Yonsei Med J.
2015 Sep;56(5):1328-1337. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.5.1328.
Influence of Parent Artery Segmentation and Boundary Conditions on Hemodynamic Characteristics of Intracranial Aneurysms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Cerebrovascular Center, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ybkim69@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2163625
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.5.1328
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to explore the influence of segmentation of the upstream and downstream parent artery and hemodynamic boundary conditions (BCs) on the evaluated hemodynamic factors for the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis of intracranial aneurysms.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
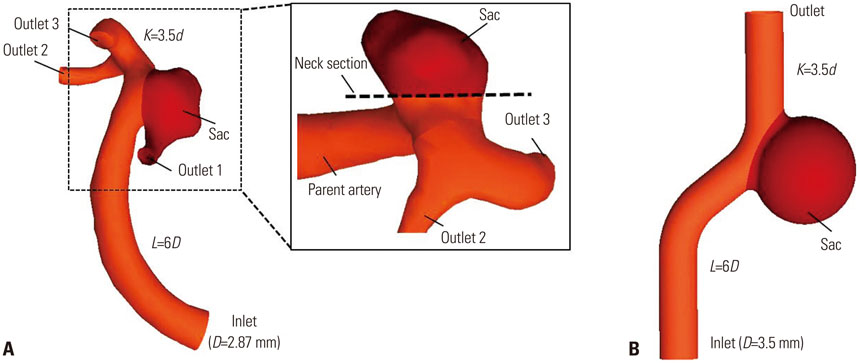
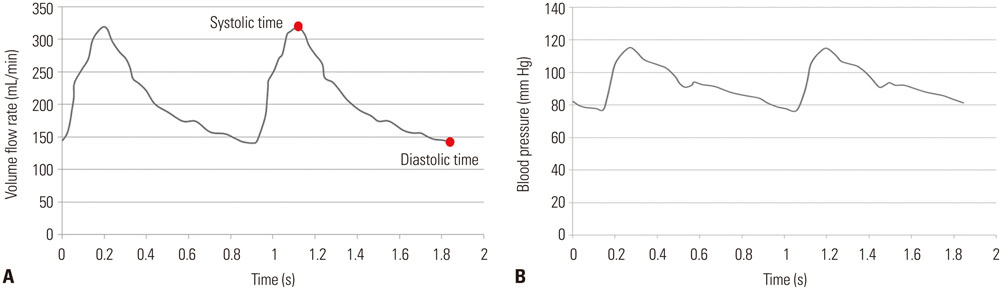
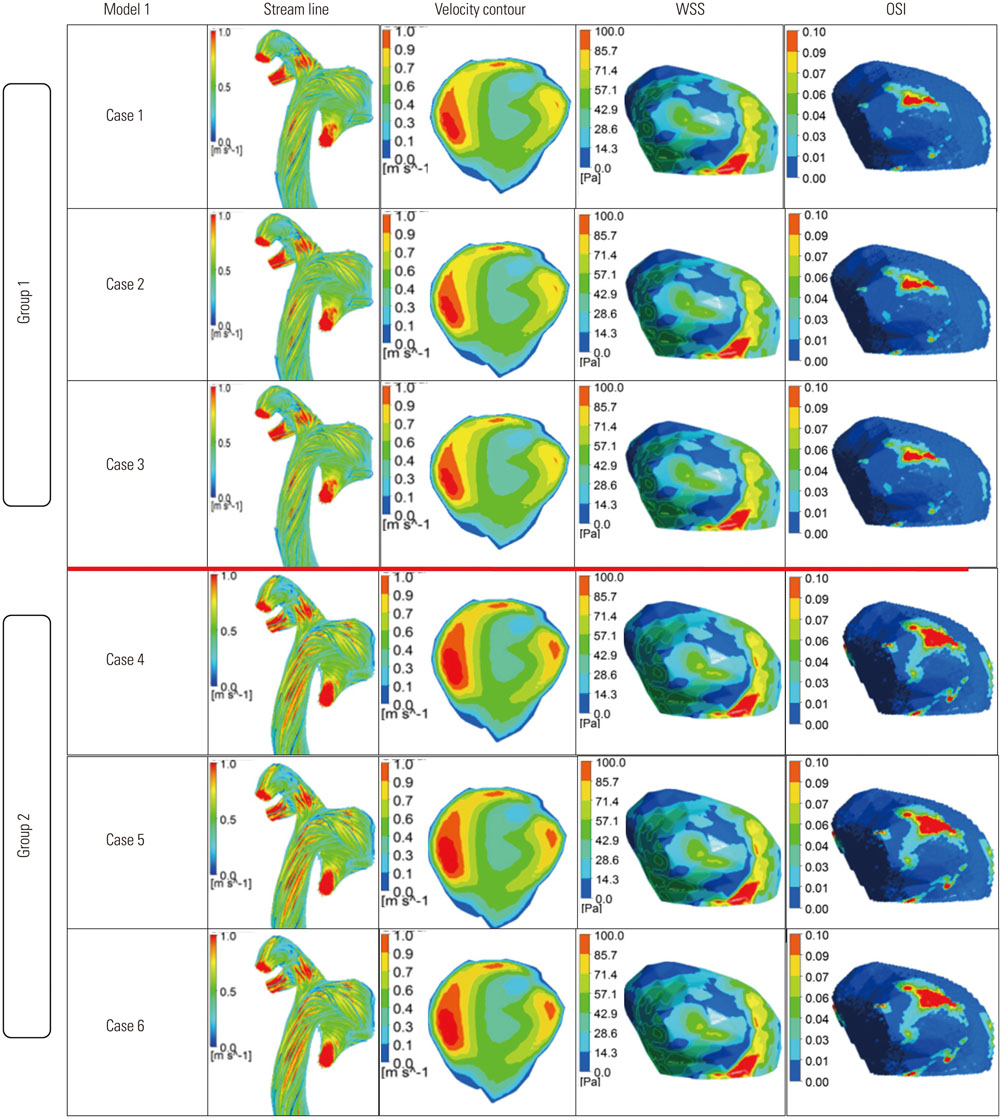
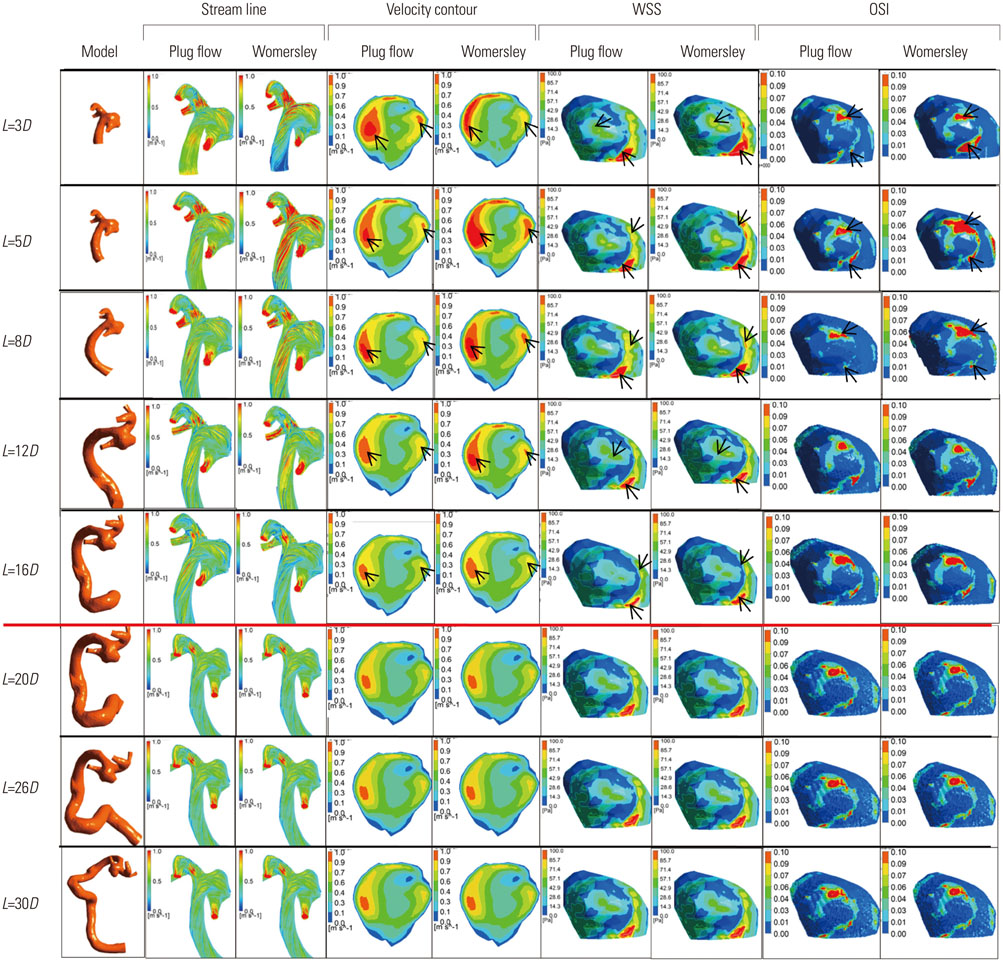
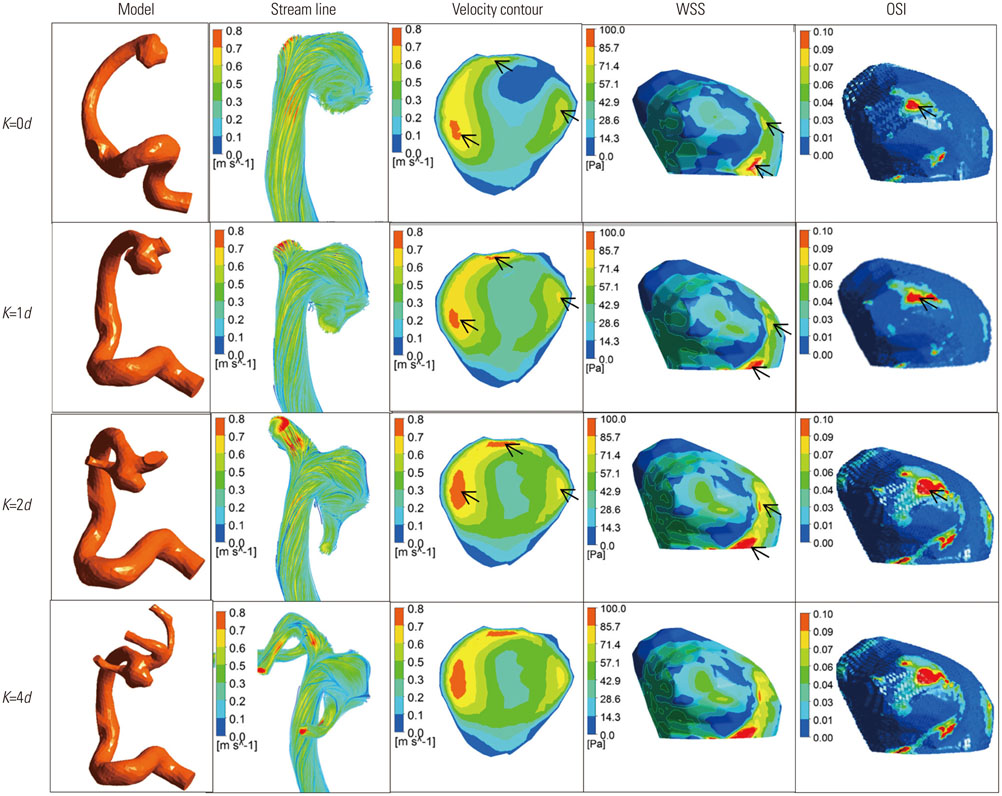
Three dimensional patient-specific aneurysm models were analyzed by applying various combinations of inlet and outlet BCs. Hemodynamic factors such as velocity pattern, streamline, wall shear stress, and oscillatory shear index at the systolic time were visualized and compared among the different cases.
RESULTS
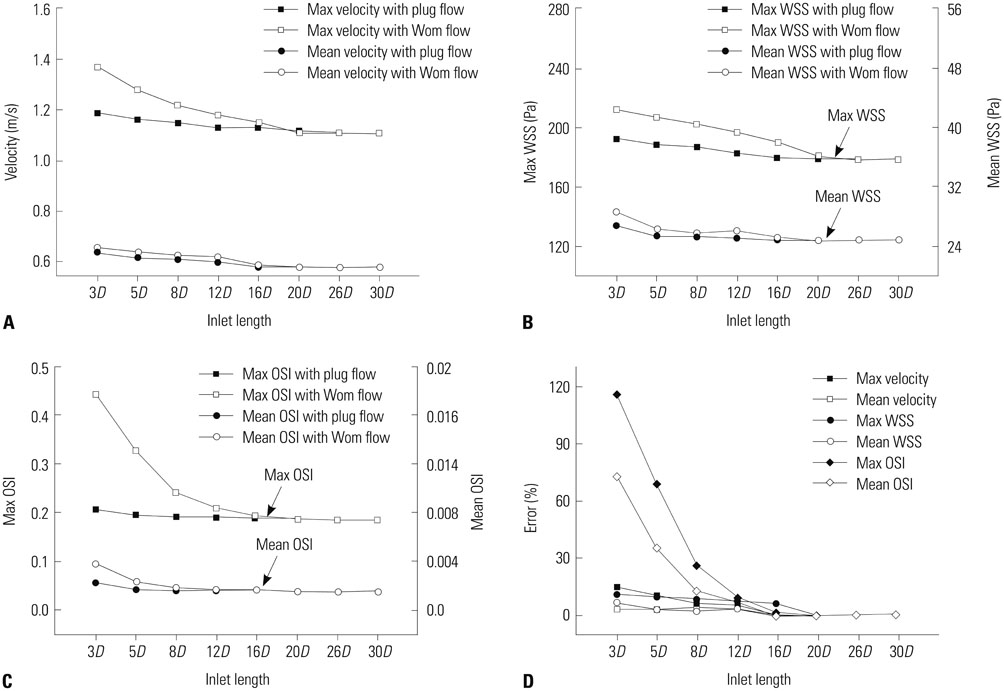
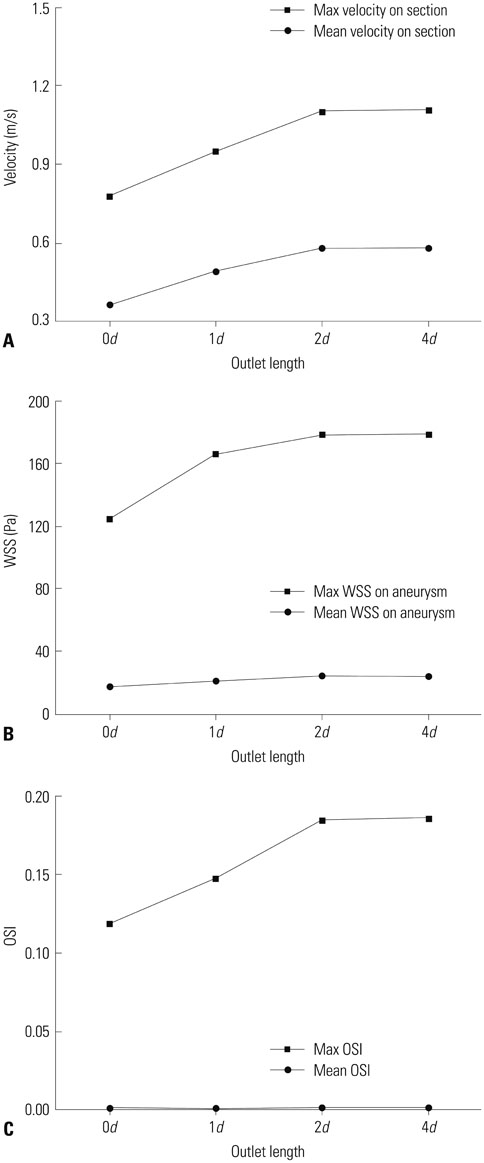
Hemodynamic factors were significantly affected by the inlet BCs while there was little influence of the outlet BCs. When the inlet length was relatively short, different inlet BCs showed different hemodynamic factors and the calculated hemodynamic factors were also dependent on the inlet length. However, when the inlet length (L) was long enough (L>20D, where D is the diameter of inlet section), the hemodynamic factors became similar regardless of the inlet BCs and lengths. The error due to different inlet BCs was negligible. The effect of the outlet length on the hemodynamic factors was similar to that of the inlet length.
CONCLUSION
Simulated hemodynamic factors are highly sensitive to inlet BCs and upstream parent artery segmentation. The results of this work can provide an insight into how to build models and to apply BCs for more accurate estimation of hemodynamic factors from CFD simulations of intracranial aneurysms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim YB, Hong CK, Chung J, Joo JY, Huh SK. Long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes of wrap-clipping strategies for unclippable cerebral aneurysms. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:401–409.2. Lim YC, Kim CH, Kim YB, Joo JY, Shin YS, Chung J. Incidence and risk factors for rebleeding during cerebral angiography for ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Yonsei Med J. 2015; 56:403–409.3. Cebral JR, Castro MA, Burgess JE, Pergolizzi RS, Sheridan MJ, Putman CM. Characterization of cerebral aneurysms for assessing risk of rupture by using patient-specific computational hemodynamics models. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:2550–2559.4. Hassan T, Timofeev EV, Saito T, Shimizu H, Ezura M, Matsumoto Y, et al. A proposed parent vessel geometry-based categorization of saccular intracranial aneurysms: computational flow dynamics analysis of the risk factors for lesion rupture. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103:662–680.
Article5. Shojima M, Oshima M, Takagi K, Torii R, Hayakawa M, Katada K, et al. Magnitude and role of wall shear stress on cerebral aneurysm: computational fluid dynamic study of 20 middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Stroke. 2004; 35:2500–2505.
Article6. Steinman DA, Milner JS, Norley CJ, Lownie SP, Holdsworth DW. Image-based computational simulation of flow dynamics in a giant intracranial aneurysm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:559–566.7. Zakaria H, Robertson AM, Kerber CW. A parametric model for studies of flow in arterial bifurcations. Ann Biomed Eng. 2008; 36:1515–1530.8. Zeng Z, Kallmes DF, Durka MJ, Ding Y, Lewis D, Kadirvel R, et al. Sensitivity of CFD based hemodynamic results in rabbit aneurysm models to idealizations in surrounding vasculature. J Biomech Eng. 2010; 132:091009.9. Baek H, Jayaraman MV, Richardson PD, Karniadakis GE. Flow instability and wall shear stress variation in intracranial aneurysms. J R Soc Interface. 2010; 7:967–988.
Article10. Cebral JR, Castro MA, Appanaboyina S, Putman CM, Millan D, Frangi AF. Efficient pipeline for image-based patient-specific analysis of cerebral aneurysm hemodynamics: technique and sensitivity. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005; 24:457–467.
Article11. Castro MA, Putman CM, Cebral JR. Computational fluid dynamics modeling of intracranial aneurysms: effects of parent artery segmentation on intra-aneurysmal hemodynamics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1703–1709.12. Reymond P, Merenda F, Perren F, Rüfenacht D, Stergiopulos N. Validation of a one-dimensional model of the systemic arterial tree. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009; 297:H208–H222.13. Radaelli AG, Augsburger L, Cebral JR, Ohta M, Rüfenacht DA, Balossino R, et al. Reproducibility of haemodynamical simulations in a subject-specific stented aneurysm model--a report on the Virtual Intracranial Stenting Challenge 2007. J Biomech. 2008; 41:2069–2081.
Article14. Pereira VM, Brina O, Marcos Gonzales A, Narata AP, Bijlenga P, Schaller K, et al. Evaluation of the influence of inlet boundary conditions on computational fluid dynamics for intracranial aneurysms: a virtual experiment. J Biomech. 2013; 46:1531–1539.15. Marzo A, Singh P, Reymond P, Stergiopulos N, Patel U, Hose R. Influence of inlet boundary conditions on the local haemodynamics of intracranial aneurysms. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2009; 12:431–444.
Article16. Cebral JR, Castro MA, Soto O, Löhner R, Alperin N. Blood flow models of the circle of Willis from magnetic resonance data. J Eng Math. 2003; 47:369–386.17. Lu G, Huang L, Zhang XL, Wang SZ, Hong Y, Hu Z, et al. Influence of hemodynamic factors on rupture of intracranial aneurysms: patient-specific 3D mirror aneurysms model computational fluid dynamics simulation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1255–1261.
Article18. Kono K, Fujimoto T, Shintani A, Terada T. Hemodynamic characteristics at the rupture site of cerebral aneurysms: a case study. Neurosurgery. 2012; 71:E1202–E1208.19. Taylor CA, Hughes TJR, Zarins CK. Finite element modeling of blood flow in arteries. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 1998; 158:155–196.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of Distal Intracranial Catheters for Better Working View of Cerebral Aneurysms Hidden by Parent Artery or Its Branches: A Technical Note
- Multiple Cerebral Aneurysms on Single Parent Artery
- Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms Associated with Multiplication of Anterior Communicating Artery
- Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms: A Case Report of Patient with Nine Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms
- Comparison of CT Angiography and Digital Subtraction Angiography in the Evaluation of Intracranial Aneurysmal Neck