J Korean Fract Soc.
2015 Jan;28(1):65-70. 10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.65.
Irreducible Open Dorsal Dislocation of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. osdryskim@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Uijeongbu Paik General Hospital, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- KMID: 1774099
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.65
Abstract
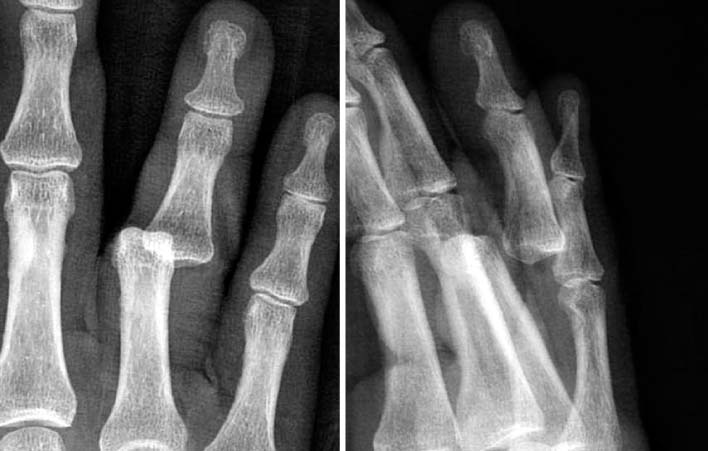
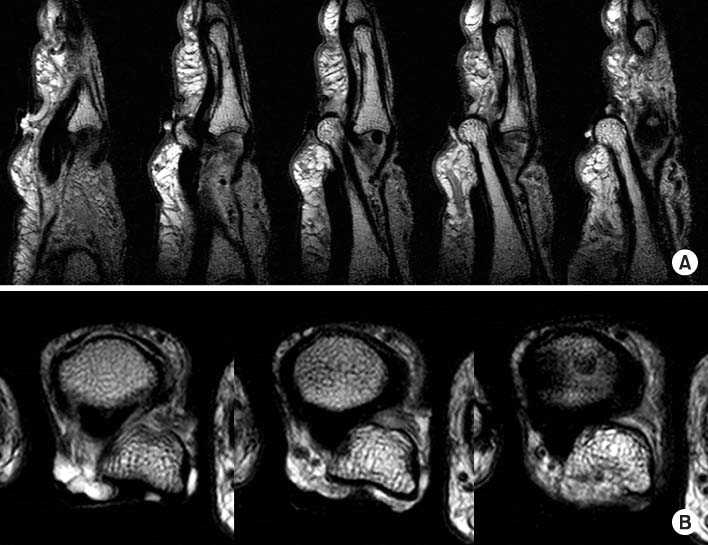
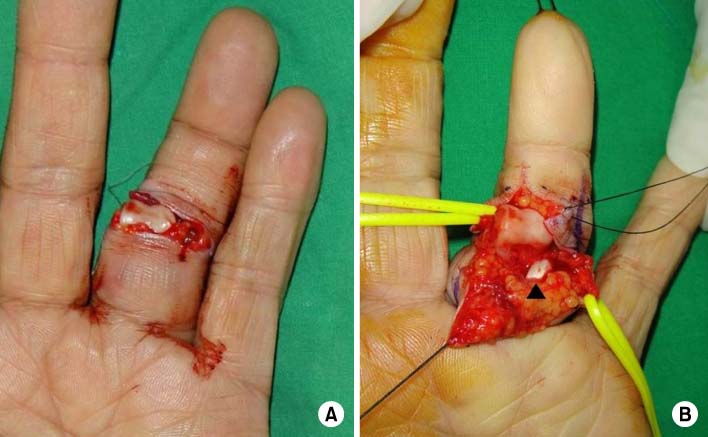
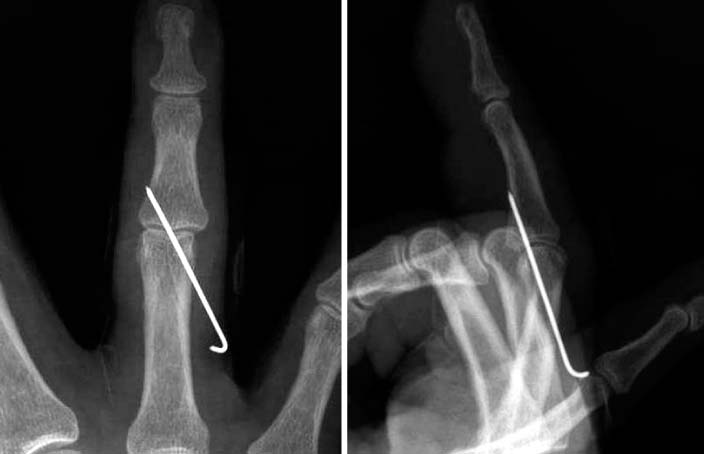
- Dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint is a common injury in the orthopedic department. In most cases, the joint is reduced simply by closed manipulation. However, in rare cases, the joint is not reducible by closed manipulation, therefore, surgery is required. We report on a case of irreducible open dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint which was surgically treated. Because the flexor tendon interposed between the head of the proximal phalanx and the base of the middle phalanx, we could reduce the joint only after repositioning of the flexor tendon.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Merrell G, Slade JF. Dislocations and Ligament Injuries in the Digits. In : Wolfe SW, Hotchikiss RN, Pederson WC, Kozin SH, editors. Green's operative hand surgery. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2011. p. 291–332.2. Calfee RP, Sommerkamp TG. Fracture-dislocation about the finger joints. J Hand Surg Am. 2009; 34:1140–1147.
Article3. Muraoka S, Furue Y, Kawashima M. Irreducible open dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint: a case report. Hand Surg. 2010; 15:61–64.
Article4. Kilgore ES Jr, Newmeyer WL, Brown LG. Post-traumatic trapped dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Trauma. 1976; 16:481–487.
Article5. Takami H, Takahashi S, Ando M. Irreducible open dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001; 121:232–233.
Article6. Green SM, Posner MA. Irreducible dorsal dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:85–87.7. Kjeldal I. Irreducible compound dorsal dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the finger. J Hand Surg Br. 1986; 11:49–50.
Article8. Stern PJ, Lee AF. Open dorsal dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:364–370.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Irreducible Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Thumb: A Case Report
- A Case Report of Irreducible Anterior Dislocation of Proximal Interphalangeal Joint of a Finger
- Interphalangeal Dislocation of Great Toe with Incarcerated Sesamoid Bone: Report of Two Cases
- Irreducible Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe with Lateral Collateral Ligament Entrapment: A Case Report
- Fracture Dislocation of the interphalangeal Joint of Great Toe: Report of Three Cases