Int J Stem Cells.
2016 May;9(1):3-8. 10.15283/ijsc.2016.9.1.3.
SoxD Transcription Factors: Multifaceted Players of Neural Development
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Life Science, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. jkim1964@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2164155
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc.2016.9.1.3
Abstract
- SoxD transcription factor subfamily includes three members, Sox5, Sox6, and Sox13. Like other Sox genes, they contain the High-Mobility-Group (HMG) box as the DNA binding domain but in addition feature the subgroup-specific leucine zipper motif. SoxD genes are expressed in diverse cell types in multiple organs during embryogenesis and in adulthood. Among the cells expressing them are those present in the developing nervous system including neural stem (or progenitor) cells as well as differentiating neurons and oligodendrocytes. SoxD transcription factors do not contain distinct activator or repressor domain, and they are believed to function in modulation of other transcription factors in promoter- specific manners. This brief review article will attempt to summarize the latest studies on the function of SoxD genes in embryogenesis with a particular emphasis on the regulation of neural development.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. She ZY, Yang WX. SOX family transcription factors involved in diverse cellular events during development. Eur J Cell Biol. 2015; 94:547–563. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2015.08.002. PMID: 26340821.
Article2. Lefebvre V. The SoxD transcription factors--Sox5, Sox6, and Sox13--are key cell fate modulators. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010; 42:429–432. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.016. PMCID: 2826538.
Article3. Morales AV, Perez-Alcala S, Barbas JA. Dynamic Sox5 protein expression during cranial ganglia development. Dev Dyn. 2007; 236:2702–2707. DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.21282. PMID: 17685482.
Article4. Perez-Alcala S, Nieto MA, Barbas JA. LSox5 regulates RhoB expression in the neural tube and promotes generation of the neural crest. Development. 2004; 131:4455–4465. DOI: 10.1242/dev.01329. PMID: 15306568.
Article5. Stolt CC, Lommes P, Hillgärtner S, Wegner M. The transcription factor Sox5 modulates Sox10 function during melanocyte development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008; 36:5427–5440. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn527. PMID: 18703590. PMCID: 2553580.
Article6. Tanaka S, Suto A, Iwamoto T, Kashiwakuma D, Kagami S, Suzuki K, Takatori H, Tamachi T, Hirose K, Onodera A, Suzuki J, Ohara O, Yamashita M, Nakayama T, Nakajima H. Sox5 and c-Maf cooperatively induce Th17 cell differentiation via RORγt induction as downstream targets of Stat3. J Exp Med. 2014; 211:1857–1874. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20130791. PMID: 25073789. PMCID: 4144730.
Article7. Hagiwara N. Sox6, jack of all trades: a versatile regulatory protein in vertebrate development. Dev Dyn. 2011; 240:1311–1321. DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.22639. PMID: 21495113. PMCID: 3092843.
Article8. Wang Y, Bagheri-Fam S, Harley VR. SOX13 is up-regulated in the developing mouse neuroepithelium and identifies a sub-population of differentiating neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2005; 157:201–208. DOI: 10.1016/j.devbrainres.2004.12.010. PMID: 15896852.
Article9. Roose J, Korver W, Oving E, Wilson A, Wagenaar G, Markman M, Lamers W, Clevers H. High expression of the HMG box factor sox-13 in arterial walls during embryonic development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998; 26:469–476. DOI: 10.1093/nar/26.2.469. PMID: 9421502. PMCID: 147262.
Article10. Melichar HJ, Narayan K, Der SD, Hiraoka Y, Gardiol N, Jeannet G, Held W, Chambers CA, Kang J. Regulation of gammadelta versus alphabeta T lymphocyte differentiation by the transcription factor SOX13. Science. 2007; 315:230–233. DOI: 10.1126/science.1135344. PMID: 17218525.
Article11. Smits P, Li P, Mandel J, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Behringer RR, de Crombrugghe B, Lefebvre V. The transcription factors L-Sox5 and Sox6 are essential for cartilage formation. Dev Cell. 2001; 1:277–290. DOI: 10.1016/S1534-5807(01)00003-X. PMID: 11702786.
Article12. Ikeda T, Kawaguchi H, Kamekura S, Ogata N, Mori Y, Nakamura K, Ikegawa S, Chung UI. Distinct roles of Sox5, Sox6, and Sox9 in different stages of chondrogenic differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab. 2005; 23:337–340. DOI: 10.1007/s00774-005-0610-y. PMID: 16133682.
Article13. Akiyama H, Lefebvre V. Unraveling the transcriptional regulatory machinery in chondrogenesis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2011; 29:390–395. DOI: 10.1007/s00774-011-0273-9. PMID: 21594584. PMCID: 3354916.
Article14. Liu CF, Lefebvre V. The transcription factors SOX9 and SOX5/SOX6 cooperate genome-wide through super-enhancers to drive chondrogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43:8183–8203. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv688. PMID: 26150426. PMCID: 4787819.
Article15. Cantù C, Ierardi R, Alborelli I, Fugazza C, Cassinelli L, Piconese S, Bosè F, Ottolenghi S, Ferrari G, Ronchi A. Sox6 enhances erythroid differentiation in human erythroid progenitors. Blood. 2011; 117:3669–3679. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-282350. PMID: 21263153.
Article16. Quiat D, Voelker KA, Pei J, Grishin NV, Grange RW, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Concerted regulation of myofiber-specific gene expression and muscle performance by the transcriptional repressor Sox6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:10196–10201. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1107413108. PMID: 21633012. PMCID: 3121857.
Article17. Cohen-Barak O, Yi Z, Hagiwara N, Monzen K, Komuro I, Brilliant MH. Sox6 regulation of cardiac myocyte development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003; 31:5941–5948. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg807. PMID: 14530442. PMCID: 219484.
Article18. Leone DP, Srinivasan K, Chen B, Alcamo E, McConnell SK. The determination of projection neuron identity in the developing cerebral cortex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008; 18:28–35. DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.05.006. PMID: 18508260. PMCID: 2483251.
Article19. Lai T, Jabaudon D, Molyneaux BJ, Azim E, Arlotta P, Menezes JR, Macklis JD. SOX5 controls the sequential generation of distinct corticofugal neuron subtypes. Neuron. 2008; 57:232–247. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.12.023. PMID: 18215621.
Article20. Kwan KY, Lam MM, Krsnik Z, Kawasawa YI, Lefebvre V, Sestan N. SOX5 postmitotically regulates migration, post-migratory differentiation, and projections of subplate and deep-layer neocortical neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:16021–16026. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806791105. PMID: 18840685. PMCID: 2572944.
Article21. Azim E, Jabaudon D, Fame RM, Macklis JD. SOX6 controls dorsal progenitor identity and interneuron diversity during neocortical development. Nat Neurosci. 2009; 12:1238–1247. DOI: 10.1038/nn.2387. PMID: 19657336. PMCID: 2903203.
Article22. Batista-Brito R, Rossignol E, Hjerling-Leffler J, Denaxa M, Wegner M, Lefebvre V, Pachnis V, Fishell G. The cell-intrinsic requirement of Sox6 for cortical interneuron development. Neuron. 2009; 63:466–481. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.08.005. PMID: 19709629. PMCID: 2773208.
Article23. Panman L, Papathanou M, Laguna A, Oosterveen T, Volakakis N, Acampora D, Kurtsdotter I, Yoshitake T, Kehr J, Joodmardi E, Muhr J, Simeone A, Ericson J, Perlmann T. Sox6 and Otx2 control the specification of substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. Cell Rep. 2014; 8:1018–1025. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.016. PMID: 25127144.
Article24. Baroti T, Schillinger A, Wegner M, Claus Stolt C. Sox13 functionally complements the related Sox5 and Sox6 as important developmental modulators in mouse spinal cord oligodendrocytes. J Neurochem. 2015; DOI: 10.1111/jnc.13414. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 26525805.
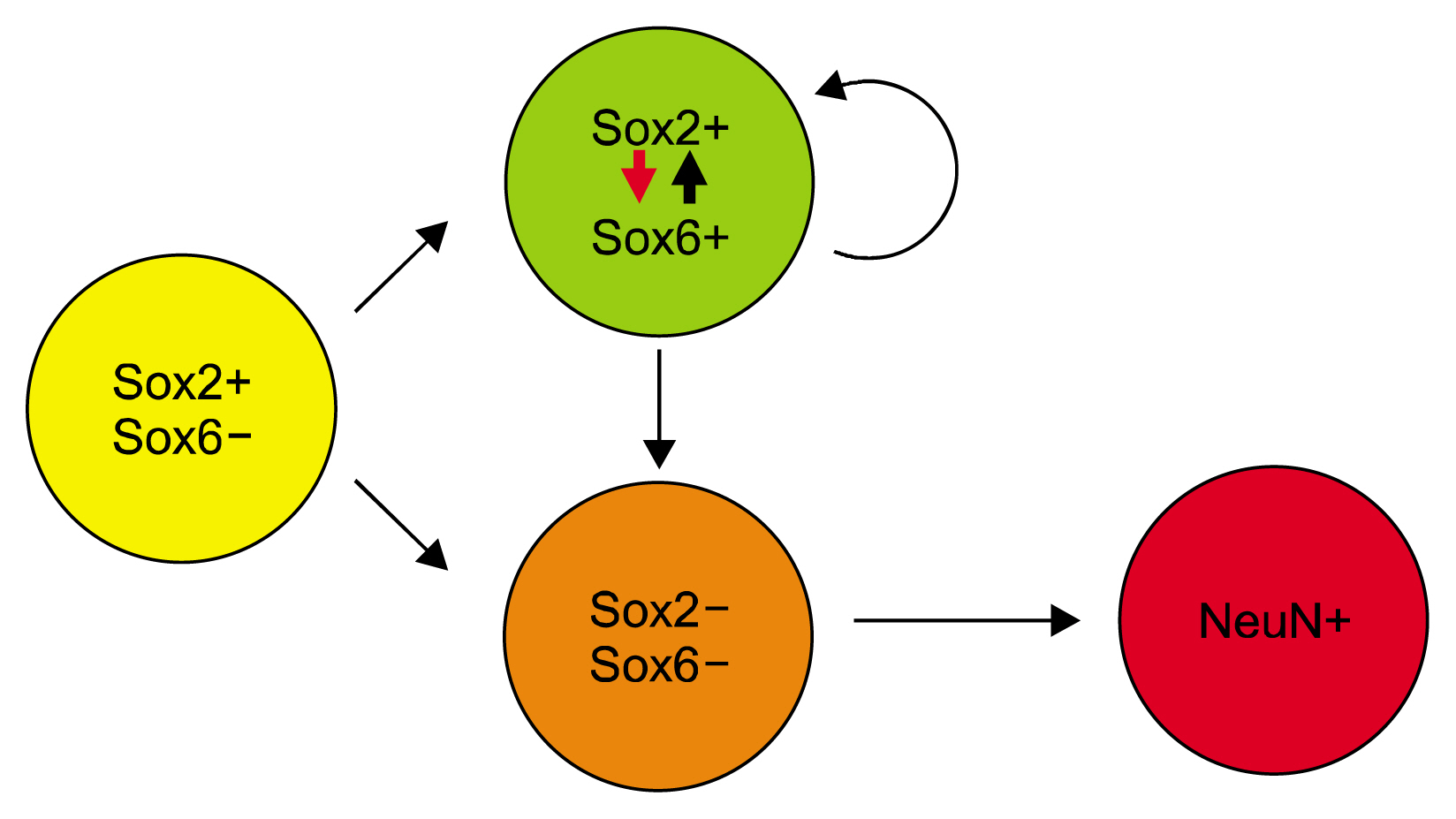
Article25. Lee KE, Seo J, Shin J, Ji EH, Roh J, Kim JY, Sun W, Muhr J, Lee S, Kim J. Positive feedback loop between Sox2 and Sox6 inhibits neuronal differentiation in the developing central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:2794–2799. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1308758111. PMID: 24501124. PMCID: 3932859.
Article26. Quiroga AC, Stolt CC, Diez del Corral R, Dimitrov S, Pérez-Alcalá S, Sock E, Barbas JA, Wegner M, Morales AV. Sox5 controls dorsal progenitor and interneuron specification in the spinal cord. Dev Neurobiol. 2015; 75:522–538. DOI: 10.1002/dneu.22240.
Article27. Stolt CC, Schlierf A, Lommes P, Hillgärtner S, Werner T, Kosian T, Sock E, Kessaris N, Richardson WD, Lefebvre V, Wegner M. SoxD proteins influence multiple stages of oligodendrocyte development and modulate SoxE protein function. Dev Cell. 2006; 11:697–709. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.08.011. PMID: 17084361.
Article28. Sarkar A, Hochedlinger K. The sox family of transcription factors: versatile regulators of stem and progenitor cell fate. Cell Stem Cell. 2013; 12:15–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.12.007. PMID: 23290134. PMCID: 3608206.
Article29. Bylund M, Andersson E, Novitch BG, Muhr J. Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1-3 activity. Nat Neurosci. 2003; 6:1162–1168. DOI: 10.1038/nn1131. PMID: 14517545.
Article30. Nordin K, LaBonne C. Sox5 Is a DNA-binding cofactor for BMP R-Smads that directs target specificity during patterning of the early ectoderm. Dev Cell. 2014; 31:374–382. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.10.003. PMID: 25453832. PMCID: 4255363.
Article31. Iguchi H, Urashima Y, Inagaki Y, Ikeda Y, Okamura M, Tanaka T, Uchida A, Yamamoto TT, Kodama T, Sakai J. SOX6 suppresses cyclin D1 promoter activity by interacting with beta-catenin and histone deacetylase 1, and its down-regulation induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:19052–19061. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M700460200. PMID: 17412698.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sox9 regulates development of neural crest and otic placode in a time- and dose-dependent fashion
- The Comparison of Psychological Characteristics between Korean and Japanese Women Pro-Basketball Players
- Go and the Brain: Cognitive and Neural Impacts of Training
- Comparisons of dental arches and crowdings between musical wind-instrument players groups and non-wind instrument players group
- Musculoskeletal Disorders and Related Factors of Symphony Orchestra Players