Infant Pertussis and Household Transmission in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. kjhan@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2157980
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.12.1547
Abstract
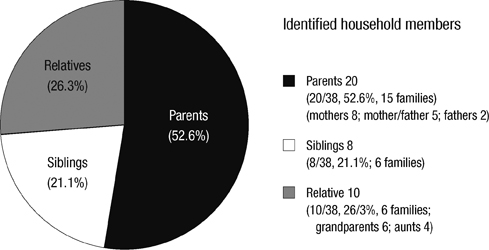
- A recent resurgence of pertussis has raised public health concerns even in developed countries with high vaccination coverage. The aim of this study was to describe the clinical characteristics of infant pertussis, and to determine the relative importance of household transmission in Korea. The multicenter study was prospectively conducted from January 2009 to September 2011. We identified the demographic and clinical data from these patients and performed the diagnostic tests for pertussis in their household contacts. Twenty-one patients with confirmed pertussis were included in the analysis. All infections occurred in infants younger than 6 months of age (mean age, 2.5 months) who had not completed the primary DTaP vaccination except for one patient. Infants without immunization history had a significant higher lymphocytosis and longer duration of hospital stay compared to those with immunization. All were diagnosed with PCR (100%), however, culture tests showed the lowest sensitivity (42.9%). Presumed source of infection in household contacts was documented in 85.7%, mainly parents (52.6%). Pertussis had a major morbidity in young infants who were not fully immunized. Household members were responsible for pertussis transmission of infants in whom a source could be identified. The control of pertussis through booster vaccination with Tdap in family who is taking care of young infants is necessary in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bordetella pertussis/genetics
Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis Vaccines/immunology
Female
Humans
Immunization, Secondary
Infant
Length of Stay
Lymphocytosis/etiology
Male
Parents
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Prospective Studies
Republic of Korea
Whooping Cough/diagnosis/immunology/*transmission
Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis Vaccines
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Seroprevalence of Pertussis in Healthcare Workers without Adult Pertussis Vaccine Use at a University Hospital in Korea
Won Suk Choi, Su Hyun Kim, Dae Won Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(50):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e321.Knowledge and Acceptability about Adult Pertussis Immunization in Korean Women of Childbearing Age
Hyun Sun Ko, Yun Seong Jo, Yeun Hee Kim, Yong-Gyu Park, Jeong Ha Wie, Juyoung Cheon, Hee Bong Moon, Young Lee, Jong Chul Shin
Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(4):1071-1078. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1071.Vaccination guideline for Immigrant in Korea by Korean Society of Infectious Diseases
Joon-Sup Yeom, Ki Tae Kwon, Jacob Lee, Yoo Bin Suh, Hae Suk Cheong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Hee Jin Cheong, ,
Infect Chemother. 2015;47(2):145-153. doi: 10.3947/ic.2015.47.2.145.Revised Adult Immunization Guideline Recommended by the Korean Society of Infectious Diseases, 2014
Won Suk Choi, Jung-Hyun Choi, Ki Tae Kwon, Kyung Seo, Min A Kim, Sang-Oh Lee, Young Jin Hong, Jin-Soo Lee, Joon Young Song, Ji Hwan Bang, Hee-Jung Choi, Young-Hwa Choi, Dong Gun Lee, Hee Jin Cheong, ,
Infect Chemother. 2015;47(1):68-79. doi: 10.3947/ic.2015.47.1.68.Updates of adult immunization in Korea
Hyun-Young Shin, Byung Wook Yoo
J Korean Med Assoc. 2020;63(2):128-134. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2020.63.2.128.A survey of the domestic epidemiological characteristics and clinical manifestations of pertussis
Seock Hwa Yoon, Yong Hee Hong, Hee Kyung Lee, Jong Hyun Lee, Meeyong Shin
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(1):54-61. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.1.54.Detection of Respiratory Viruses and Atypical Bacterial Pathogens in Infants with Acute Respiratory Infections Using Multiplex PCR
Soo Jin Yoo, Jeong-U Han, Bo-Moon Shin
Ann Clin Microbiol. 2014;17(3):86-90. doi: 10.5145/ACM.2014.17.3.86.
Reference
-
1. Crespo I, Cardenosa N, Godoy P, Carmona G, Sala MR, Barrabeig I, Alvarez J, Minguel S, Camps N, Cayla J, et al. Epidemiology of pertussis in a country with high vaccination coverage. Vaccine. 2011. 29:4244–4248.2. Güriş D, Strebel PM, Bardenheier B, Brennan M, Tachdjian R, Finch E, Wharton M, Livengood JR. Changing epidemiology of pertussis in the United States: increasing reported incidence among adolescents and adults, 1990-1996. Clin Infect Dis. 1999. 28:1230–1237.3. Celentano LP, Massari M, Paramatti D, Salmaso S, Tozzi AE. Resurgence of pertussis in Europe. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. 24:761–765.4. Wymann MN, Richard JL, Vidondo B, Heininger U. Prospective pertussis surveillance in Switzerland, 1991-2006. Vaccine. 2011. 29:2058–2065.5. Edwards KM. Overview of pertussis: focus on epidemiology, sources of infection, and long term protection after infant vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. 24:S104–S108.6. Crowcroft NS, Pebody RG. Recent developments in pertussis. Lancet. 2006. 367:1926–1936.7. Cherry JD. The science and fiction of the "resurgence" of pertussis. Pediatrics. 2003. 112:405–406.8. Wood N, McIntyre P. Pertussis: review of epidemiology, diagnosis, management and prevention. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2008. 9:201–211. quiz 11-2.9. Mooi FR, van Loo IH, van Gent M, He Q, Bart MJ, Heuvelman KJ, de Greeff SC, Diavatopoulos D, Teunis P, Nagelkerke N, et al. Bordetella pertussis strains with increased toxin production associated with pertussis resurgence. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009. 15:1206–1213.10. Greenberg DP, von König CH, Heininger U. Health burden of pertussis in infants and children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. 24:S39–S43.11. Elliott E, McIntyre P, Ridley G, Morris A, Massie J, McEniery J, Knight G. National study of infants hospitalized with pertussis in the acellular vaccine era. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. 23:246–252.12. Kim EY, Lee MS. Related factors of age-appropriate immunization among urban-rural children aged 24-35 months in a 2005 population-based survey in Nonsan, Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2011. 52:104–112.13. Park B, Lee YK, Cho LY, Go UY, Yang JJ, Ma SH, Choi BY, Lee MS, Lee JS, Choi EH, et al. Estimation of nationwide vaccination coverage and comparison of interview and telephone survey methodology for estimating vaccination status. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. 26:711–719.14. Hong JY. Update on pertussis and pertussis immunization. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. 53:629–633.15. CDC. Surveillance data of nationally notifiable communiable diseases (annual reporting pertussis). accessed on 12 August 2012. Available at http://www.cdc.go.kr.16. Glare EM, Paton JC, Premier RR, Lawrence AJ, Nisbet IT. Analysis of a repetitive DNA sequence from Bordetella pertussis and its application to the diagnosis of pertussis using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990. 28:1982–1987.17. Reischl U, Lehn N, Sanden GN, Loeffelholz MJ. Real-time PCR assay targeting IS481 of Bordetella pertussis and molecular basis for detecting Bordetella holmesii. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:1963–1966.18. Rohani P, Drake JM. The decline and resurgence of pertussis in the US. Epidemics. 2011. 3:183–188.19. Mikelova LK, Halperin SA, Scheifele D, Smith B, Ford-Jones E, Vaudry W, Jadavji T, Law B, Moore D. Predictors of death in infants hospitalized with pertussis: a case-control study of 16 pertussis deaths in Canada. J Pediatr. 2003. 143:576–581.20. Haberling DL, Holman RC, Paddock CD, Murphy TV. Infant and maternal risk factors for pertussis-related infant mortality in the United States, 1999 to 2004. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009. 28:194–198.21. Lin YC, Yao SM, Yan JJ, Chen YY, Chiang CS, Wu HS, Li SY. Epidemiological shift in the prevalence of pertussis in Taiwan: implications for pertussis vaccination. J Med Microbiol. 2007. 56:533–537.22. Skowronski DM, De Serres G, MacDonald D, Wu W, Shaw C, Macnabb J, Champagne S, Patrick DM, Halperin SA. The changing age and seasonal profile of pertussis in Canada. J Infect Dis. 2002. 185:1448–1453.23. Wirsing von König CH, Postels-Multani S, Bogaerts H, Bock HL, Laukamp S, Kiederle S, Schmitt HJ. Factors influencing the spread of pertussis in households. Eur J Pediatr. 1998. 157:391–394.24. Baron S, Njamkepo E, Grimprel E, Begue P, Desenclos JC, Drucker J, Guiso N. Epidemiology of pertussis in French hospitals in 1993 and 1994: thirty years after a routine use of vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998. 17:412–418.25. Goh A, Chong CY, Tee N, Loo LH, Yeo JG, Chan YH. Pertussis--an under-diagnosed disease with high morbidity in Singapore children. Vaccine. 2011. 29:2503–2507.26. Simmerman JM, Chu D, Chang H. Implications of unrecognized severe acute respiratory syndrome. Nurse Pract. 2003. 28:21–31.27. Bisgard KM, Pascual FB, Ehresmann KR, Miller CA, Cianfrini C, Jennings CE, Rebmann CA, Gabel J, Schauer SL, Lett SM. Infant pertussis: who was the source? Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. 23:985–989.28. Wendelboe AM, Njamkepo E, Bourillon A, Floret DD, Gaudelus J, Gerber M, Grimprel E, Greenberg D, Halperin S, Liese J, et al. Transmission of Bordetella pertussis to young infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007. 26:293–299.29. Kretsinger K, Broder KR, Cortese MM, Joyce MP, Ortega-Sanchez I, Lee GM, Tiwari T, Cohn AC, Slade BA, Iskander JK, et al. Preventing tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis among adults: use of tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid and acellular pertussis vaccine recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) and recommendation of ACIP, supported by the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC), for use of Tdap among health-care personnel. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006. 55:1–37.30. Nilsson L, Lepp T, von Segebaden K, Hallander H, Gustafsson L. Pertussis vaccination in infancy lowers the incidence of pertussis disease and the rate of hospitalisation after one and two doses: analyses of 10 years of pertussis surveillance. Vaccine. 2012. 30:3239–3247.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recommendation for the use of newly introduced Tdap vaccine in Korea
- Update on pertussis and pertussis immunization
- Geospatial Analysis of Age-specific SARS-CoV-2 Transmission Patterns in Households, Korea
- Investigation on the Immunity to Pertussis in the Korea
- Rates of Adverse Reactions Associated with Modified DPT Vaccine in Korean Infants and Children