J Korean Fract Soc.
2009 Apr;22(2):110-113. 10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.110.
Irreducible Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe with Lateral Collateral Ligament Entrapment: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. biojeong@khmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1470024
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.110
Abstract
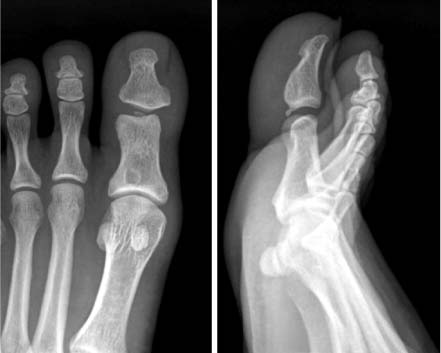
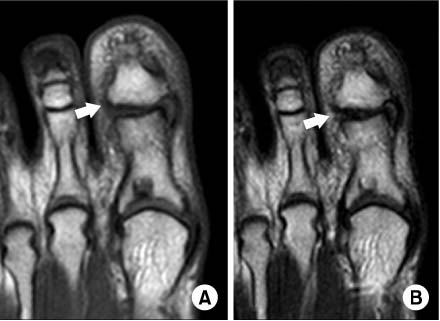
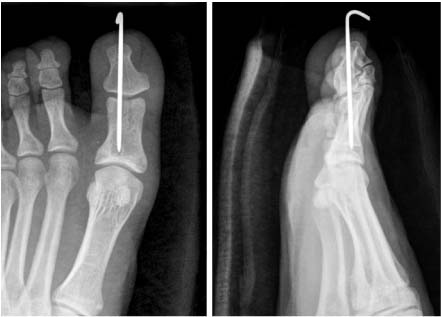
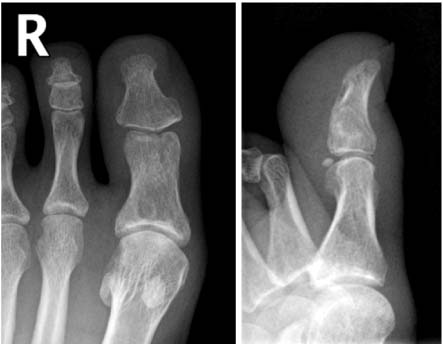
- Dislocations of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe that are irreducible are very rare. Invagination of the plantar plate or the sesamoid bone into the IP joint, which prevents reduction. To our knowledge, however, dislocations of the IP joint of the great toe that were irreducible because of lateral collateral ligament entrapment, not invagination of the plantar plate or the sesamoid bone, have not been reported by any English literature. We report a 29-year-old ballet dancer who sustained an irreducible dislocation of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe owing to lateral collateral ligament entrapment.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Open Reduction of a Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe Neglected for 6 Weeks
Jae Kwang Kim, Rag-Gyu Kim
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2011;46(5):426-430. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.5.426.
Reference
-
1. Berger JL, LeGeyt MT, Ghobadi R. Incarcerated subhallucal sesamoid of the great toe: irreducible dislocation of the great toe by an accessory sesamoid bone. Am J Orthop. 1997; 26:226–228.2. Bucholz RW, Heckman JD. Rockwood and Green's fracture in adult. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2001. p. 2238.3. Dave D, Jayaraj VP, James SE. Intra-articular sesamoid dislocation of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe. Injury. 1993; 24:198–199.
Article4. Kursunoglu S, Resnick D, Goergen T. Traumatic dislocation with sesamoid entrapment in the interphalangeal joint of the great toe. J Trauma. 1987; 27:959–961.
Article5. Miki T, Yamamura T, Kitai T. An irreducible dislocation of the great toe Report of two cases and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 230:200–206.6. Muller GM. Dislocation of sesamoid of hallux. Lancet. 1944; 243:789.
Article7. Nelson TL, Uggen W. Irreducible dorsal dislocation of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981; 157:110–112.
Article8. Salleh R, Beischer A, Edwards WH. Disorder of the hallucal interphalangeal joint. Foot Ankle Clin. 2005; 10:129–140.9. Shin YW, Choi IH, Rhee NK. Open lateral collateral ligament injury of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe in adolescents during taekwondo. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36:158–161.
Article10. Yasuda T, Fujio K, Tamura K. Irreducible dorsal dislocation of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe: report of two cases. Foot Ankle. 1990; 10:331–336.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fracture Dislocation of the interphalangeal Joint of Great Toe: Report of Three Cases
- Interphalangeal Dislocation of Great Toe with Incarcerated Sesamoid Bone: Report of Two Cases
- Open Reduction of a Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe Neglected for 6 Weeks
- Dislocations of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Tow with Interposition of a Seamoid Bone: A Report of Two Cases
- Irreducible Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Thumb: A Case Report