Fossa navicularis magna detection on cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences, School of Dental Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA. azs16@case.edu
- 2Division of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
- KMID: 2160157
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2016.46.1.47
Abstract
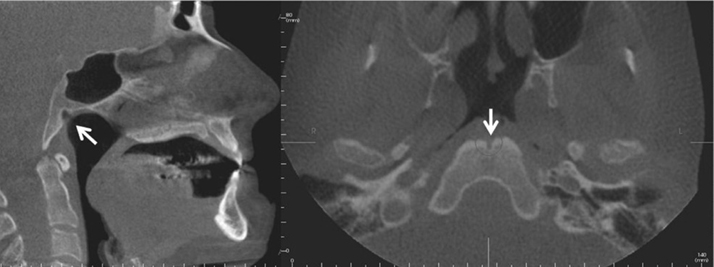
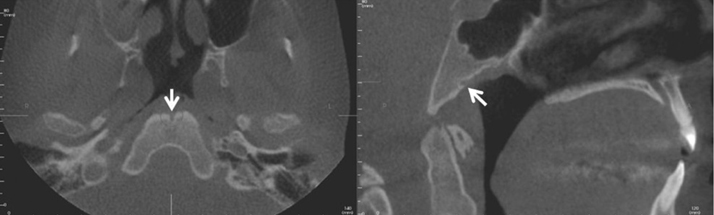
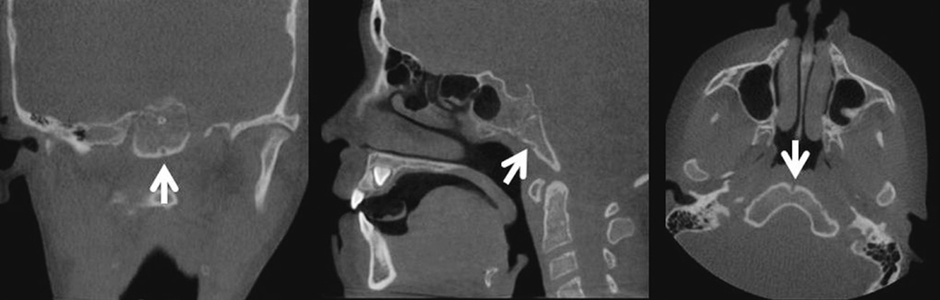
- Herein, we report and discuss the detection of fossa navicularis magna, a close radiographic anatomic variant of canalis basilaris medianus of the basiocciput, as an incidental finding in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging. The CBCT data of the patients in question were referred for the evaluation of implant sites and to rule out pathology in the maxilla and mandible. CBCT analysis showed osseous, notch-like defects on the inferior aspect of the clivus in all four cases. The appearance of fossa navicularis magna varied among the cases. In some, it was completely within the basiocciput and mimicked a small rounded, corticated, lytic defect, whereas it appeared as a notch in others. Fossa navicularis magna is an anatomical variant that occurs on the inferior aspect of the clivus. The pertinent literature on the anatomical variations occurring in this region was reviewed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Rare finding of Eustachian tube calcifications with cone-beam computed tomography
Ali Z. Syed, Anna Hawkins, Leela Subashini Alluri, Buthainah Jadallah, Kiran Shahid, Michael Landers, Hussein M. Assaf
Imaging Sci Dent. 2017;47(4):275-279. doi: 10.5624/isd.2017.47.4.275.Evaluation of morphometric features of fossa navicularis using cone-beam computed tomography in a Turkish subpopulation
Guldane Magat
Imaging Sci Dent. 2019;49(3):209-212. doi: 10.5624/isd.2019.49.3.209.Investigation of the prevalence and main features of skull-base anomalies and characteristics of the sphenoid sinus using cone-beam computed tomography
Aslıhan Akbulut, Oğuzhan Demirel, Kaan Orhan
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;48(4):207-218. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.4.207.
Reference
-
1. Neelakantan A, Rana AK. Benign and malignant diseases of the clivus. Clin Radiol. 2014; 69:1295–1303.
Article2. Shah A, Goel A. Clival dysgenesis associated with Chiari Type 1 malformation and syringomyelia. J Clin Neurosci. 2010; 17:400–401.
Article3. Segal N, Atamne E, Shelef I, Zamir S, Landau D. Intracranial infection caused by spreading through the fossa naviclaris magna - a case report and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 77:1919–1921.
Article4. Prabhu SP, Zinkus T, Cheng AG, Rahbar R. Clival osteomyelitis resulting from spread of infection through the fossa navicularis magna in a child. Pediatr Radiol. 2009; 39:995–998.
Article5. Collins HB Jr. Frequency and distribution of fossa pharyngea in human crania. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1927; 11:101–106.
Article6. Krmpotić-Nemanić J, Vinter I, Ehrenfreund T, Marusić A. Age-related changes in the anatomical landmarks of the osseous epipharynx. Ann Anat. 2006; 188:459–467.
Article7. Ginat DT, Ellika SK, Corrigan J. Multi-detector-row computed tomography imaging of variant skull base foramina. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2013; 37:481–485.
Article8. Currarino G. Canalis basilaris medianus and related defects of the basiocciput. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988; 9:208–211.9. Beltramello A, Puppini G, El-Dalati G, Girelli M, Cerini R, Sbarbati A, et al. Fossa navicularis magna. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:1796–1798.10. Quereshy FA, Savell TA, Palomo JM. Applications of cone beam computed tomography in the practice of oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:791–796.
Article11. Ben Salem D, Duvillard C. Fossa navicularis: anatomic variation at the skull base. Clin Anat. 2006; 19:365.
Article12. Marom T, Russo E, Ben Salem D, Roth Y. Nasopharyngeal cysts. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 73:1063–1070.
Article13. Cankal F, Ugur HC, Tekdemir I, Elhan A, Karahan T, Sevim A. Fossa navicularis: anatomic variation at the skull base. Clin Anat. 2004; 17:118–122.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of morphometric features of fossa navicularis using cone-beam computed tomography in a Turkish subpopulation
- Anomalies of the clivus of interest in dental practice: A systematic review
- Mandibular condyle position in cone beam computed tomography
- Three-dimensional imaging modalities in endodontics
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report