Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Mar;20(1):44-52. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.1.44.
Improvement of Fat Suppression and Artifact Reduction Using IDEAL Technique in Head and Neck MRI at 3T
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. pengoon@gmail.com
- KMID: 2161369
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.1.44
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To quantitatively and qualitatively compare fat-suppressed MRI quality using iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL) with that using frequency selective fat-suppression (FSFS) T2- and postcontrast T1-weighted fast spin-echo images of the head and neck at 3T.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
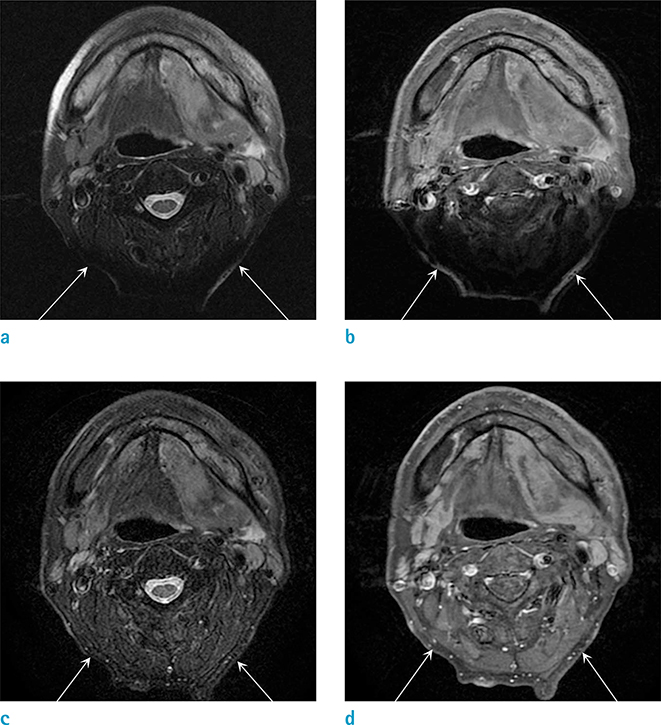
The study was approved by our Institutional Review Board. Prospective MR image analysis was performed in 36 individuals at a single-center. Axial fat suppressed T2- and postcontrast T1-weighted images with IDEAL and FSFS were compared. Visual assessment was performed by two independent readers with respect to; 1) metallic artifacts around oral cavity, 2) susceptibility artifacts around upper airway, paranasal sinus, and head-neck junction, 3) homogeneity of fat suppression, 4) image sharpness, 5) tissue contrast of pathologies and lymph nodes. The signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) for each image sequence were assessed.
RESULTS
Both IDEAL fat suppressed T2- and T1-weighted images significantly reduced artifacts around airway, paranasal sinus, and head-neck junction, and significantly improved homogeneous fat suppression in compared to those using FSFS (P < 0.05 for all). IDEAL significantly decreased artifacts around oral cavity on T2-weighted images (P < 0.05, respectively) and improved sharpness, lesion-to-tissue, and lymph node-to-tissue contrast on T1-weighted images (P < 0.05 for all). The mean SNRs were significantly improved on both T1- and T2-weighted IDEAL images (P < 0.05 for all).
CONCLUSIONS
IDEAL technique improves image quality in the head and neck by reducing artifacts with homogeneous fat suppression, while maintaining a high SNR.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ross MR, Schomer DF, Chappell P, Enzmann DR. MR imaging of head and neck tumors: comparison of T1-weighted contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed images with conventional T2-weighted and fast spin-echo T2-weighted images. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 163:173–178.2. Finkenzeller T, Zorger N, Kuhnel T, et al. Novel application of T1-weighted BLADE sequences with fat suppression compared to TSE in contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging of the neck: cutting-edge images? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 37:660–668.3. Petersilge CA, Lewin JS, Duerk JL, Yoo JU, Ghaneyem AJ. Optimizing imaging parameters for MR evaluation of the spine with titanium pedicle screws. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 166:1213–1218.4. Gerdes CM, Kijowski R, Reeder SB. IDEAL imaging of the musculoskeletal system: robust water fat separation for uniform fat suppression, marrow evaluation, and cartilage imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:W284–W291.5. Chen CA, Lu W, John CT, et al. Multiecho IDEAL gradientecho water-fat separation for rapid assessment of cartilage volume at 1.5 T: initial experience. Radiology. 2009; 252:561–556.6. Kijowski R, Woods MA, Lee KS, et al. Improved fat suppression using multipeak reconstruction for IDEAL chemical shift fat-water separation: application with fast spin echo imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 29:436–442.7. Grayev A, Shimakawa A, Cousins J, Turski P, Brittain J, Reeder S. Improved time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography with IDEAL water-fat separation. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 29:1367–1374.8. Murakami M, Mori H, Kunimatsu A, et al. Postsurgical spinal magnetic resonance imaging with iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2011; 35:16–20.9. Cha JG, Jin W, Lee MH, et al. Reducing metallic artifacts in postoperative spinal imaging: usefulness of IDEAL contrastenhanced T1- and T2-weighted MR imaging--phantom and clinical studies. Radiology. 2011; 259:885–893.10. Ren AJ, Guo Y, Tian SP, Shi LJ, Huang MH. MR imaging of the spine at 3.0T with T2-weighted IDEAL fast recovery fast spin-echo technique. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:44–45.11. Lee JB, Cha JG, Lee MH, Lee YK, Lee EH, Jeon CH. Usefulness of IDEAL T2-weighted FSE and SPGR imaging in reducing metallic artifacts in the postoperative ankles with metallic hardware. Skeletal Radiol. 2013; 42:239–247.12. Aoki T, Yamashita Y, Oki H, et al. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and leastsquares estimation (IDEAL) of the wrist and finger at 3T: comparison with chemical shift selective fat suppression images. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 37:733–738.13. Costa DN, Pedrosa I, McKenzie C, Reeder SB, Rofsky NM. Body MRI using IDEAL. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:1076–1084.14. Fuller S, Reeder S, Shimakawa A, et al. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL) fast spin-echo imaging of the ankle: initial clinical experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:1442–1447.15. Reeder SB, Pineda AR, Wen Z, et al. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL): application with fast spin-echo imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2005; 54:636–644.16. Barger AV, DeLone DR, Bernstein MA, Welker KM. Fat signal suppression in head and neck imaging using fast spin-echo-IDEAL technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1292–1294.17. Ma J, Jackson EF, Kumar AJ, Ginsberg LE. Improving fatsuppressed T2-weighted imaging of the head and neck with 2 fast spin-echo dixon techniques: initial experiences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:42–45.18. Chang HC, Juan CJ, Chiu HC, et al. Parotid fat contents in healthy subjects evaluated with iterative decomposition with echo asymmetry and least squares fat-water separation. Radiology. 2013; 267:918–923.19. Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO. Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007; 26:375–385.20. Tartaglino LM, Flanders AE, Vinitski S, Friedman DP. Metallic artifacts on MR images of the postoperative spine: reduction with fast spin-echo techniques. Radiology. 1994; 190:565–569.21. Laakman RW, Kaufman B, Han JS, et al. MR imaging in patients with metallic implants. Radiology. 1985; 157:711–714.22. Bellon EM, Haacke EM, Coleman PE, Sacco DC, Steiger DA, Gangarosa RE. MR artifacts: a review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986; 147:1271–1281.23. Delfaut EM, Beltran J, Johnson G, Rousseau J, Marchandise X, Cotten A. Fat suppression in MR imaging: techniques and pitfalls. Radiographics. 1999; 19:373–382.24. Frahm J, Haase A, Hanicke W, Matthaei D, Bomsdorf H, Helzel T. Chemical shift selective MR imaging using a whole-body magnet. Radiology. 1985; 156:441–444.25. Ma J. Dixon techniques for water and fat imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 28:543–558.26. Shellock FG. MR imaging of metallic implants and materials: a compilation of the literature. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988; 151:811–814.27. New PF, Rosen BR, Brady TJ, et al. Potential hazards and artifacts of ferromagnetic and nonferromagnetic surgical and dental materials and devices in nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology. 1983; 147:139–148.28. Shellock FG, Morisoli S, Kanal E. MR procedures and biomedical implants, materials, and devices: 1993 update. Radiology. 1993; 189:587–599.29. Taber KH, Herrick RC, Weathers SW, Kumar AJ, Schomer DF, Hayman LA. Pitfalls and artifacts encountered in clinical MR imaging of the spine. Radiographics. 1998; 18:1499–1521.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MR Imaging of the Spine at 3.0T with T2-Weighted IDEAL Fast Recovery Fast Spin-Echo Technique
- Comparison of Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants versus Standard Filtered Back Projection: Value of Postoperative CT after Hip Replacement
- MRI of Normal Pancreas: Comparison of T2-Weighted Pulse Sequences Using Turbo Spin Echo, Turbo Spin Echo with Fat Suppression, HASTE and HASTE with Fat Suppression
- Practical Application of Iterative Decomposition of Water and Fat with Echo Asymmetry and Least-Squares Estimation (IDEAL) Imaging in Minimizing Metallic Artifacts
- The Efficacy of the Alternating Technique in TEOAE Suppression by Contralateral Acoustic Stimulation