Yonsei Med J.
2015 Sep;56(5):1408-1414. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.5.1408.
Pharmacodynamic Estimate of Propofol-Induced Sedation and Airway Obstruction Effects in Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hanesth@yuhs.ac
- 2Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2163637
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.5.1408
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Sedatives must be carefully titrated for patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) as oversedation may lead to disastrous respiratory outcomes. This study aimed to investigate the relations between the effect-site concentration (Ce) of propofol and sedation and airway obstruction levels in patients with OSAHS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
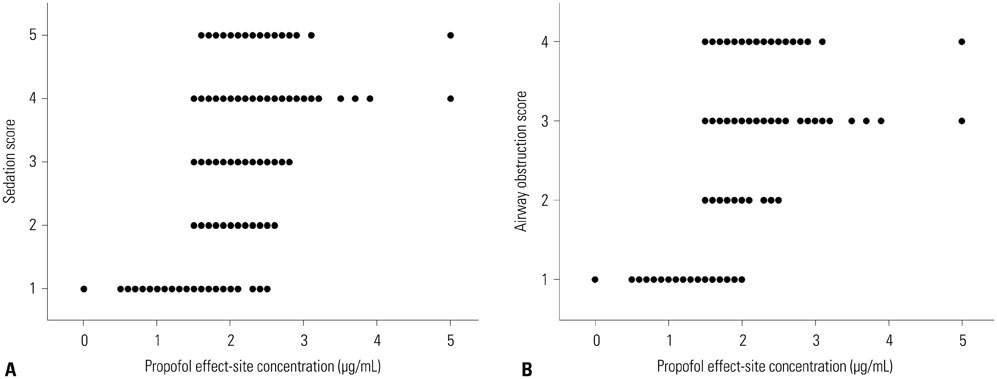
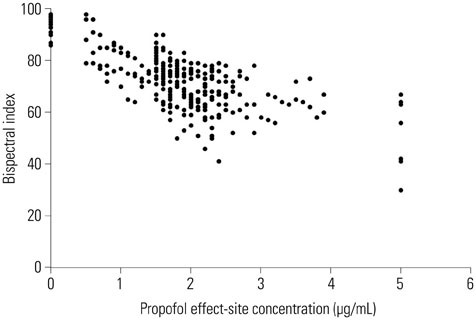
In 25 patients with OSAHS, sedation was induced by 2% propofol using target-controlled infusion. Sedation and airway obstruction levels were assessed using the Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale and a four-category scale, respectively. The relationships between propofol Ce and sedation and airway obstruction were evaluated using a sigmoid Emax model. Pharmacodynamic modeling incorporating covariates was performed using the Nonlinear Mixed Effects Modeling VII software.
RESULTS
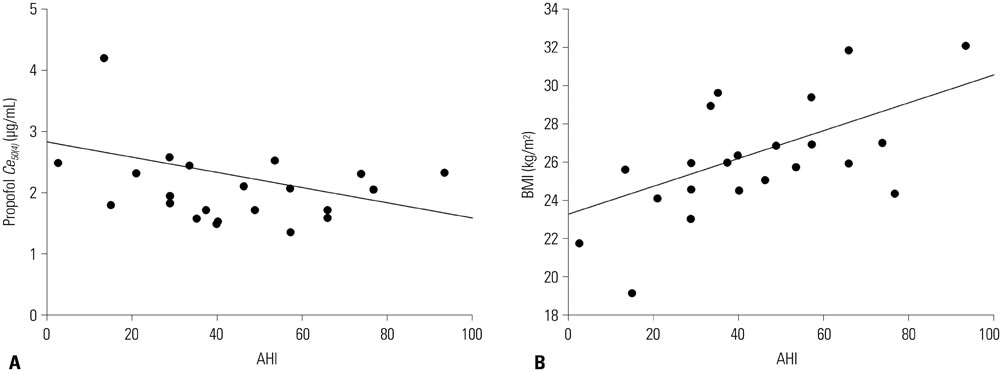
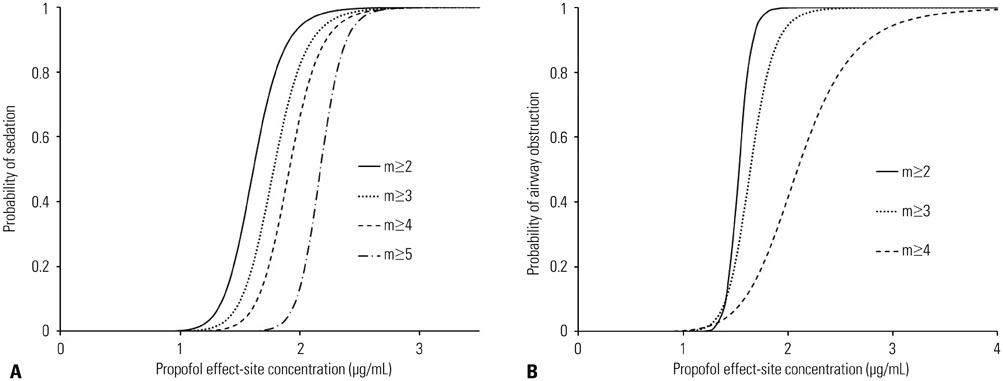
Increased propofol Ce correlated with the depth of sedation and the severity of airway obstruction. Predicted Ce50(m) (Ce associated with 50% probability of an effect> or =m) for sedation scores (m> or =2, 3, 4, and 5) and airway-obstruction scores (m> or =2, 3, and 4) were 1.61, 1.78, 1.91, and 2.17 microg/mL and 1.53, 1.64, and 2.09 microg/mL, respectively. Including the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) as a covariate in the analysis of Ce50(4) for airway obstruction significantly improved the performance of the basic model (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
The probability of each sedation and airway obstruction score was properly described using a sigmoid Emax model with a narrow therapeutic range of propofol Ce in OSAHS patients. Patients with high AHI values need close monitoring to ensure that airway patency is maintained during propofol sedation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Airway Obstruction/*drug therapy
Anesthesia
Anesthetics, Intravenous/blood/pharmacokinetics/*pharmacology
Female
Humans
Hypnotics and Sedatives/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Male
Middle Aged
Probability
Propofol/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Sleep Apnea, Obstructive/physiopathology
Anesthetics, Intravenous
Hypnotics and Sedatives
Propofol
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Simulation Study of Propofol Effect-Site Concentration for Appropriate Sedation in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Brain MRI: Pharmacodynamic Analysis
Se Hee Na, Young Song, So Yeon Kim, Hyo-Jin Byon, Hwan-Ho Jung, Dong Woo Han
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(6):1216-1221. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.6.1216.
Reference
-
1. Skues MA, Prys-Roberts C. The pharmacology of propofol. J Clin Anesth. 1989; 1:387–400.
Article2. Fábregas N, Rapado J, Gambús PL, Valero R, Carrero E, Salvador L, et al. Modeling of the sedative and airway obstruction effects of propofol in patients with Parkinson disease undergoing stereotactic surgery. Anesthesiology. 2002; 97:1378–1386.
Article3. Eastwood PR, Platt PR, Shepherd K, Maddison K, Hillman DR. Collapsibility of the upper airway at different concentrations of propofol anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2005; 103:470–477.
Article4. Sundaram S, Bridgman SA, Lim J, Lasserson TJ. Surgery for obstructive sleep apnoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; CD001004.5. Benumof JL. Creation of observational unit may decrease sleep apnea risk. APSF Newsletter. 2002; 17:39.6. Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 165:1217–1239.7. Schnider TW, Minto CF, Gambus PL, Andresen C, Goodale DB, Shafer SL, et al. The influence of method of administration and covariates on the pharmacokinetics of propofol in adult volunteers. Anesthesiology. 1998; 88:1170–1182.
Article8. Schnider TW, Minto CF, Shafer SL, Gambus PL, Andresen C, Goodale DB, et al. The influence of age on propofol pharmacodynamics. Anesthesiology. 1999; 90:1502–1516.
Article9. Chernik DA, Gillings D, Laine H, Hendler J, Silver JM, Davidson AB, et al. Validity and reliability of the Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale: study with intravenous midazolam. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1990; 10:244–251.10. Collop NA, Anderson WM, Boehlecke B, Claman D, Goldberg R, Gottlieb DJ, et al. Clinical guidelines for the use of unattended portable monitors in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in adult patients. Portable Monitoring Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J Clin Sleep Med. 2007; 3:737–747.11. Dhonneur G, Combes X, Leroux B, Duvaldestin P. Postoperative obstructive apnea. Anesth Analg. 1999; 89:762–767.
Article12. Chung F, Crago RR. Sleep apnoea syndrome and anaesthesia. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1982; 29:439–445.
Article13. Krauss B, Green SM. Sedation and analgesia for procedures in children. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:938–945.
Article14. Jung M, Hofmann C, Kiesslich R, Brackertz A. Improved sedation in diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: propofol is an alternative to midazolam. Endoscopy. 2000; 32:233–238.
Article15. Olmos M, Ballester JA, Vidarte MA, Elizalde JL, Escobar A. The combined effect of age and premedication on the propofol requirements for induction by target-controlled infusion. Anesth Analg. 2000; 90:1157–1161.
Article16. McClune S, McKay AC, Wright PM, Patterson CC, Clarke RS. Synergistic interaction between midazolam and propofol. Br J Anaesth. 1992; 69:240–245.
Article17. Marsh B, White M, Morton N, Kenny GN. Pharmacokinetic model driven infusion of propofol in children. Br J Anaesth. 1991; 67:41–48.
Article18. Rabelo FA, Küpper DS, Sander HH, Fernandes RM, Valera FC. Polysomnographic evaluation of propofol-induced sleep in patients with respiratory sleep disorders and controls. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:2300–2305.
Article19. Rabelo FA, Braga A, Küpper DS, De Oliveira JA, Lopes FM, de Lima Mattos PL, et al. Propofol-induced sleep: polysomnographic evaluation of patients with obstructive sleep apnea and controls. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 142:218–224.20. Kyzer S, Charuzi I. Obstructive sleep apnea in the obese. World J Surg. 1998; 22:998–1001.
Article21. Li QY, Huang SG, Li M, Liu JL, Wan HY. BMI is an independent risk factor for snoring in Chinese women aged over 30 years. Sleep Breath. 2009; 13:289–293.
Article22. Masui K, Upton RN, Doufas AG, Coetzee JF, Kazama T, Mortier EP, et al. The performance of compartmental and physiologically based recirculatory pharmacokinetic models for propofol: a comparison using bolus, continuous, and target-controlled infusion data. Anesth Analg. 2010; 111:368–379.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anesthetic management for simultaneous drug-induced sleep endoscopy and maxillomandibular advancement in a patient with obstructive sleep apnea
- Upper airway studies in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- Two Cases of Pediatric Obstructive Hypoventilation Managed with Upper Airway Surgery
- Surgical Management for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome
- The Role of Endothelin-1 in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Pulmonary Hypertension