pancreatitis complicated by pseudocystocolonic fistula
- Percutaneous catheter drainage of intraabdominal abscesses and fluid