J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2016 Mar;21(1):29-37. 10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.1.29.
Clinical Results of Dynamic External Fixation for Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Fracture Dislocation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. tjlee@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2161161
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.1.29
Abstract
- PURPOSE
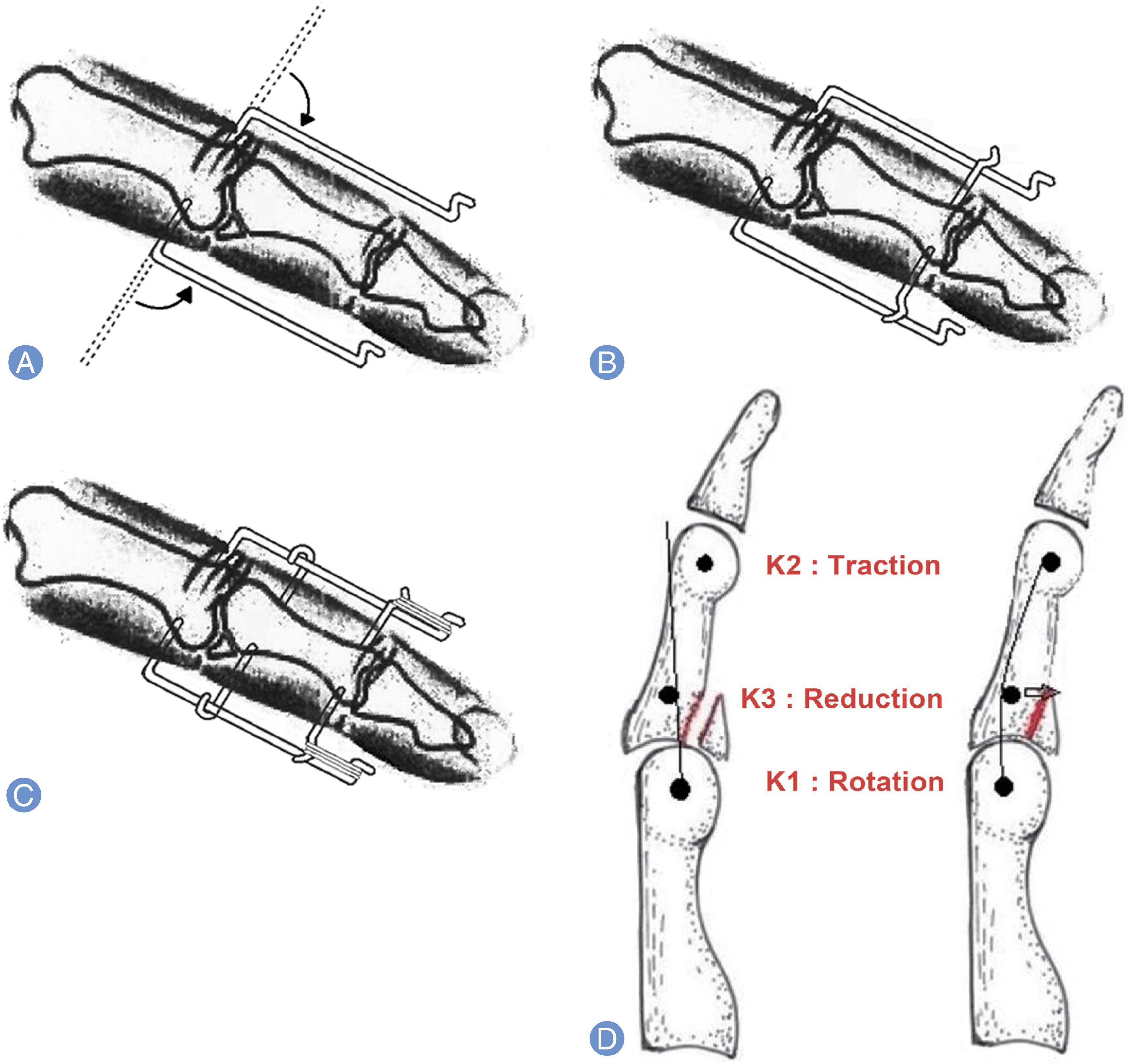
We evaluated clinical outcomes after treating patients with proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint fracture-dislocation with dynamic external fixator with which early joint motion can be undertaken to prevent joint stiffness effectively and fixate joints firmly.
METHODS
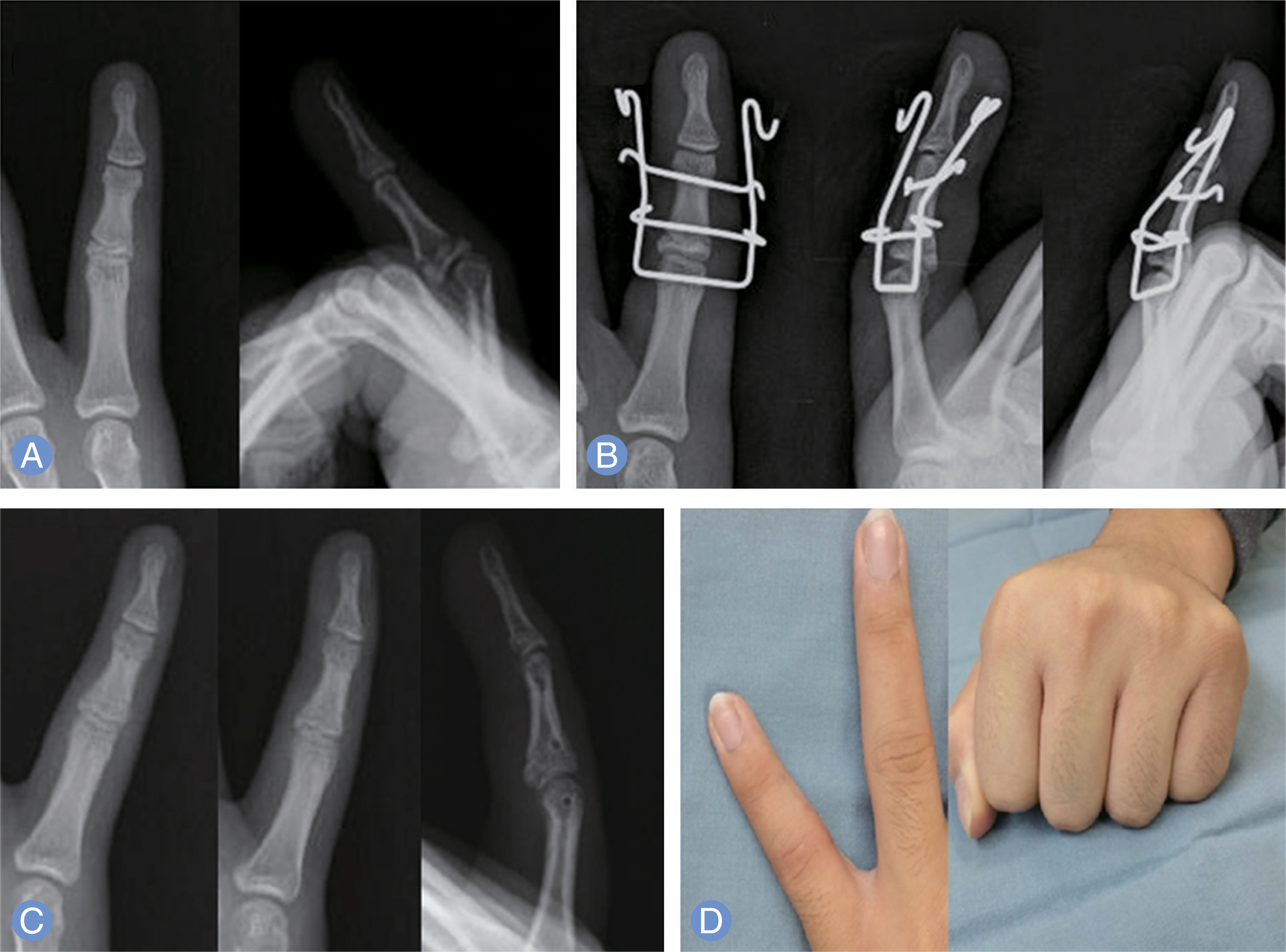
Dynamic external fixators were applied for 20 fracture-dislocation of the PIP joints in 19 patients. The joints involved were 2nd PIP joint in two patients, 3rd PIP joint in three patients, 4th PIP joint in five patients, 5th PIP joint in eight patients. One patient had both 3rd and 4th PIP joint fracture-dislocation. Surgery was performed at least within four weeks. The mean age of the patients was 30.5 years (range, 15-54 years) and the mean follow-up duration was 1.85 years (range, 1-2.3 years) years. All patients were clinically and radiologically assessed on an outpatient basis after being discharged.
RESULTS
At the final follow-up, the mean range of motion of PIP joints in flexion was 100.1° (flexion range, 88°-110°), the mean extension lag was 3.0° (extension range, 0°-10°), and the mean visual analogue scale score was 0.8. On anterior-posterior and lateral radiographs, congruity of the joint was satisfactory and 1 mm step off was present in three cases.
CONCLUSION
We attained satisfactory clinical outcomes on the recovery of joint movement and joint congruity after treating PIP joint fracture-dislocation injury with dynamic external fixator.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatment of Neglected Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture Dislocation Using a Traction Device: A Case Report
Yongun Cho, Jai Hyung Park, Se-Jin Park, Ingyu Lee, Eugene Kim
J Korean Fract Soc. 2019;32(4):222-226. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.222.
Reference
-
1. AladinA. DavisTR. Dorsal fracture-dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint: a comparative study of percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation. J Hand Surg Br. 2005; 30:120–8.
Article2. InanamiH. NinomiyaS. OkutsuI. TaruiT. Dynamic external finger fixator for fracture dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1993; 18:160–4.
Article3. FreibergA. Management of proximal interphalangeal joint injuries. Can J Plast Surg. 2007; 15:199–203.
Article4. HamerDW. QuintonDN. Dorsal fracture subluxation of the proximal interphalangeal joints treated by extension block splintage. J Hand Surg Br. 1992; 17:586–90.
Article5. ViegasSF. Extension block pinning for proximal interphalangeal joint fracture dislocations: preliminary report of a new technique. J Hand Surg Am. 1992; 17:896–901.
Article6. WilliamsRM. KiefhaberTR. SommerkampTG. SternPJ. Treatment of unstable dorsal proximal interphalangeal fracture/dislocations using a hemi-hamate autograft. J Hand Surg Am. 2003; 28:856–65.
Article7. LeeJY. TeohLC. Dorsal fracture dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint treated by open reduction and interfragmentary screw fixation: indications, approaches and results. J Hand Surg Br. 2006; 31:138–46.
Article8. DionysianE. EatonRG. The long-term outcome of volar plate arthroplasty of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 2000; 25:429–37.
Article9. AgeeJM. Unstable fracture dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the fingers: a preliminary report of a new treatment technique. J Hand Surg Am. 1978; 3:386–9.
Article10. RulandRT. HoganCJ. CannonDL. SladeJF. Use of dynamic distraction external fixation for unstable fracture-dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33:19–25.
Article11. HastingsH2nd. ErnstJM. Dynamic external fixation for fractures of the proximal interphalangeal joint. Hand Clin. 1993; 9:659–74.
Article12. KrakauerJD. SternPJ. Hinged device for fractures involving the proximal interphalangeal joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (327):29–37.
Article13. SalterRB. The physiologic basis of continuous passive motion for articular cartilage healing and regeneration. Hand Clin. 1994; 10:211–9.
Article14. SchenckRR. Dynamic traction and early passive movement for fractures of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1986; 11:850–8.
Article15. AgeeJM. Unstable fracture dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint: treatment with the force couple splint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (214):101–12.16. DebusG. CourvoisierA. WimseyS. PradelP. MoutetF. Pins and rubber traction system for intra-articular proximal interphalangeal joint fractures revisited. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2010; 35:396–401.
Article17. BadiaA. RianoF. RavikoffJ. KhouriR. Gonzalez-HernandezE. OrbayJL. Dynamic intradigital external fixation for proximal interphalangeal joint fracture dislocations. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30:154–60.
Article18. GaulJSJr. RosenbergSN. Fracture-dislocation of the middle phalanx at the proximal interphalangeal joint: repair with a simple intradigital traction-fixation device. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1998; 27:682–8.19. HynesMC. GiddinsGE. Dynamic external fixation for pilon fractures of the interphalangeal joints. J Hand Surg Br. 2001; 26:122–4.
Article20. SyedAA. AgarwalM. BoomeR. Dynamic external fixator for pilon fractures of the proximal interphalangeal joints: a simple fixator for a complex fracture. J Hand Surg Br. 2003; 28:137–41.
Article21. DuteilleF. PasquierP. LimA. DautelG. Treatment of complex interphalangeal joint fractures with dynamic external traction: a series of 20 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 111:1623–9.
Article22. DeshmukhSC. KumarD. MathurK. ThomasB. Complex fracture-dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the hand: results of a modified pins and rubbers traction system. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:406–12.23. SuzukiY. MatsunagaT. SatoS. YokoiT. The pins and rubbers traction system for treatment of comminuted intraarticular fractures and fracture-dislocations in the hand. J Hand Surg Br. 1994; 19:98–107.
Article24. EllisSJ. ChengR. ProkopisP. . Treatment of proximal interphalangeal dorsal fracture-dislocation injuries with dynamic external fixation: a pins and rubber band system. J Hand Surg Am. 2007; 32:1242–50.
Article25. De SmetL. BooneP. Treatment of fracture-dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint using the Suzuki external fixator. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16:668–71.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Neglected Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture Dislocation Using a Traction Device: A Case Report
- Treatment of Fracture - Dislocation of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
- External Dynamic Traction Device for Fracture of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint of the Finger
- Fracture Dislocation of the interphalangeal Joint of Great Toe: Report of Three Cases
- Irreducible Open Dorsal Dislocation of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint: A Case Report