J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 Jan;78(1):22-29. 10.3348/jksr.2018.78.1.22.
Comparison of Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants versus Standard Filtered Back Projection: Value of Postoperative CT after Hip Replacement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea. jachoi88@gmail.com
- KMID: 2399302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.78.1.22
Abstract
- PURPOSE
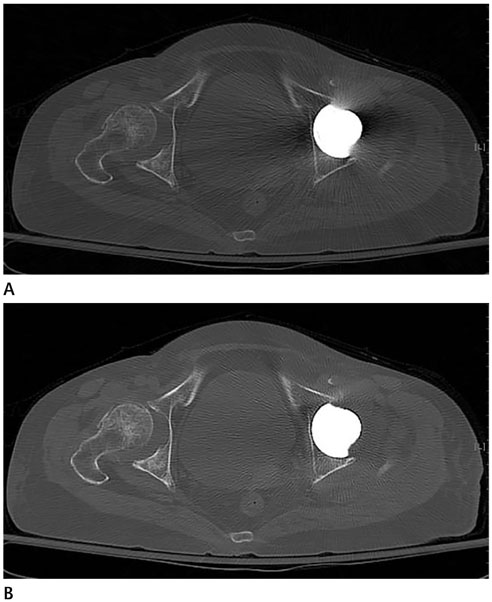
To evaluate Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants (O-MAR, Philips Healthcare) technique compared with standard filtered back projection (SFBP) technique on post-operative hip CT regarding image noise reduction and detection of post-operative complications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
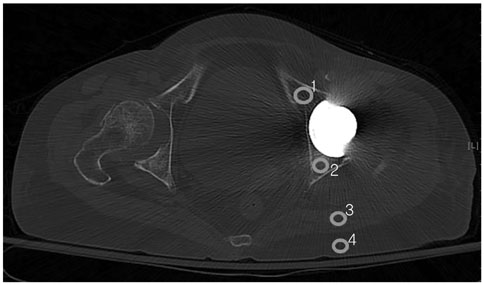
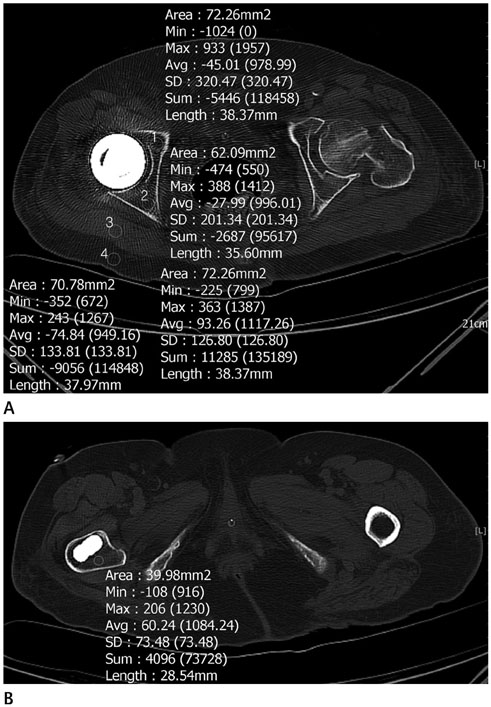
Fifty-six hip CT scans after hip replacement with SFBP technique and O-MAR application were retrospectively reviewed. Region of interests (ROIs) were drawn at levels wherein acetabular cup and femoral head were largest at anterior and posterior acetabula, gluteus maximus muscle, subcutaneous fat adjacent to gluteus maximus muscle, and in area adjacent to prosthesis stem wherein lesser trochanter is largest. Hounsfield units (HU) were measured to evaluate artifact quantitatively; mean and standard deviations (SDs) calculated and compared. Periprosthetic complications were evaluated, and visibility rated between two reconstruction techniques; 1-SFBP better, 2-SFBP same as O-MAR, 3-O-MAR better.
RESULTS
Average HU was significantly lower in O-MAR at posterior acetabulum, gluteus maximus muscle, and subcutaneous fat (p < 0.05). SD for HU was significantly lower in O-MAR at all ROIs (p < 0.05). Mean visibility of periprosthetic complications was 2.0, so equivalent.
CONCLUSION
Reconstruction with O-MAR technique in post-operative hip CT scans after hip replacement yielded statistically significant decrease in image noise. However, visibility of periprosthetic complications was not impacted by reconstruction technique.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miller TT. Imaging of hip arthroplasty. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:3802–3812.
Article2. Roth TD, Maertz NA, Parr JA, Buckwalter KA, Choplin RH. CT of the hip prosthesis: appearance of components, fixation, and complications. Radiographics. 2012; 32:1089–1107.
Article3. Cahir JG, Toms AP, Marshall TJ, Wimhurst J, Nolan J. CT and MRI of hip arthroplasty. Clin Radiol. 2007; 62:1163–1171.
Article4. Gondim Teixeira PA, Meyer JB, Baumann C, Raymond A, Sirveaux F, Coudane H, et al. Total hip prosthesis CT with single-energy projection-based metallic artifact reduction: impact on the visualization of specific periprosthetic soft tissue structures. Skeletal Radiol. 2014; 43:1237–1246.
Article5. Lee MJ, Kim S, Lee SA, Song HT, Huh YM, Kim DH, et al. Overcoming artifacts from metallic orthopedic implants at high-field-strength MR imaging and multi-detector CT. Radiographics. 2007; 27:791–803.
Article6. Willemink MJ, de Jong PA, Leiner T, de Heer LM, Nievelstein RA, Budde RP, et al. Iterative reconstruction techniques for computed tomography part 1: technical principles. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:1623–1631.
Article7. Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants (O-MAR). White paper. Philips CT Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare. Accessed Aug 20, 2017. Available at: clinical.netforum.healthcare.philips.com/us_en/Explore/White-Papers/CT/Metal-Artifact-Reduction-for-Orthopedic-Implants-(O-MAR).8. Subhas N, Polster JM, Obuchowski NA, Primak AN, Dong FF, Herts BR, et al. Imaging of arthroplasties: improved image quality and lesion detection with iterative metal artifact reduction, a new CT metal artifact reduction technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016; 207:378–385.
Article9. Jeong S, Kim SH, Hwang EJ, Shin CI, Han JK, Choi BI. Usefulness of a metal artifact reduction algorithm for orthopedic implants in abdominal CT: phantom and clinical study results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 204:307–317.
Article10. Gupta A, Subhas N, Primak AN, Nittka M, Liu K. Metal artifact reduction: standard and advanced magnetic resonance and computed tomography techniques. Radiol Clin North Am. 2015; 53:531–547.11. Long SS, Surrey D, Nazarian LN. Common sonographic findings in the painful hip after hip arthroplasty. J Ultrasound Med. 2012; 31:301–312.
Article12. Kalender WA, Hebel R, Ebersberger J. Reduction of CT artifacts caused by metallic implants. Radiology. 1987; 164:576–577.
Article13. Gervaise A, Osemont B, Lecocq S, Noel A, Micard E, Felblinger J, et al. CT image quality improvement using Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction with wide-volume acquisition on 320-detector CT. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22:295–301.
Article14. Morsbach F, Bickelhaupt S, Wanner GA, Krauss A, Schmidt B, Alkadhi H. Reduction of metal artifacts from hip prostheses on CT images of the pelvis: value of iterative reconstructions. Radiology. 2013; 268:237–244.
Article15. Higashigaito K, Angst F, Runge VM, Alkadhi H, Donati OF. Metal artifact reduction in pelvic computed tomography with hip prostheses: comparison of virtual monoenergetic extrapolations from dual-energy computed tomography and an iterative metal artifact reduction algorithm in a phantom study. Invest Radiol. 2015; 50:828–834.16. Wang F, Xue H, Yang X, Han W, Qi B, Fan Y, et al. Reduction of metal artifacts from alloy hip prostheses in computer tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014; 38:828–833.
Article17. Bongers MN, Schabel C, Thomas C, Raupach R, Notohamiprodjo M, Nikolaou K, et al. Comparison and combination of dual-energy- and iterative-based metal artefact reduction on hip prosthesis and dental implants. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0143584.
Article18. Subhas N, Primak AN, Obuchowski NA, Gupta A, Polster JM, Krauss A, et al. Iterative metal artifact reduction: evaluation and optimization of technique. Skeletal Radiol. 2014; 43:1729–1735.
Article19. Winklhofer S, Benninger E, Spross C, Morsbach F, Rahm S, Ross S, et al. CT metal artefact reduction for internal fixation of the proximal humerus: value of mono-energetic extrapolation from dual-energy and iterative reconstructions. Clin Radiol. 2014; 69:e199–e206.
Article20. Kotsenas AL, Michalak GJ, DeLone DR, Diehn FE, Grant K, Halaweish AF, et al. CT metal artifact reduction in the spine: can an iterative reconstruction technique improve visualization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015; 36:2184–2190.
Article21. Morsbach F, Wurnig M, Kunz DM, Krauss A, Schmidt B, Kollias SS, et al. Metal artefact reduction from dental hardware in carotid CT angiography using iterative reconstructions. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:2687–2694.
Article22. Yu L, Li H, Mueller J, Kofler JM, Liu X, Primak AN, et al. Metal artifact reduction from reformatted projections for hip prostheses in multislice helical computed tomography: techniques and initial clinical results. Invest Radiol. 2009; 44:691–696.23. Lee YH, Park KK, Song HT, Kim S, Suh JS. Metal artefact reduction in gemstone spectral imaging dual-energy CT with and without metal artefact reduction software. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22:1331–1340.
Article24. Malan DF, Botha CP, Kraaij G, Joemai RM, van der, Nelissen RG, et al. Measuring femoral lesions despite CT metal artefacts: a cadaveric study. Skeletal Radiol. 2012; 41:547–555.
Article25. Verburg JM, Seco J. CT metal artifact reduction method correcting for beam hardening and missing projections. Phys Med Biol. 2012; 57:2803–2818.
Article26. Wilson JM, Christianson OI, Richard S, Samei E. A methodology for image quality evaluation of advanced CT systems. Med Phys. 2013; 40:031908.
Article27. Hilgers G, Nuver T, Minken A. The CT number accuracy of a novel commercial metal artifact reduction algorithm for large orthopedic implants. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2014; 15:4597.
Article28. A new method for metal artifact reduction in CT. International Conference in X-ray Computed Tomography, 2011. Accessed Feb 6, 2017. Available at: https://repository.tudelft.nl/assets/uuid:22d5815d-dcfe-48df-93a4-9d1c4e8e85fc/MS-33.229.pdf.29. Andersson KM, Norrman E, Geijer H, Krauss W, Cao Y, Jendeberg J, et al. Visual grading evaluation of commercially available metal artefact reduction techniques in hip prosthesis computed tomography. Br J Radiol. 2016; 89:20150993.
Article30. Han SC, Chung YE, Lee YH, Park KK, Kim MJ, Kim KW. Metal artifact reduction software used with abdominopelvic dual-energy CT of patients with metal hip prostheses: assessment of image quality and clinical feasibility. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014; 203:788–795.
Article31. Buckwalter KA, Lin C, Ford JM. Managing postoperative artifacts on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2011; 15:309–319.
Article32. White LM, Buckwalter KA. Technical considerations: CT and MR imaging in the postoperative orthopedic patient. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2002; 6:5–17.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- U-net based metal segmentation on projection domain for metal artifact reduction in dental CT
- Comparison of Metal Artifact Reduction Algorithms in Patients with Hip Prostheses: Virtual Monoenergetic Images vs. Orthopedic Metal Artifact Reduction
- Value and Clinical Application of Orthopedic Metal Artifact Reduction Algorithm in CT Scans after Orthopedic Metal Implantation
- Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron-Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Adverse Local Tissue Reactions near Metal Implants after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Preliminary Report
- Metal-on-metal Articulation of Total Hip Replacement