Yonsei Med J.
2008 Oct;49(5):857-859. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.5.857.
Rescue Treatment with Intra-arterial Tirofiban Infusion and Emergent Carotid Stenting
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kylee@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2158207
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.5.857
Abstract
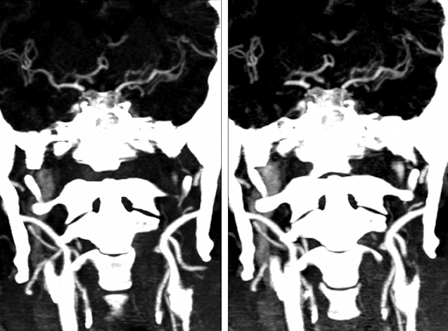
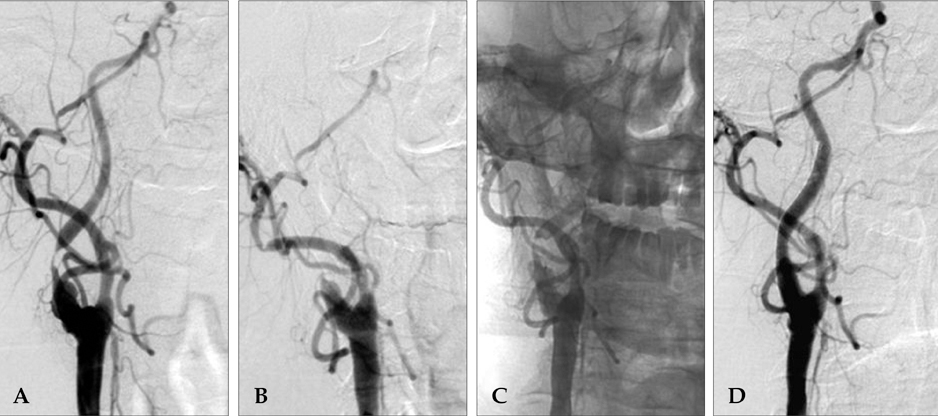
- Rapid arterial rethrombosis is associated with high-grade residual stenosis and usually occurs at the site of the initial occlusion, resulting in reocclusion of the recanalized artery. Platelets may play an active role in such rethrombosis after thrombolytic-induced clot lysis. Given that glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blockers, like tirofiban, prevent thrombus formation by inhibiting the final common pathway of platelet aggregation, they may be helpful for treating rethrombosis after thrombolysis. A 64-year-old man presented with an acute ischemic stroke due to internal carotid artery (ICA) occlusion. The ICA was recanalized by intravenous thrombolysis but reoccluded shortly after recanalization. The reoccluded ICA was successfully recanalized using intra-arterial tirofiban. A carotid stent was subsequently inserted to relieve severe stenosis and to prevent recurrent stroke. Here, we report a case of rescue treatment of a successfully recanalized ICA by intra- arterial tirofiban. We suggest that rescue use of intra-arterial tirofiban may be effective and safe, especially in hemorrhage prone situations, due to the relatively lower dose of tirofiban compared with intravenous doses.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Adjuvant Tirofiban Injection Through Deployed Solitaire Stent As a Rescue Technique After failed Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Stroke
Jung Hwa Seo, Hae Woong Jeong, Sung Tae Kim, Eun-Gyu Kim
Neurointervention. 2015;10(1):22-27. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2015.10.1.22.
Reference
-
1. Alexandrov AV, Grotta JC. Arterial reocclusion in stroke patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Neurology. 2002. 59:862–867.
Article2. Qureshi AI, Siddiqui AM, Kim SH, Hanel RA, Xavier AR, Kirmani JF, et al. Reocclusion of recanalized arteries during intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. 25:322–328.3. Heo JH, Lee KY, Kim SH, Kim DI. Immediate reocclusion following a successful thrombolysis in acute stroke: a pilot study. Neurology. 2003. 60:1684–1687.4. Seitz RJ, Meisel S, Moll M, Wittsack HJ, Junghans U, Siebler M. The effect of combined thrombolysis with rtPA and tirofiban on ischemic brain lesions. Neurology. 2004. 62:2110–2112.
Article5. Straub S, Junghans U, Jovanovic V, Wittsack HJ, Seitz RJ, Siebler M. Systemic thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and tirofiban in acute middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 2004. 35:705–709.
Article6. Lee KY, Heo JH, Lee SI, Yoon PH. Rescue treatment with abciximab in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2001. 56:1585–1587.
Article7. The EPIC Investigators. Use of a monoclonal antibody directed against the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor in high-risk coronary angioplasty. N Engl J Med. 1994. 330:956–961.8. Wallace RC, Furlan AJ, Moliterno DJ, Stevens GH, Masaryk TJ, Perl J 2nd. Basilar artery rethrombosis: successful treatment with platelet glycoprotein IIB/IIA receptor inhibitor. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997. 18:1257–1260.9. Liebeskind DS, Pollard JR, Schwartz ED, Cucchiara BL, McGarvey ML, Hurst RW. Vertebrobasilar thrombolysis with intravenous tirofiban: case report. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2002. 13:81–84.10. Ho DS, Wang Y, Chui M, Wang Y, Ho SL, Cheung RT. Intracarotid abciximab injection to abort impending ischemic stroke during carotid angioplasty. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2001. 11:300–304.11. Rukshin V, Azarbal B, Finkelstein A, Shah PK, Cercek B, Tsang V, et al. Effects of GP IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor tirofiban (aggrastat) in ex vivo canine arteriovenous shunt model of stent thrombosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2003. 41:615–624.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adjuvant Tirofiban Injection Through Deployed Solitaire Stent As a Rescue Technique After failed Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Stroke
- Outcomes of Emergent Carotid Artery Stenting within 6 Hours of Symptom Onset in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Intra-arterial and Intravenous Tirofiban Infusion for Thromboembolism during Endovascular Coil Embolization of Cerebral Aneurysm
- Rescue Use of Tirofiban for Acute Carotid In-Stent Thrombosis
- Primary stent retrieval for acute intracranial large artery occlusion due to atherosclerotic disease