J Korean Fract Soc.
2019 Oct;32(4):222-226. 10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.222.
Treatment of Neglected Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture Dislocation Using a Traction Device: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Konkuk University, Chungju, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul, Korea. eugeneos@naver.com
- KMID: 2468685
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.222
Abstract
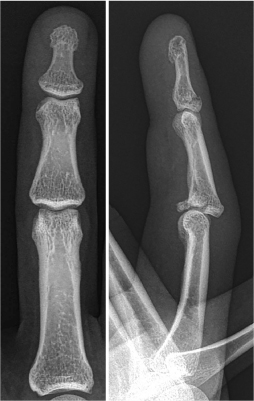
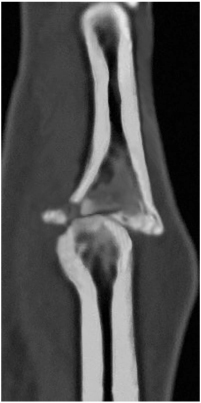
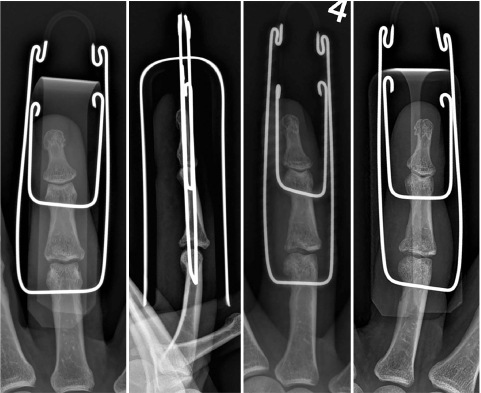
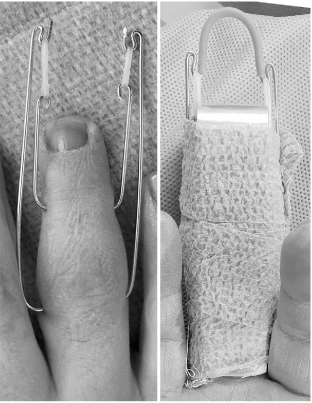
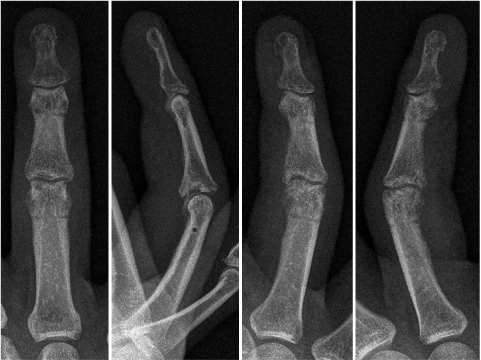
- This paper reports the use of a traction device for the treatment of neglected proximal interphalangeal fracture dislocations. A 44-year-old man with a fracture dislocation of a right ring finger proximal interphalangeal joint was admitted 17 days after the injury. Closed reduction and external fixation were performed using a dynamic traction device and C-arm under a brachial plexus block. Passive range of motion exercise was started after two weeks postoperatively and active range of motion exercise was started after three weeks. The traction device was removed after five weeks. No infection occurred during the traction period. No subluxation or displacement was observed on the X-ray taken two months postoperatively. The active range of motion of the proximal interphalangeal joint was 90°. The patient was satisfied with the functional result of the treatment with the traction device. The dynamic traction device is an effective treatment for neglected fracture dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint of a finger.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Syed AA, Agarwal M, Boome R. Dynamic external fixator for pilon fractures of the proximal interphalangeal joints: a simple fixator for a complex fracture. J Hand Surg Br. 2003; 28:137–141.
Article2. Einhorn TA. The cell and molecular biology of fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 355 Suppl. S7–S21.
Article3. Green E, Lubahn JD, Evans J. Risk factors, treatment, and outcomes associated with nonunion of the midshaft humerus fracture. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2005; 14:64–72.4. Bernstein J, Monaghan BA, Silber JS, DeLong WG. Taxonomy and treatment: a classification of fracture classifications. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997; 79:706–707. discussion 708–709.5. Schenck RR. Dynamic traction and early passive movement for fractures of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1986; 11:850–858.
Article6. Rawes ML, Oni OO. Swan-neck deformity as a complication of the Agee technique. J Hand Surg Br. 1995; 20:255–257.
Article7. Duteille F, Pasquier P, Lim A, Dautel G. Treatment of complex interphalangeal joint fractures with dynamic external traction: a series of 20 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 111:1623–1629.
Article8. Badia A, Riano F, Ravikoff J, Khouri R, Gonzalez-Hernandez E, Orbay JL. Dynamic intradigital external fixation for proximal interphalangeal joint fracture dislocations. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30:154–160.
Article9. Kim SW, Lee CC, Ko SH, Hwang IY, Kim MS, Jin WY. Use of a distraction dynamic external fixator in the treatment of comminuted middle phalanx base fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2019; 32:1–5.
Article10. Shin EH, Park JS, Lee TJ. Clinical results of dynamic external fixation for proximal interphalangeal joint fracture dislocation. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2016; 21:29–37.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fracture Dislocation of the interphalangeal Joint of Great Toe: Report of Three Cases
- External Dynamic Traction Device for Fracture of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint of the Finger
- Open Reduction of a Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe Neglected for 6 Weeks
- Treatment of Fracture - Dislocation of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
- Treatment of Neglected Fracture-Dislocation of the Ankle Using llizarov Device: A case report