J Pathol Transl Med.
2016 May;50(3):197-203. 10.4132/jptm.2016.03.09.
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Concomitant EGFR, KRAS, and ALK Mutation: Clinicopathologic Features of 12 Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hanjho@skku.edu
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2164596
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.09
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS), and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were thought to be mutually exclusive, some tumors harbor concomitant mutations. Discovering a driver mutation on the basis of morphologic features and therapeutic responses with mutation analysis can be used to understand pathogenesis and predict resistance in targeted therapy.
METHODS
In 6,637 patients with NSCLC, 12 patients who had concomitant mutations were selected and clinicopathologic features were reviewed. Clinical characteristics included sex, age, smoking history, previous treatment, and targeted therapy with response and disease-free survival. Histologic features included dominant patterns, nuclear and cytoplasmic features.
RESULTS
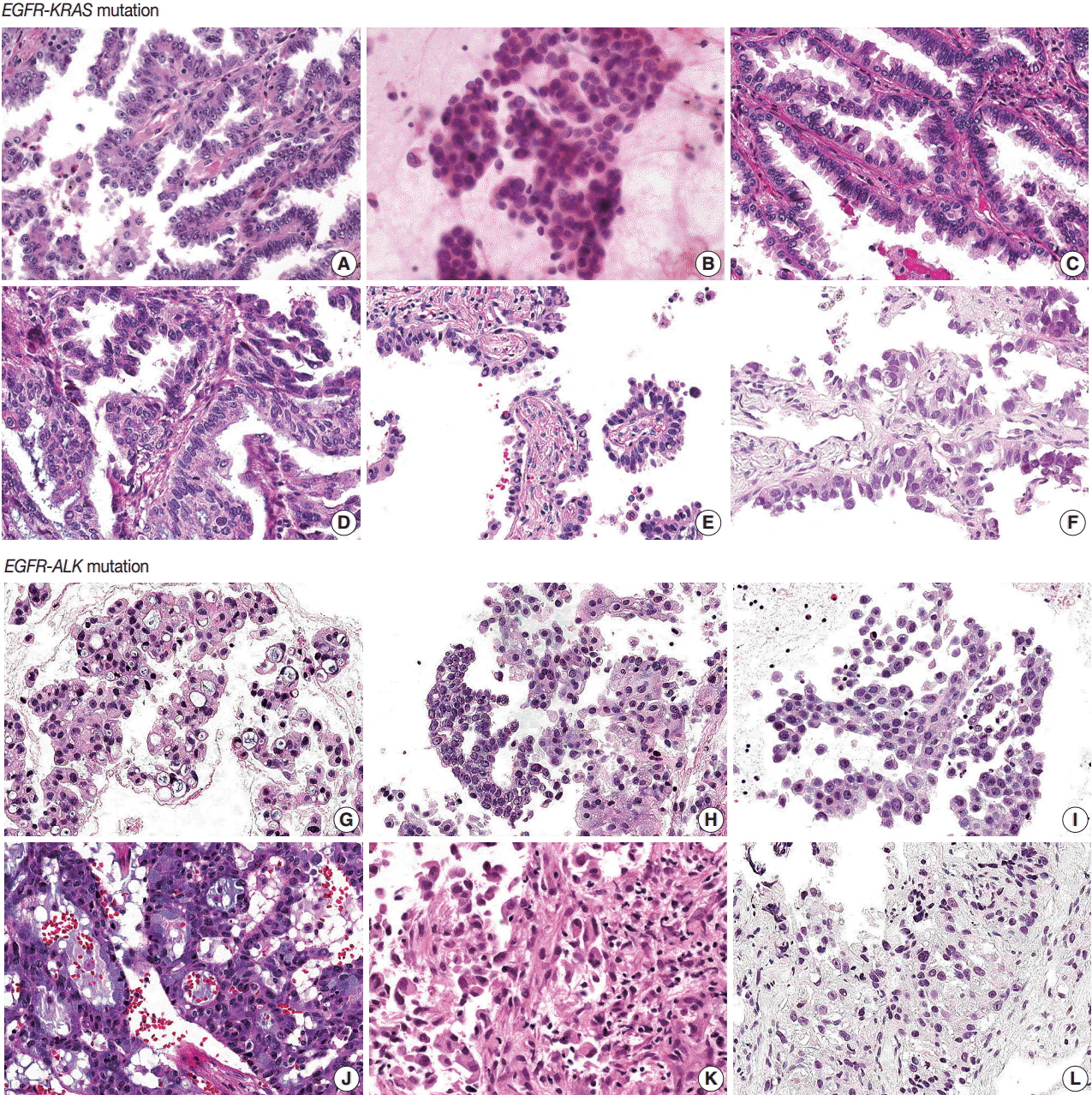
All patients were diagnosed with adenocarcinoma and had an EGFR mutation. Six patients had concomitant KRAS mutations and the other six had KRAS mutations. Five of six EGFR-KRAS mutation patients showed papillary and acinar histologic patterns with hobnail cells. Three of six received EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and showed partial response for 7-29 months. All six EGFR-ALK mutation patients showed solid or cribriform patterns and three had signet ring cells. Five of six EGFR-ALK mutation patients received EGFR TKI and/or ALK inhibitor and four showed partial response or stable disease, except for one patient who had acquired an EGFR mutation.
CONCLUSIONS
EGFR and ALK mutations play an important role as driver mutations in double mutated NSCLC, and morphologic analysis can be used to predict treatment response.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–39.
Article2. Riely GJ, Marks J, Pao W. KRAS mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009; 6:201–5.3. Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1693–703.
Article4. Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007; 448:561–6.5. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:5–29.
Article6. Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004; 304:1497–500.7. Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:823–59.
Article8. Narita Y, Matsushima Y, Shiroiwa T, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of EGFR mutation testing and gefitinib as first-line therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2015; 90:71–7.9. Gainor JF, Varghese AM, Ou SH, et al. ALK rearrangements are mutually exclusive with mutations in EGFR or KRAS: an analysis of 1,683 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:4273–81.10. Tiseo M, Gelsomino F, Boggiani D, et al. EGFR and EML4-ALK gene mutations in NSCLC: a case report of erlotinib-resistant patient with both concomitant mutations. Lung Cancer. 2011; 71:241–3.11. Lee JK, Kim TM, Koh Y, et al. Differential sensitivities to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC harboring EGFR mutation and ALK translocation. Lung Cancer. 2012; 77:460–3.12. Baldi L, Mengoli MC, Bisagni A, Banzi MC, Boni C, Rossi G. Concomitant EGFR mutation and ALK rearrangement in lung adenocarcinoma is more frequent than expected: report of a case and review of the literature with demonstration of genes alteration into the same tumor cells. Lung Cancer. 2014; 86:291–5.13. Won JK, Keam B, Koh J, et al. Concomitant ALK translocation and EGFR mutation in lung cancer: a comparison of direct sequencing and sensitive assays and the impact on responsiveness to tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Ann Oncol. 2015; 26:348–54.14. Paik JH, Choe G, Kim H, et al. Screening of anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement by immunohistochemistry in non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Thorac Oncol. 2011; 6:466–72.15. Bai H, Wang Z, Wang Y, et al. Detection and clinical significance of intratumoral EGFR mutational heterogeneity in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e54170.16. Yang JJ, Zhang XC, Su J, et al. Lung cancers with concomitant EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements: diverse responses to EGFR-TKI and crizotinib in relation to diverse receptors phosphorylation. Clin Cancer Res. 2014; 20:1383–92.17. Choi YL, Sun JM, Cho J, et al. EGFR mutation testing in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive evaluation of real-world practice in an East Asian tertiary hospital. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e56011.18. Sun Y, Ren Y, Fang Z, et al. Lung adenocarcinoma from East Asian never-smokers is a disease largely defined by targetable oncogenic mutant kinases. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:4616–20.
Article19. Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Mino-Kenudson M, et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:4247–53.20. Ninomiya H, Hiramatsu M, Inamura K, et al. Correlation between morphology and EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinomas significance of the micropapillary pattern and the hobnail cell type. Lung Cancer. 2009; 63:235–40.21. Rekhtman N, Ang DC, Riely GJ, Ladanyi M, Moreira AL. KRAS mutations are associated with solid growth pattern and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes in lung adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2013; 26:1307–19.
Article22. Nishino M, Klepeis VE, Yeap BY, et al. Histologic and cytomorphologic features of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1462–72.23. Ha SY, Choi SJ, Cho JH, et al. Lung cancer in never-smoker Asian females is driven by oncogenic mutations, most often involving EGFR. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:5465–74.
Article24. Choi IH, Kim DW, Ha SY, Choi YL, Lee HJ, Han J. Analysis of histologic features suspecting anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-expressing pulmonary adenocarcinoma. J Pathol Transl Med. 2015; 49:310–7.
Article25. Sasaki T, Koivunen J, Ogino A, et al. A novel ALK secondary mutation and EGFR signaling cause resistance to ALK kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:6051–60.26. Kim S, Kim TM, Kim DW, et al. Heterogeneity of genetic changes associated with acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:415–22.27. Kuo YW, Wu SG, Ho CC, Shih JY. Good response to gefitinib in lung adenocarcinoma harboring coexisting EML4-ALK fusion gene and EGFR mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:2039–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of EGFR and KRAS Mutation by Pyrosequencing Analysis in Cytologic Samples of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- A case of concomitant EGFR/ALK alteration against a mutated EGFR background in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma
- Clinical Features Reflect Exon Sites of EGFR Mutations in Patients with Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- Mutation-Driven Immune Microenvironments in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Unrevealing Patterns through Cluster Analysis
- Histologic Features of ALK-Expressing Adenocarciomas of the Lung