Korean J Neurotrauma.
2016 Apr;12(1):11-17. 10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.1.11.
Early Decompression of Acute Subdural Hematoma for Postoperative Neurological Improvement: A Single Center Retrospective Review of 10 Years
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Guro Teun Teun Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. nsyoons@gmail.com
- KMID: 2163009
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.1.11
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
This study was conducted to investigate survival related factors, as well as to evaluate the effects of early decompression on acute subdural hematoma (ASDH).
METHODS
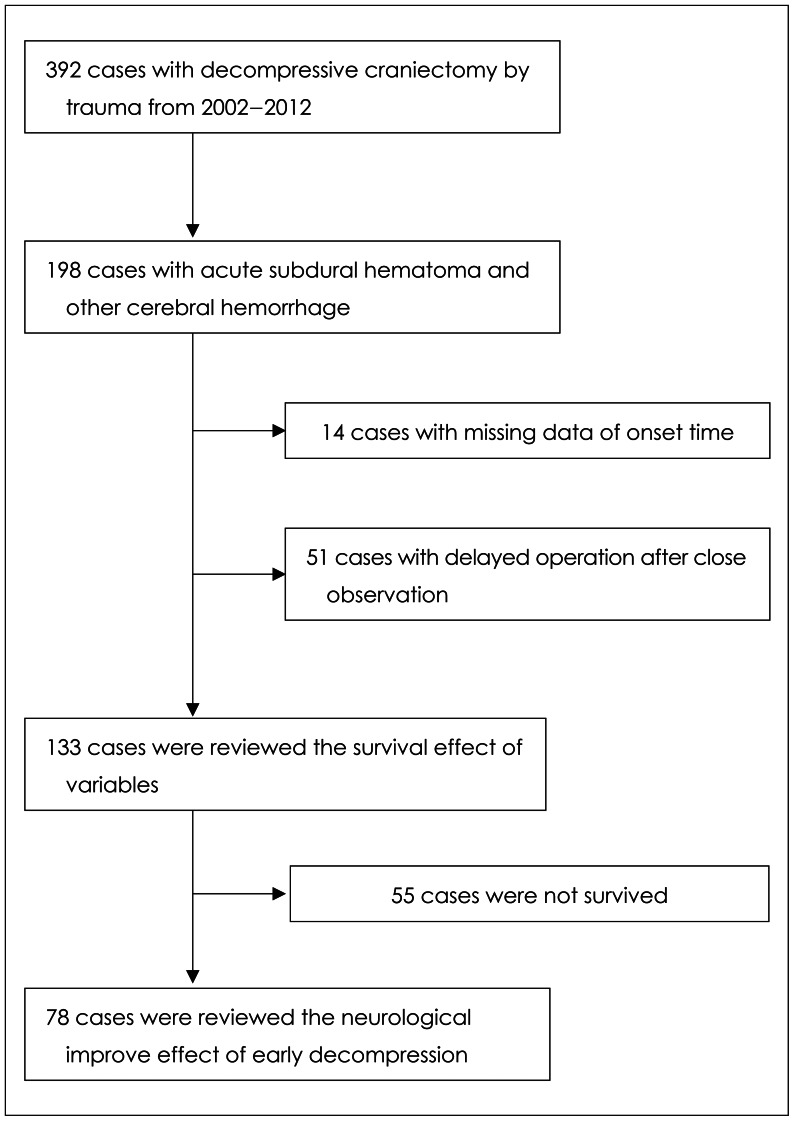
We retrospectively reviewed cases of decompressive craniectomy (DC) for decade. In total, 198 cases of DC involved ASDH were available for review, and 65 cases were excluded due to missing data on onset time and a delayed operation after closed observation with medical care. Finally, 133 cases of DC with ASDH were included in this study, and various factors including the time interval between trauma onset and operation were evaluated.
RESULTS
In the present study, survival rate after DC in patients with ASDH was shown to be related to patient age (50 years old, p=0.012), brain compression ratio (p=0.042) and brain stem compression (p=0.020). Sex, preoperative mental status, and time interval between trauma onset and operation were not related with survival rate. Among those that survived (n=78), improvements in Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of more than three points, compared to preoperative measurement, were more frequently observed among the early (less than 3 hours between trauma onset and operation) decompressed cases (p=0.013). However, improvements of more than 4 or 5 points on the GCS were not affected by early decompression.
CONCLUSION
Early decompression of ASDH was not correlated with survival rate, but was related with neurological improvement (more than three points on the GCS). Accordingly, early decompression in ASDH, if indicated, may be of particular benefit.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aarabi B, Hesdorffer DC, Ahn ES, Aresco C, Scalea TM, Eisenberg HM. Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant swelling due to severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 2006; 104:469–467. PMID: 16619648.
Article2. Akins PT, Guppy KH. Sinking skin flaps, paradoxical herniation, and external brain tamponade: a review of decompressive craniectomy management. Neurocrit Care. 2008; 9:269–276. PMID: 18064408.
Article3. Albanèse J, Leone M, Alliez JR, Kaya JM, Antonini F, Alliez B, et al. Decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury: evaluation of the effects at one year. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31:2535–2538. PMID: 14530763.
Article4. Brain Trauma Foundation. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Congress of Neurological Surgeons. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2007; 24(Suppl 1):S1–S106.5. Bullock MR, Chesnut R, Ghajar J, Gordon D, Hartl R, Newell DW, et al. Surgical management of acute subdural hematomas. Neurosurgery. 2006; 58(3 Suppl):S16–S24. discussion Si-SivPMID: 16710968.
Article6. Cavuşoğ lu H, Kaya RA, Türkmenoğlu ON, Aydin Y. Value of early unilateral decompressive craniectomy in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2010; 16:119–124. PMID: 20517764.7. Cianchi G, Bonizzoli M, Zagli G, di Valvasone S, Biondi S, Ciapetti M, et al. Late decompressive craniectomyafter traumatic brain injury: neurological outcome at 6 months after ICU discharge. J Trauma Manag Outcomes. 2012; 6:8. PMID: 22867014.
Article8. Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Arabi YM, Davies AR, D'Urso P, et al. Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1493–1502. PMID: 21434843.
Article9. Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Wolfe R, Ponsford J, Davies A, et al. Early decompressive craniectomy for patients with severe traumatic brain injury and refractory intracranial hypertension--a pilot randomized trial. J Crit Care. 2008; 23:387–393. PMID: 18725045.
Article10. Csókay A, Emelifeonwu JA, Fügedi L, Valálik I, Láng J. The importance of very early decompressive craniectomy as a prevention to avoid the sudden increase of intracranial pressure in children with severe traumatic brain swelling (retrospective case series). Childs Nerv Syst. 2012; 28:441–444. PMID: 22207401.
Article11. Eberle BM, Schnüriger B, Inaba K, Gruen JP, Demetriades D, Belzberg H. Decompressive craniectomy: surgical control of traumatic intracranial hypertension may improve outcome. Injury. 2010; 41:894–898. PMID: 21574279.
Article12. Figaji AA, Fieggen AG, Peter JC. Early decompressive craniotomy in children with severe traumatic brain injury. Childs Nerv Syst. 2003; 19:666–673. PMID: 12908115.
Article13. Gaab MR, Rittierodt M, Lorenz M, Heissler HE. Traumatic brain swelling and operative decompression: a prospective investigation. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 1990; 51:326–328. PMID: 2089928.
Article14. Guerra WK, Gaab MR, Dietz H, Mueller JU, Piek J, Fritsch MJ. Surgical decompression for traumatic brain swelling: indications and results. J Neurosurg. 1999; 90:187–196. PMID: 9950487.
Article15. Helmy A, Vizcaychipi M, Gupta AK. Traumatic brain injury: intensive care management. Br J Anaesth. 2007; 99:32–42. PMID: 17556349.
Article16. Hutchinson PJ, Menon DK, Kirkpatrick PJ. Decompressive craniectomy in traumatic brain injury--time for randomised trials? Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005; 147:1–3. PMID: 15614466.17. Jiang JY, Xu W, Li WP, Xu WH, Zhang J, Bao YH, et al. Efficacy of standard trauma craniectomy for refractory intracranial hypertension with severe traumatic brain injury: a multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled study. J Neurotrauma. 2005; 22:623–628. PMID: 15941372.
Article18. Juul N, Morris GF, Marshall SB, Marshall LF. Intracranial hypertension and cerebral perfusion pressure: influence on neurological deterioration and outcome in severe head injury. The Executive Committee of the International Selfotel Trial. J Neurosurg. 2000; 92:1–6. PMID: 10616075.19. Kim JY, Hyun DK, Yoon SH, Park HS, Kim EY, Park HC, et al. Prediction of postoperative drainage volume and brain expansion of chronic subdural hematoma: supplementary study-clinical study. J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc. 2010; 6:33–37.
Article20. Kunze E, Meixensberger J, Janka M, Sörensen N, Roosen K. Decompressive craniectomy in patients with uncontrollable intracranial hypertension. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 1998; 71:16–18. PMID: 9779131.
Article21. Münch E, Horn P, Schürer L, Piepgras A, Paul T, Schmiedek P. Management of severe traumatic brain injury by decompressive craniectomy. Neurosurgery. 2000; 47:315–322. discussion 322-323PMID: 10942004.
Article22. Marshall LF. Head injury: recent past, present, and future. Neurosurgery. 2000; 47:546–561. PMID: 10981741.
Article23. Marshall LF, Smith RW, Shapiro HM. The outcome with aggressive treatment in severe head injuries. Part I: the significance of intracranial pressure monitoring. J Neurosurg. 1979; 50:20–25. PMID: 758374.24. Meier U, Ahmadi S, Killeen T, Al-Zain FT, Lemcke J. Long-term outcomes following decompressive craniectomy for severe head injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2008; 102:29–31. PMID: 19388283.25. Menon DK. Cerebral protection in severe brain injury: physiological determinants of outcome and their optimisation. Br Med Bull. 1999; 55:226–258. PMID: 10695089.
Article26. Messing-Jünger AM, Marzog J, Wöbker G, Sabel M, Bock WJ. Decompressive craniectomy in severe brain injury. Zentralbl Neurochir. 2003; 64:171–177. PMID: 14634882.
Article27. Miller JD, Becker DP, Ward JD, Sullivan HG, Adams WE, Rosner MJ. Significance of intracranial hypertension in severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 1977; 47:503–516. PMID: 903804.
Article28. Oh CH, Hyun DK, Yoon SH, Park HS, Kim EY, Park HC, et al. The relationship between postoperative drainage volume and brain shifting index in chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc. 2008; 4:70–76.
Article29. Oh CH, Park CO, Hyun DK, Park HC, Yoon SH. Comparative study of outcomes between shunting after cranioplasty and in cranioplasty after shunting in large concave flaccid cranial defect with hydrocephalus. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 44:211–216. PMID: 19096679.
Article30. Piek J. Decompressive surgery in the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002; 8:134–138. PMID: 12386514.
Article31. Polin RS, Shaffrey ME, Bogaev CA, Tisdale N, Germanson T, Bocchicchio B, et al. Decompressive bifrontal craniectomy in the treatment of severe refractory posttraumatic cerebral edema. Neurosurgery. 1997; 41:84–92. discussion 92-94PMID: 9218299.
Article32. Sahuquillo J, Arikan F. Decompressive craniectomy for the treatment of refractory high intracranial pressure in traumatic brain injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006; CD003983. PMID: 16437469.
Article33. Schirmer CM, Ackil AA Jr, Malek AM. Decompressive Craniectomy. Neurocrit Care. 2008; 8:456–470. PMID: 18392785.
Article34. Stiver SI. Complications of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 26:E7. PMID: 19485720.
Article35. Taylor A, Butt W, Rosenfeld J, Shann F, Ditchfield M, Lewis E, et al. A randomized trial of very early decompressive craniectomy in children with traumatic brain injury and sustained intracranial hypertension. Childs Nerv Syst. 2001; 17:154–162. PMID: 11305769.
Article36. Timofeev I, Czosnyka M, Nortje J, Smielewski P, Kirkpatrick P, Gupta A, et al. Effect of decompressive craniectomy on intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal compensation following traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2008; 108:66–73. PMID: 18173312.
Article37. Ucar T, Akyuz M, Kazan S, Tuncer R. Role of decompressive surgery in the management of severe head injuries: prognostic factors and patient selection. J Neurotrauma. 2005; 22:1311–1318. PMID: 16305319.
Article38. Wen L, Wang H, Wang F, Gong JB, Li G, Huang X, et al. A prospective study of early versus late craniectomy after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2011; 25:1318–1324. PMID: 21902550.
Article39. Williams RF, Magnotti LJ, Croce MA, Hargraves BB, Fischer PE, Schroeppel TJ, et al. Impact of decompressive craniectomy on functional outcome after severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma. 2009; 66:1570–1574. discussion 1574-1576PMID: 19509616.
Article40. Woertgen C, Rothoerl RD, Schebesch KM, Albert R. Comparison of craniotomy and craniectomy in patients with acute subdural haematoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2006; 13:718–721. PMID: 16904897.
Article41. Xiao B, Wu FF, Zhang H, Ma YB. A randomized study of urgent computed tomography-based hematoma puncture and aspiration in the emergency department and subsequent evacuation using craniectomy versus craniectomy only. J Neurosurg. 2012; 117:566–573. PMID: 22769066.
Article42. Yang XF, Wen L, Shen F, Li G, Lou R, Liu WG, et al. Surgical complications secondary to decompressive craniectomy in patients with a head injury: a series of 108 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008; 150:1241–1247. discussion 1248PMID: 19005615.
Article43. Yang XJ, Hong GL, Su SB, Yang SY. Complications induced by decompressive craniectomies after traumatic brain injury. Chin J Traumatol. 2003; 6:99–103. PMID: 12659705.44. Yoo DS, Kim DS, Cho KS, Huh PW, Park CK, Kang JK. Ventricular pressure monitoring during bilateral decompression with dural expansion. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91:953–959. PMID: 10584840.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneously Rapid Resolution of Acute Subdural Hemorrhage with Severe Midline Shift
- Intraoperative Development of Contralateral Subdural Hematoma during Evacuation of Acute Subdural Hematoma: Case Report
- Acute-on-chronic subdural hematoma by spinal anesthesia in a patient with undiagnosed chronic subdural hematoma: A case report
- A Study of the Progression from Acute Subdural Hematoma to Chronic Stage Requiring Surgical Treatment
- Two Cases of Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm Complicated by Massive Subdural Hematoma