J Pathol Transl Med.
2016 May;50(3):246-249. 10.4132/jptm.2015.10.08.
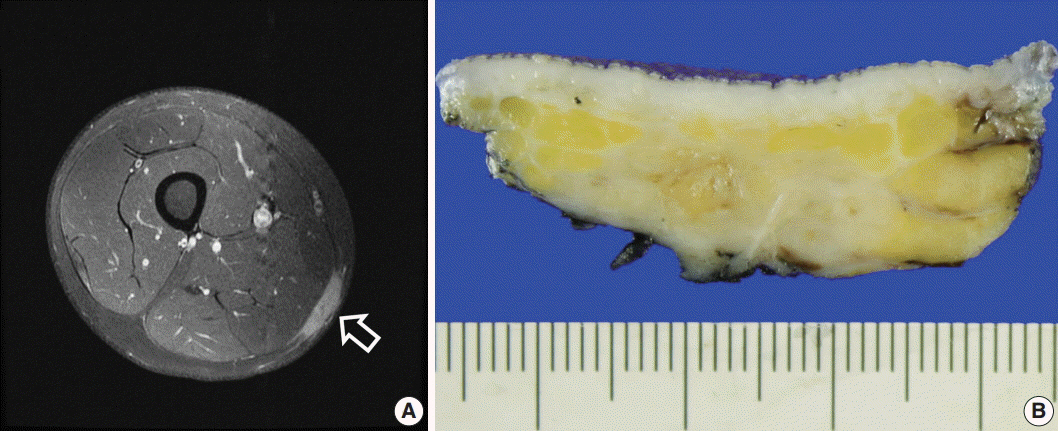
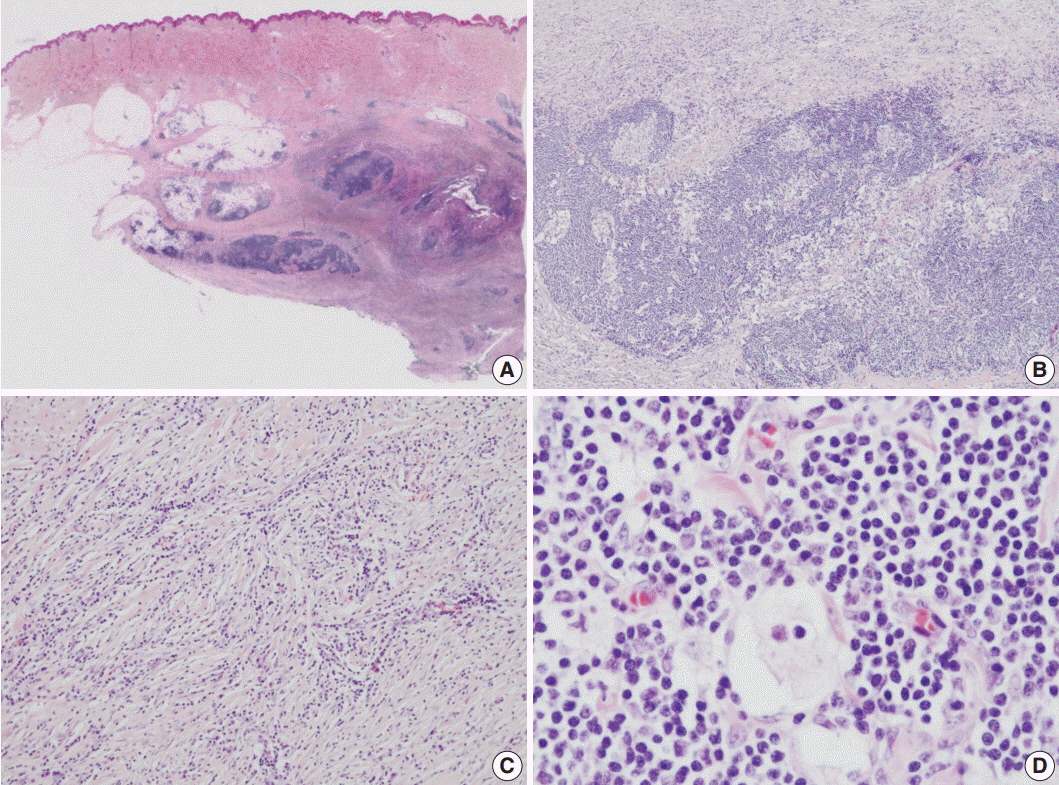
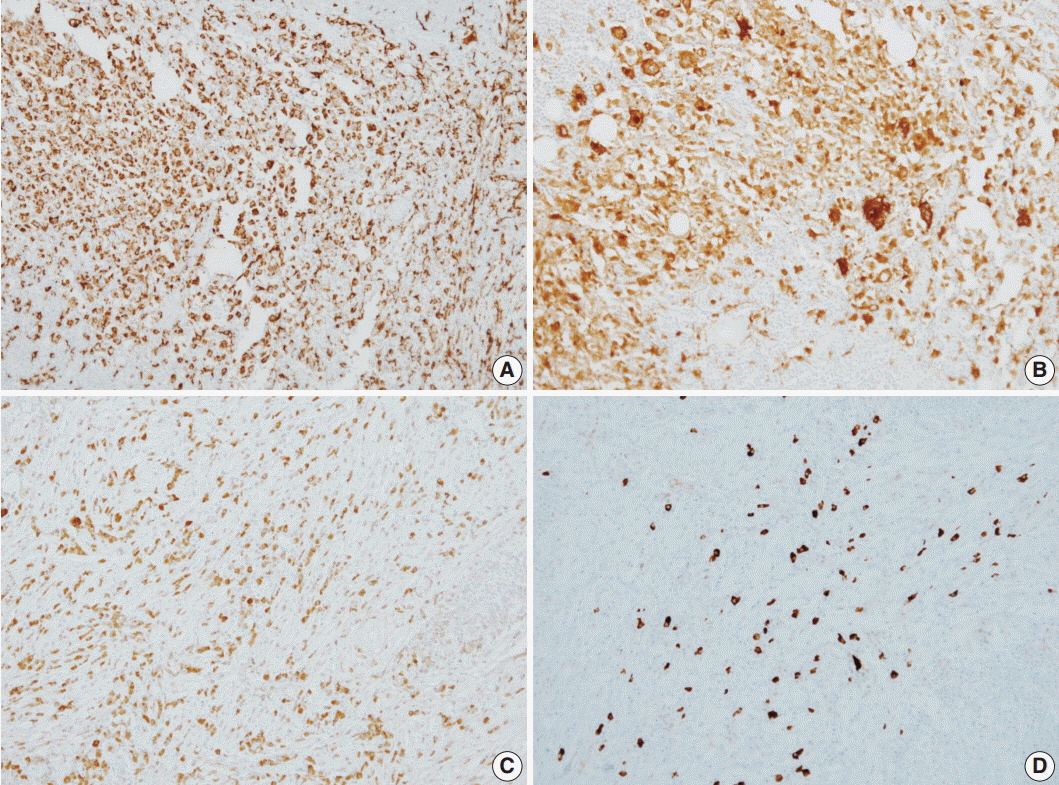
Soft Tissue Roasi-Dorfman Disease with Features of IgG4-Related Disease in a Patient with a History of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nicekyumi@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2164604
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.10.08
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: a newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969; 87:63–70.2. Zhang X, Hyjek E, Vardiman J. A subset of Rosai-Dorfman disease exhibits features of IgG4-related disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 2013; 139:622–32.
Article3. Bi Y, Huo Z, Meng Y, et al. Extranodal Rosai-Dorfman disease involving the right atrium in a 60-year-old male. Diagn Pathol. 2014; 9:115.
Article4. Al-Daraji W, Anandan A, Klassen-Fischer M, Auerbach A, Marwaha JS, Fanburg-Smith JC. Soft tissue Rosai-Dorfman disease: 29 new lesions in 18 patients, with detection of polyomavirus antigen in 3 abdominal cases. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2010; 14:309–16.
Article5. Montgomery EA, Meis JM, Frizzera G. Rosai-Dorfman disease of soft tissue. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992; 16:122–9.
Article6. Kong YY, Kong JC, Shi DR, et al. Cutaneous rosai-dorfman disease: a clinical and histopathologic study of 25 cases in China. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:341–50.7. Young PM, Kransdorf MJ, Temple HT, Mousavi F, Robinson PG. Rosai-Dorfman disease presenting as multiple soft tissue masses. Skeletal Radiol. 2005; 34:665–9.
Article8. Kuo TT, Chen TC, Lee LY, Lu PH. IgG4-positive plasma cells in cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: an additional immunohistochemical feature and possible relationship to IgG4-related sclerosing disease. J Cutan Pathol. 2009; 36:1069–73.
Article9. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181–92.10. Thomas CG, Patel RM, Bergfeld WF. Cytophagic and S-100 protein immunoreactive myeloid leukemia cutis. J Cutan Pathol. 2010; 37:390–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unusual Manifestation of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease Involving the Upper Arm: A Case Report
- Rosai-Dorfman Disease: Report of a Case Associated with IgG4-Related Sclerotic Lesions
- Myeloid Sarcoma of Peritoneum in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Inversion of Chromosome 16
- A t(3;3)(q21;q26) Acute Myeloid Leukemia with the Philadelphia Chromosome as a Secondary Change
- Rosai-Dorfman Disease in the Breast with Increased IgG4 Expressing Plasma Cells: A Case Report